C Program: Binary Tree deletion with BST maintenance
5. Binary Tree Deletion Extensions
Write a C program that implements a deletion function for a binary tree. Allow users to delete nodes while maintaining the binary search tree structure.
Sample Solution:
C Code:
// Including necessary header files
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
// Structure for a binary tree node
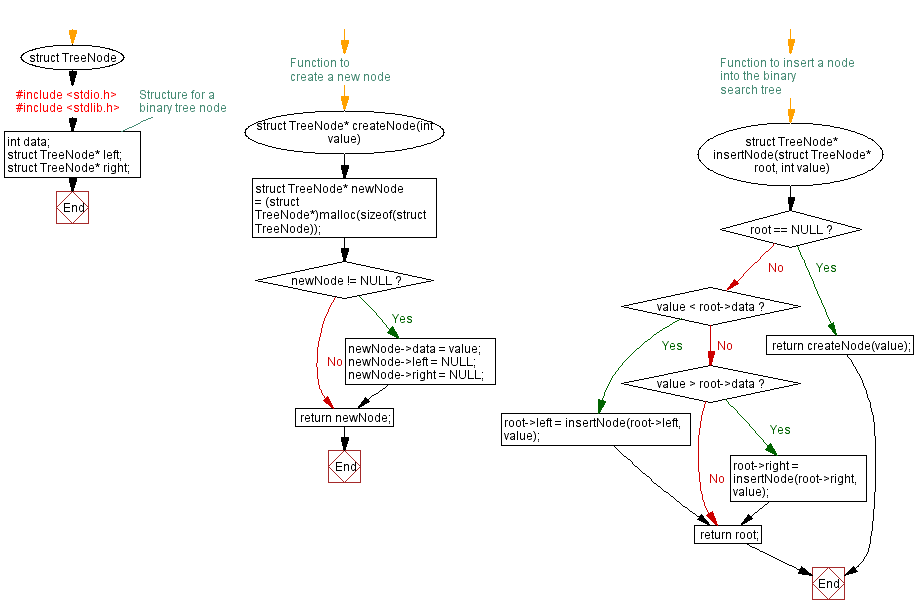
struct TreeNode {
int data;
struct TreeNode* left;
struct TreeNode* right;
};
// Function to create a new node
struct TreeNode* createNode(int value) {
struct TreeNode* newNode = (struct TreeNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct TreeNode));
if (newNode != NULL) {
newNode->data = value;
newNode->left = NULL;
newNode->right = NULL;
}
return newNode;
}
// Function to insert a node into the binary search tree
struct TreeNode* insertNode(struct TreeNode* root, int value) {
if (root == NULL) {
return createNode(value);
}
if (value < root->data) {
root->left = insertNode(root->left, value);
} else if (value > root->data) {
root->right = insertNode(root->right, value);
}
return root;
}
// Function to find the minimum value node in a BST
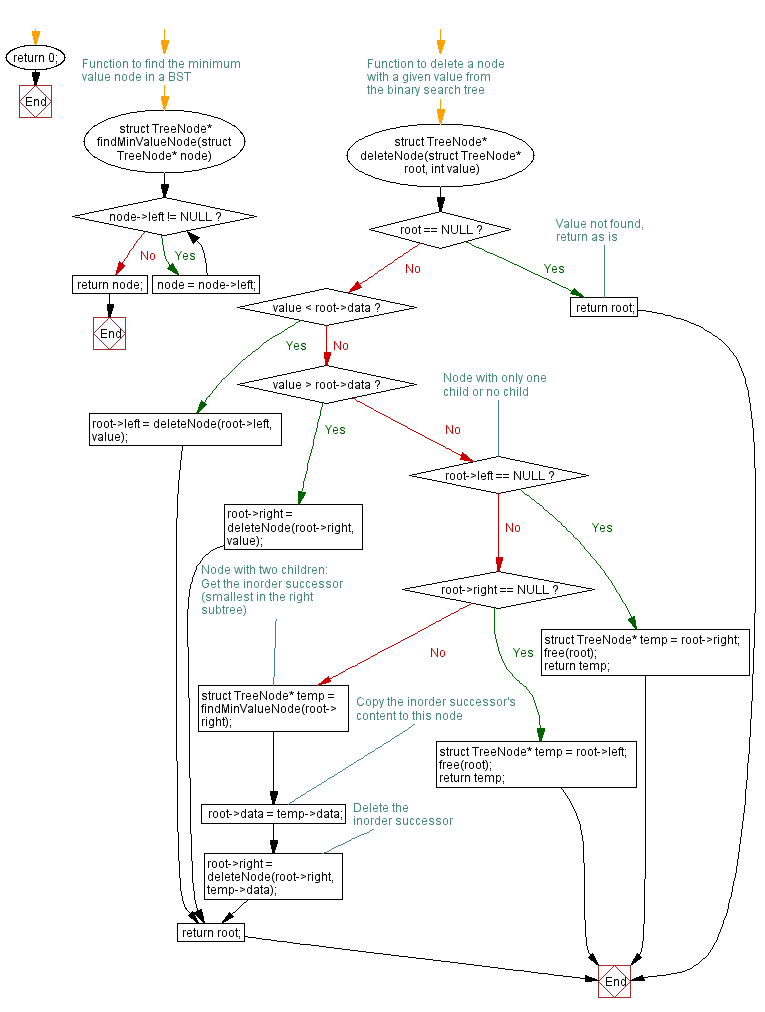
struct TreeNode* findMinValueNode(struct TreeNode* node) {
while (node->left != NULL) {
node = node->left;
}
return node;
}
// Function to delete a node with a given value from the binary search tree
struct TreeNode* deleteNode(struct TreeNode* root, int value) {
if (root == NULL) {
return root; // Value not found, return as is
}
if (value < root->data) {
root->left = deleteNode(root->left, value);
} else if (value > root->data) {
root->right = deleteNode(root->right, value);
} else {
// Node with only one child or no child
if (root->left == NULL) {
struct TreeNode* temp = root->right;
free(root);
return temp;
} else if (root->right == NULL) {
struct TreeNode* temp = root->left;
free(root);
return temp;
}
// Node with two children: Get the inorder successor (smallest in the right subtree)
struct TreeNode* temp = findMinValueNode(root->right);
// Copy the inorder successor's content to this node
root->data = temp->data;
// Delete the inorder successor
root->right = deleteNode(root->right, temp->data);
}
return root;
}
// Function to perform in-order traversal and print elements in sorted order
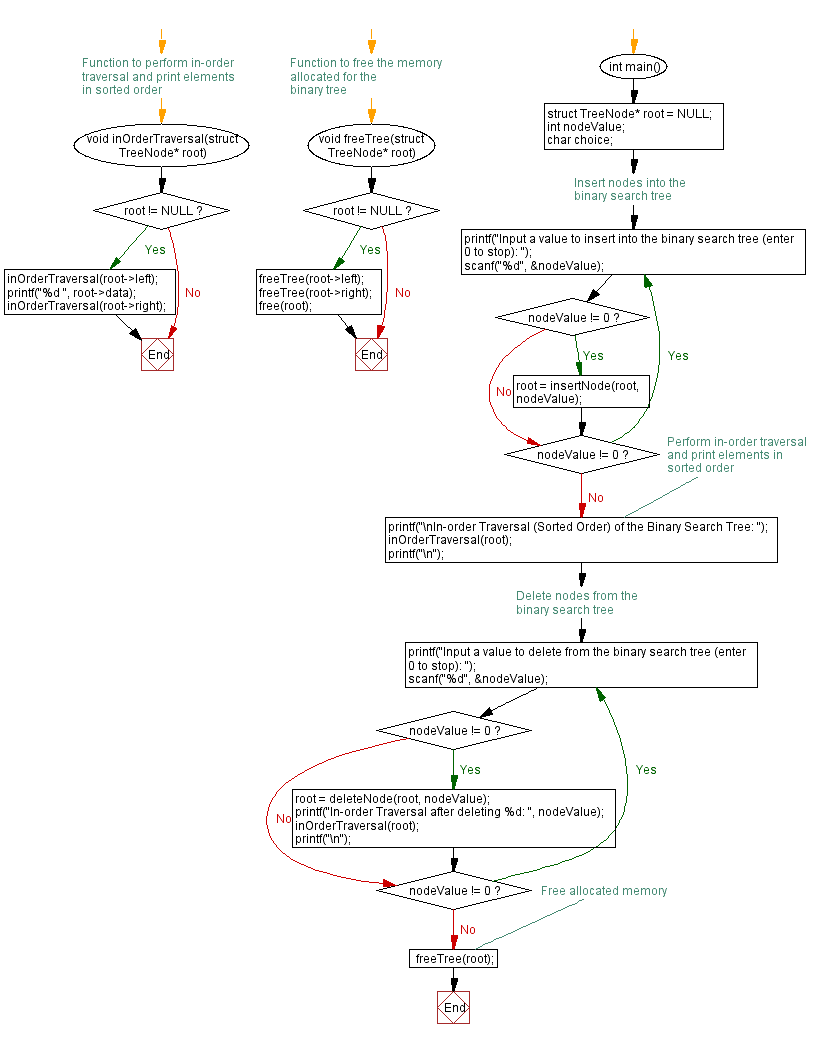
void inOrderTraversal(struct TreeNode* root) {
if (root != NULL) {
inOrderTraversal(root->left);
printf("%d ", root->data);
inOrderTraversal(root->right);
}
}
// Function to free the memory allocated for the binary tree
void freeTree(struct TreeNode* root) {
if (root != NULL) {
freeTree(root->left);
freeTree(root->right);
free(root);
}
}
int main() {
struct TreeNode* root = NULL;
int nodeValue;
char choice;
// Insert nodes into the binary search tree
do {
printf("Input a value to insert into the binary search tree (enter 0 to stop): ");
scanf("%d", &nodeValue);
if (nodeValue != 0) {
root = insertNode(root, nodeValue);
}
} while (nodeValue != 0);
// Perform in-order traversal and print elements in sorted order
printf("\nIn-order Traversal (Sorted Order) of the Binary Search Tree: ");
inOrderTraversal(root);
printf("\n");
// Delete nodes from the binary search tree
do {
printf("Input a value to delete from the binary search tree (enter 0 to stop): ");
scanf("%d", &nodeValue);
if (nodeValue != 0) {
root = deleteNode(root, nodeValue);
printf("In-order Traversal after deleting %d: ", nodeValue);
inOrderTraversal(root);
printf("\n");
}
} while (nodeValue != 0);
// Free allocated memory
freeTree(root);
return 0;
}
Output:
Input a value to insert into the binary search tree (enter 0 to stop): 75 Input a value to insert into the binary search tree (enter 0 to stop): 42 Input a value to insert into the binary search tree (enter 0 to stop): 35 Input a value to insert into the binary search tree (enter 0 to stop): 12 Input a value to insert into the binary search tree (enter 0 to stop): 10 Input a value to insert into the binary search tree (enter 0 to stop): 0 In-order Traversal (Sorted Order) of the Binary Search Tree: 10 12 35 42 75 Input a value to delete from the binary search tree (enter 0 to stop): 35 In-order Traversal after deleting 35: 10 12 42 75 Input a value to delete from the binary search tree (enter 0 to stop): 0
Explanation:
In the exercise above,
- Structure Definition:
- The program defines a structure "TreeNode" representing a node in a binary tree. Each node has an integer data value, a left child (left), and a right child (right).
- Node Creation:
- The createNode function allocates memory for a new node, initializes its data, left, and right pointers, and returns the created node.
- Node Insertion:
- The insertNode function inserts a node with a given value into the binary search tree. It recursively traverses the tree, compares values, and inserts the new node accordingly.
- Finding Minimum Value Node:
- The findMinValueNode function finds the node with the minimum value in a binary search tree. It is used during deletion.
- Node Deletion:
- The deleteNode function deletes a node with a given value from the binary search tree while maintaining the binary search tree property. It handles cases with one or two children.
- In-order Traversal:
- The inOrderTraversal function performs an in-order traversal of the binary search tree and prints the elements in sorted order.
- Freeing Memory:
- The freeTree function frees the memory allocated for the entire binary tree by recursively traversing and deallocating each node.
- Main Function:
- The main function allows users to insert nodes into the binary search tree and displays the sorted order of elements through in-order traversal.
- Users can then input values to delete from the binary search tree, and the program prints the tree after each deletion.
- Memory is freed before program completion.
Flowchart:
For more Practice: Solve these Related Problems:
- Write a C program to delete a node with two children from a BST and replace it with its in-order successor.
- Write a C program to implement both recursive and iterative deletion in a BST and compare their performance.
- Write a C program to simulate lazy deletion in a BST by marking nodes as deleted instead of physically removing them.
- Write a C program to delete a node from a BST and then automatically balance the tree by converting it into an AVL tree.
Go to:
C Programming Code Editor:
PREV : Binary Tree Height Calculation Challenges.
NEXT : Mirror Image Transformation Challenges.
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
Test your Programming skills with w3resource's quiz.
