C Program: Determine Binary Tree path with parget sum
9. Root-to-Leaf Path Sum Challenges
Write a C program to determine if a binary tree has a root-to-leaf path whose sum equals a given target sum.
Sample Solution:
C Code:
// Including necessary header files
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
// Structure for a binary tree node
struct TreeNode {
int data;
struct TreeNode* left;
struct TreeNode* right;
};
// Function to create a new node
struct TreeNode* createNode(int value) {
struct TreeNode* newNode = (struct TreeNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct TreeNode));
if (newNode != NULL) {
newNode->data = value;
newNode->left = NULL;
newNode->right = NULL;
}
return newNode;
}
// Function to check if a path with the given sum exists in the binary tree
bool hasPathSum(struct TreeNode* root, int targetSum) {
if (root == NULL) {
return false;
}
// Check if the current node is a leaf
if (root->left == NULL && root->right == NULL) {
return (targetSum - root->data) == 0;
}
// Recursively check the left and right subtrees
bool leftPath = hasPathSum(root->left, targetSum - root->data);
bool rightPath = hasPathSum(root->right, targetSum - root->data);
return leftPath || rightPath;
}
// Function to free the memory allocated for the binary tree
void freeTree(struct TreeNode* root) {
if (root != NULL) {
freeTree(root->left);
freeTree(root->right);
free(root);
}
}
int main() {
// Build a sample binary tree
struct TreeNode* root = createNode(5);
root->left = createNode(4);
root->right = createNode(8);
root->left->left = createNode(11);
root->left->left->left = createNode(7);
root->left->left->right = createNode(2);
root->right->left = createNode(13);
root->right->right = createNode(4);
root->right->right->right = createNode(1);
// Set the target sum
int targetSum = 18;
// Check if a path with the given sum exists
if (hasPathSum(root, targetSum)) {
printf("Path with sum %d exists in the binary tree.\n", targetSum);
} else {
printf("No path with sum %d exists in the binary tree.\n", targetSum);
}
// Free allocated memory
freeTree(root);
return 0;
}
Output:
Path with sum 18 exists in the binary tree.
Explanation:
In the exercise above,
- Structure Definition:
- struct TreeNode: Represents a binary tree node with integer data and pointers to left and right children.
- Node Creation Function:
- createNode: Allocates memory for a new node, initializes its data, and sets left and right pointers to 'NULL'.
- Path Sum Checking Function:
- hasPathSum: Checks if there is a path from the root to any leaf node in the binary tree such that the sum of node values along the path equals the given 'targetSum'.
- Recursively explores the left and right subtrees.
- Tree Traversal and Sum Comparison:
- The main function builds a sample binary tree.
- Sets a targetSum variable.
- Calls hasPathSum to check if a path with the specified sum exists.
- Prints a message indicating whether such a path exists or not.
- Memory Deallocation Function:
- freeTree: Frees the memory allocated for the binary tree nodes.
- Sample Binary Tree in Main:
- Constructs a binary tree with integer values.
- Sets a target sum.
- Checks if there is a path in the tree with a sum equal to the target sum.
Flowchart:
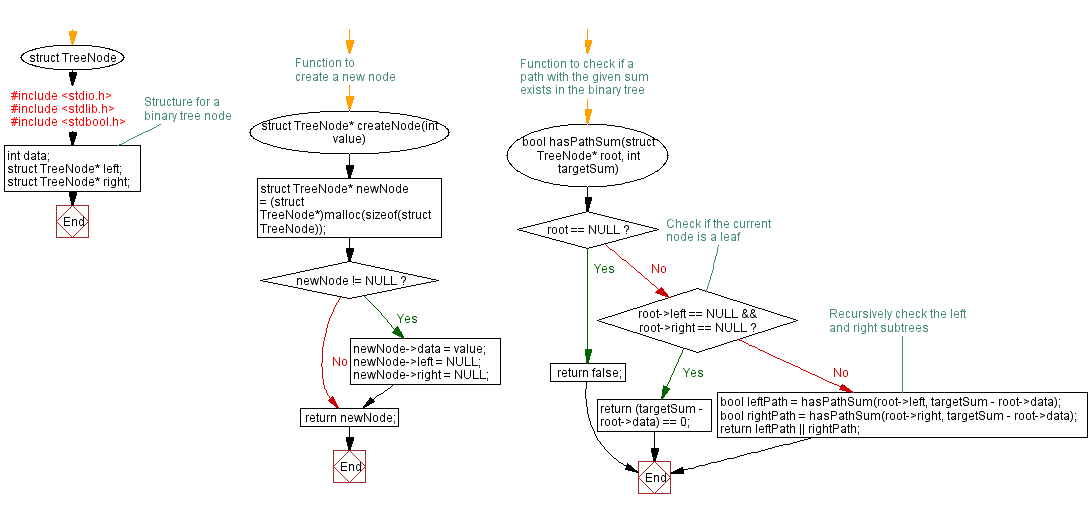
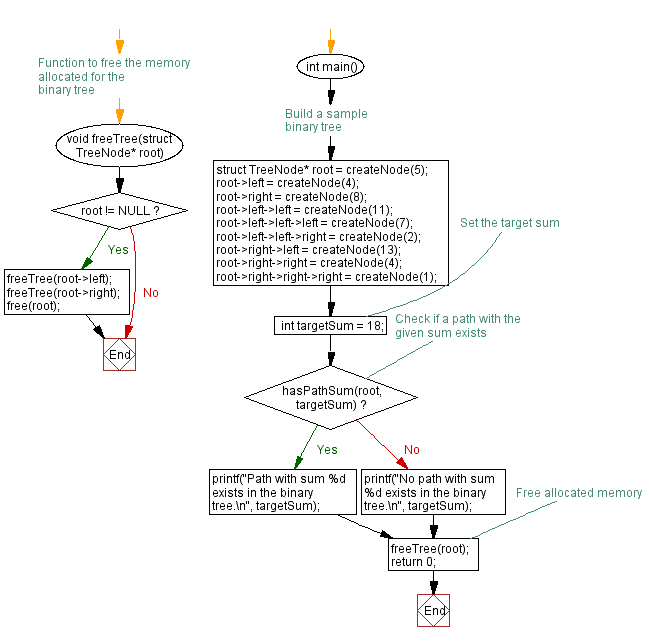
For more Practice: Solve these Related Problems:
- Write a C program to find and print all root-to-leaf paths in a binary tree that sum up to a given target value.
- Write a C program to count the number of root-to-leaf paths that equal a specified sum, handling negative numbers as well.
- Write a C program to identify the shortest root-to-leaf path that matches a given target sum.
- Write a C program to determine if there exists any root-to-leaf path with a given sum using backtracking techniques.
Go to:
PREV : Expression Tree Construction and Evaluation.
NEXT : AVL Tree Implementation Extensions.
C Programming Code Editor:
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
Test your Programming skills with w3resource's quiz.
