C Exercises: Implement a binary tree using linked list representation
27. Binary Tree via Linked List
From Wikipedia -
In computer science, a binary tree is a k-ary k=2 tree data structure in which each node has at most two children, which are referred to as the left child and the right child. A recursive definition using just set theory notions is that a (non-empty) binary tree is a tuple (L, S, R), where L and R are binary trees or the empty set and S is a singleton set containing the root. Some authors allow the binary tree to be the empty set as well.
Write a C program to implement a binary tree using linked list representation.
The function uses the "Right-Root-Left" traversal order, which means it first traverses the right subtree, then the root node, and finally the left subtree.
Sample Solution:
C Code:
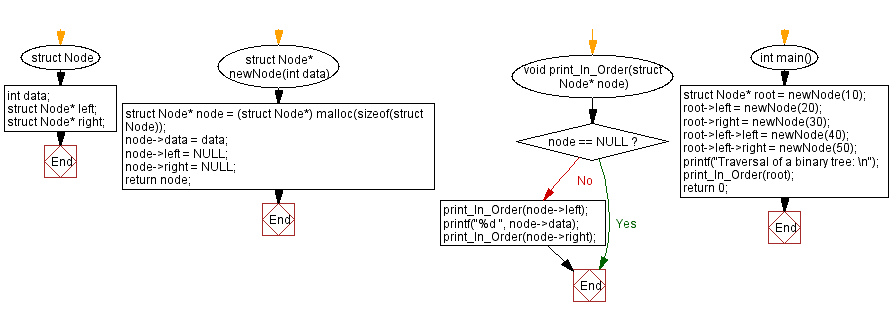
#include<stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
// Structure for defining a Node in a Binary Tree
struct Node {
int data; // Data stored in the node
struct Node* left; // Pointer to the left child node
struct Node* right; // Pointer to the right child node
};
// Function to create a new node in the Binary Tree
struct Node* newNode(int data) {
struct Node* node = (struct Node*) malloc(sizeof(struct Node)); // Allocate memory for a new node
node->data = data; // Assign the data to the new node
node->left = NULL; // Initialize left child as NULL
node->right = NULL; // Initialize right child as NULL
return node; // Return the new node
}
// Function to print the nodes of a Binary Tree in an In-Order traversal manner
void print_In_Order(struct Node* node) {
if (node == NULL) return; // If the current node is NULL, exit the function
print_In_Order(node->left); // Recursively traverse the left subtree
printf("%d ", node->data); // Print the data of the current node
print_In_Order(node->right); // Recursively traverse the right subtree
}
// Main function to demonstrate In-Order traversal of a Binary Tree
int main() {
// Create a Binary Tree with some nodes
struct Node* root = newNode(10); // Root node with data 10
root->left = newNode(20); // Left child node of the root with data 20
root->right = newNode(30); // Right child node of the root with data 30
root->left->left = newNode(40); // Left child of node with data 20 with data 40
root->left->right = newNode(50); // Right child of node with data 20 with data 50
printf("Traversal of a binary tree: \n");
print_In_Order(root); // Print the nodes of the Binary Tree in In-Order traversal
return 0; // Indicate successful completion of the program
}
Sample Output:
Traversal of a binary tree: 40 20 50 10 30
Flowchart :
For more Practice: Solve these Related Problems:
- Write a C program to build a binary search tree using linked list nodes and perform in-order traversal.
- Write a C program to implement pre-order, in-order, and post-order traversals in a binary tree represented with linked lists.
- Write a C program to insert nodes into a binary tree in level order using a queue implemented with linked lists.
- Write a C program to implement deletion of nodes in a binary tree represented using linked lists.
Go to:
PREV : Even Index Removal Variants.
NEXT : Nth Node Removal Variants.
C Programming Code Editor:
Have another way to solve this solution? Contribute your code (and comments) through Disqus.
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
