Java Abstract Classes - Abstract Shape Class with Circle and Triangle Subclasses
Write a Java program to create an abstract class Shape with abstract methods calculateArea() and calculatePerimeter(). Create subclasses Circle and Triangle that extend the Shape class and implement the respective methods to calculate the area and perimeter of each shape.
In the following program Shape is the abstract base class with two abstract methods: calculateArea() and calculatePerimeter(). The Circle and Triangle classes are subclasses of Shape and provide their own implementations for abstract methods.
Sample Solution:
Java Code:
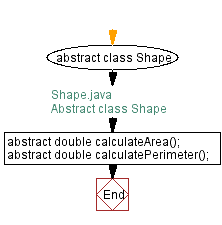
// Shape.java
// Define an abstract class named Shape
abstract class Shape {
// Declare an abstract method to calculate the area
abstract double calculateArea();
// Declare an abstract method to calculate the perimeter
abstract double calculatePerimeter();
}
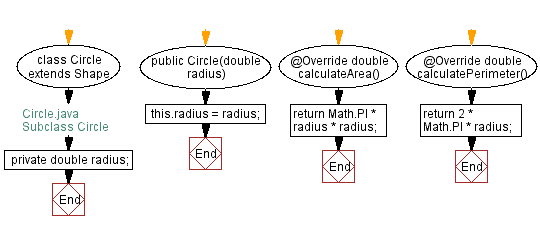
// Circle.java
// Define a subclass named Circle that extends Shape
class Circle extends Shape {
// Declare a private double variable to store the radius
private double radius;
// Constructor that accepts a radius and sets it to the radius variable
public Circle(double radius) {
this.radius = radius;
}
// Override the calculateArea method to compute the area of the circle
@Override
double calculateArea() {
// Return the area using the formula π * radius^2
return Math.PI * radius * radius;
}
// Override the calculatePerimeter method to compute the perimeter of the circle
@Override
double calculatePerimeter() {
// Return the perimeter using the formula 2 * π * radius
return 2 * Math.PI * radius;
}
}
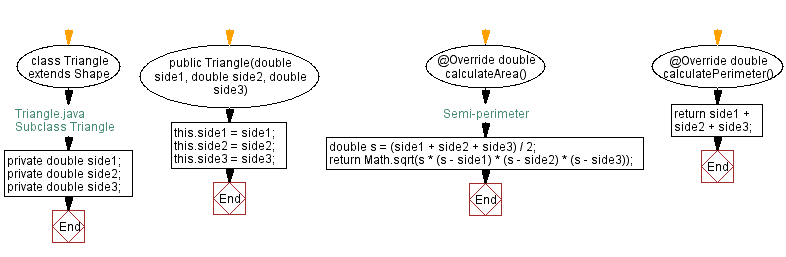
// Triangle.java
// Define a subclass named Triangle that extends Shape
class Triangle extends Shape {
// Declare private double variables to store the sides of the triangle
private double side1;
private double side2;
private double side3;
// Constructor that accepts three sides and sets them to the corresponding variables
public Triangle(double side1, double side2, double side3) {
this.side1 = side1;
this.side2 = side2;
this.side3 = side3;
}
// Override the calculateArea method to compute the area of the triangle
@Override
double calculateArea() {
// Calculate the semi-perimeter
double s = (side1 + side2 + side3) / 2;
// Return the area using Heron's formula
return Math.sqrt(s * (s - side1) * (s - side2) * (s - side3));
}
// Override the calculatePerimeter method to compute the perimeter of the triangle
@Override
double calculatePerimeter() {
// Return the perimeter by summing up all the sides
return side1 + side2 + side3;
}
}
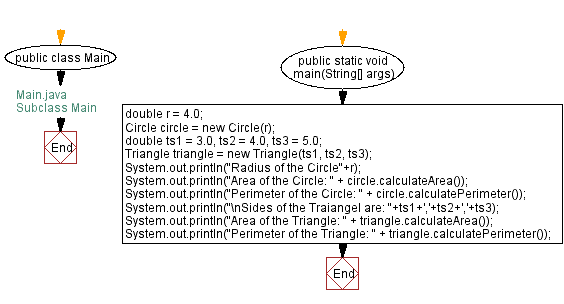
// Main.java
// Define the Main class
public class Main {
// Main method to run the program
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Declare and initialize the radius for the circle
double r = 4.0;
// Create an instance of Circle with the specified radius
Circle circle = new Circle(r);
// Declare and initialize the sides for the triangle
double ts1 = 3.0, ts2 = 4.0, ts3 = 5.0;
// Create an instance of Triangle with the specified sides
Triangle triangle = new Triangle(ts1, ts2, ts3);
// Print the radius of the circle
System.out.println("Radius of the Circle: " + r);
// Print the area of the circle by calling the calculateArea method
System.out.println("Area of the Circle: " + circle.calculateArea());
// Print the perimeter of the circle by calling the calculatePerimeter method
System.out.println("Perimeter of the Circle: " + circle.calculatePerimeter());
// Print the sides of the triangle
System.out.println("\nSides of the Triangle are: " + ts1 + ',' + ts2 + ',' + ts3);
// Print the area of the triangle by calling the calculateArea method
System.out.println("Area of the Triangle: " + triangle.calculateArea());
// Print the perimeter of the triangle by calling the calculatePerimeter method
System.out.println("Perimeter of the Triangle: " + triangle.calculatePerimeter());
}
}
Output:
Radius of the Circle4.0 Area of the Circle: 50.26548245743669 Perimeter of the Circle: 25.132741228718345 Sides of the Traiangel are: 3.0,4.0,5.0 Area of the Triangle: 6.0 Perimeter of the Triangle: 12.0
Flowchart:
For more Practice: Solve these Related Problems:
- Write a Java program where the "Triangle" subclass includes a method to determine if it is an equilateral triangle.
- Write a Java program where the "Circle" subclass implements a method to calculate circumference.
- Write a Java program where the "Shape" class includes a method to determine if the shape is 2D or 3D.
- Write a Java program where the "Triangle" subclass adds an attribute for angles and checks if it forms a valid triangle.
Go to:
Java Code Editor:
Contribute your code and comments through Disqus.
PREV : Abstract Animal Class with Lion and Tiger Subclasses.
NEXT : Abstract Bank Account Class with Savings and Current Accounts.
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
