Java: Divide a given array of integers into given k non-empty subsets whose sums are all equal
Divide Array into Equal Sum Subsets
Write a Java program to divide a given array of integers into given k non-empty subsets whose sums are all equal. Return true if all sums are equal otherwise return false.
Example:
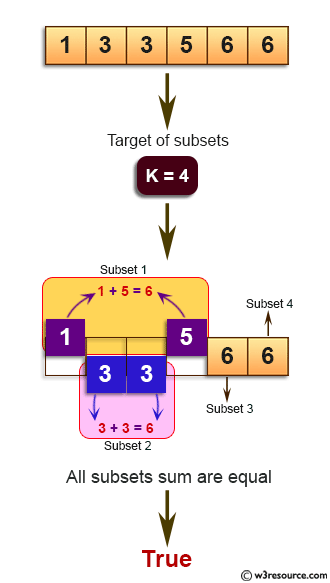
nums = {1,3,3,5,6,6}, k = 4;
4 subsets (5,1), (3, 3), (6), (6) with equal sums.
Visual Presentation:
Sample Solution:
Java Code:
// Import Arrays and other utility classes from java.util package
import java.util.Arrays;
// Main class for the solution
public class Solution {
// Main method to execute the solution
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Sample input array and target value for testing subset partitioning
int[] nums = {1, 3, 3, 5, 6, 6};
int target = 4;
// Display the original array
System.out.print("Original Array: " + Arrays.toString(nums));
// Display the target value for subsets
System.out.print("\nTarget of subsets: " + target);
// Display the result after removing duplicate characters using partition_k_subsets function
System.out.print("\nAfter removing duplicate characters: " + partition_k_subsets(nums, target));
}
// Function to recursively search for valid subsets with a specific sum
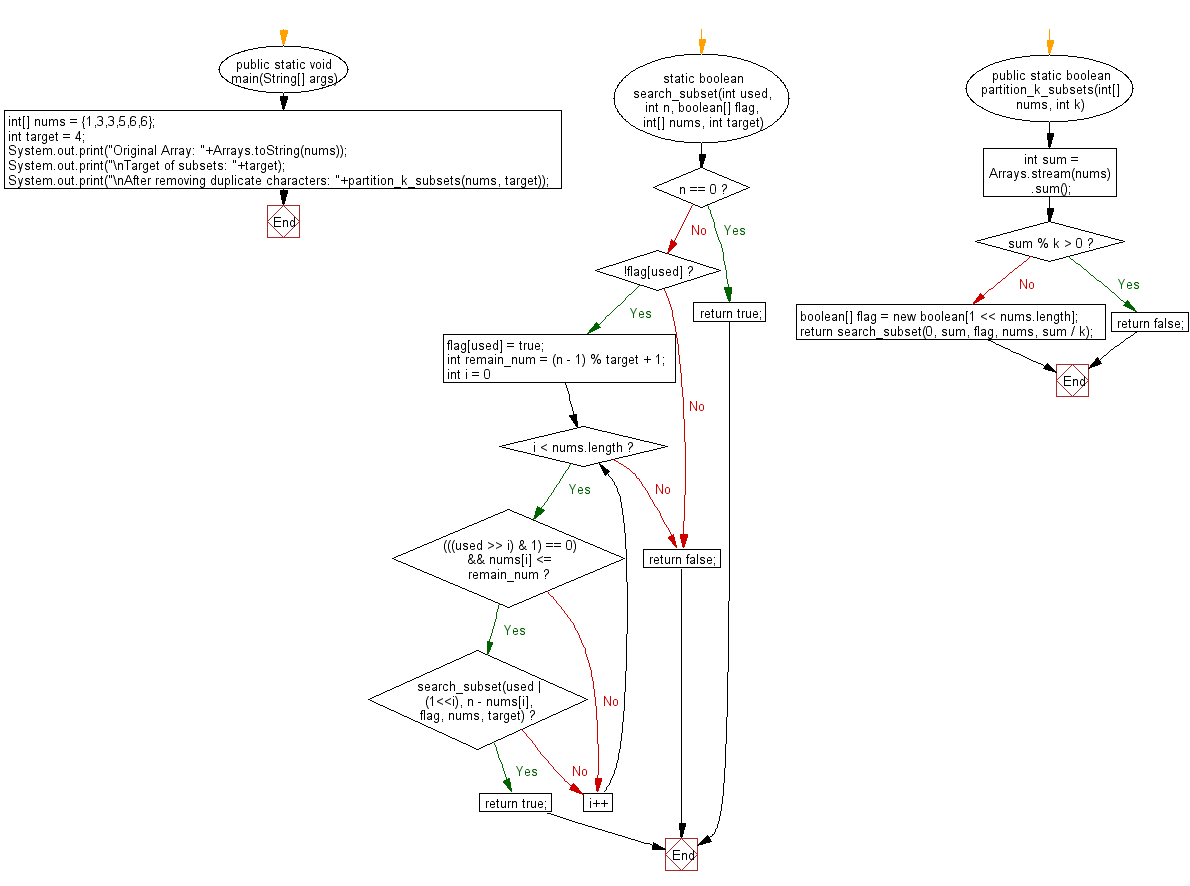
static boolean search_subset(int used, int n, boolean[] flag, int[] nums, int target) {
// Base case: all elements used, subset found
if (n == 0) {
return true;
}
// Check if the current subset has not been considered before
if (!flag[used]) {
// Mark the current subset as visited
flag[used] = true;
// Calculate the remaining sum needed for the subset
int remain_num = (n - 1) % target + 1;
// Iterate through the elements in the array
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
// Check if the current element is not used in the subset and its value is less than or equal to the remaining sum
if ((((used >> i) & 1) == 0) && nums[i] <= remain_num) {
// Recursively search for the subset with the updated parameters
if (search_subset(used | (1 << i), n - nums[i], flag, nums, target)) {
return true;
}
}
}
}
return false;
}
// Function to partition an array into k subsets with equal sum
public static boolean partition_k_subsets(int[] nums, int k) {
// Calculate the total sum of the elements in the array
int sum = Arrays.stream(nums).sum();
// Check if the sum is not divisible by k, return false
if (sum % k > 0) {
return false;
}
// Create a boolean array to track visited subsets
boolean[] flag = new boolean[1 << nums.length];
// Call the recursive search_subset function to check for valid subsets
return search_subset(0, sum, flag, nums, sum / k);
}
}
Sample Output:
Original Array: [1, 3, 3, 5, 6, 6] Target of subsets: 4 After removing duplicate characters: true
Flowchart:
For more Practice: Solve these Related Problems:
- Write a Java program to partition an array into k subsets such that the difference between the subset sums is minimized.
- Write a Java program to list all possible ways to divide an array into k non-empty subsets with equal sum using backtracking.
- Write a Java program to determine the maximum k for which an array can be partitioned into subsets with equal sum.
- Write a Java program to decide if an array can be partitioned into k equal sum subsets after removing exactly one element.
Go to:
PREV : Remove Duplicate Letters.
NEXT : Continuous Subarrays with Target Sum.
Java Code Editor:
Company: LinkedIn
Contribute your code and comments through Disqus.
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
Test your Programming skills with w3resource's quiz.
