Java Interface: Banking system classes - Bank Account, Savings Account, and Current Account
Write a Java programming to create a banking system with three classes - Bank, Account, SavingsAccount, and CurrentAccount. The bank should have a list of accounts and methods for adding them. Accounts should be an interface with methods to deposit, withdraw, calculate interest, and view balances. SavingsAccount and CurrentAccount should implement the Account interface and have their own unique methods.
Sample Solution:
Java Code:
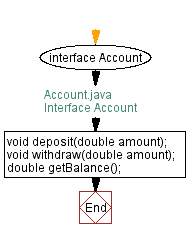
// Account.java
// Interface Account
// Declare the Account interface
interface Account {
// Declare the abstract method "deposit" to deposit a specified amount
void deposit(double amount);
// Declare the abstract method "withdraw" to withdraw a specified amount
void withdraw(double amount);
// Declare the abstract method "getBalance" to retrieve the current balance
double getBalance();
}
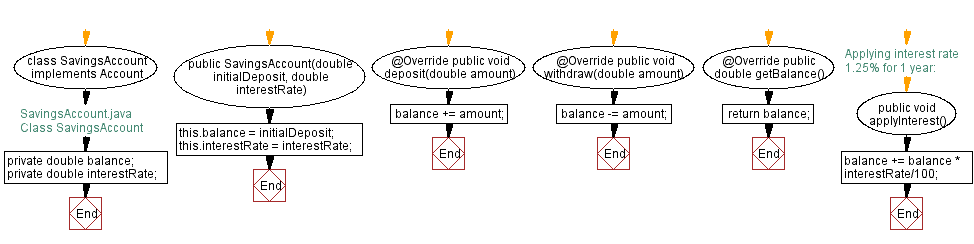
// SavingsAccount.java
// Class SavingsAccount
// Declare the SavingsAccount class, which implements the Account interface
class SavingsAccount implements Account {
// Declare private instance variables to store balance and interest rate
private double balance;
private double interestRate;
// Constructor for initializing the balance and interest rate
public SavingsAccount(double initialDeposit, double interestRate) {
this.balance = initialDeposit;
this.interestRate = interestRate;
}
// Implement the "deposit" method to add a specified amount to the balance
@Override
public void deposit(double amount) {
balance += amount;
}
// Implement the "withdraw" method to subtract a specified amount from the balance
@Override
public void withdraw(double amount) {
balance -= amount;
}
// Implement the "getBalance" method to retrieve the current balance
@Override
public double getBalance() {
return balance;
}
// Method to apply interest to the balance
public void applyInterest() {
// Applying interest rate (in percentage) to the balance for 1 year
balance += balance * interestRate / 100;
}
}
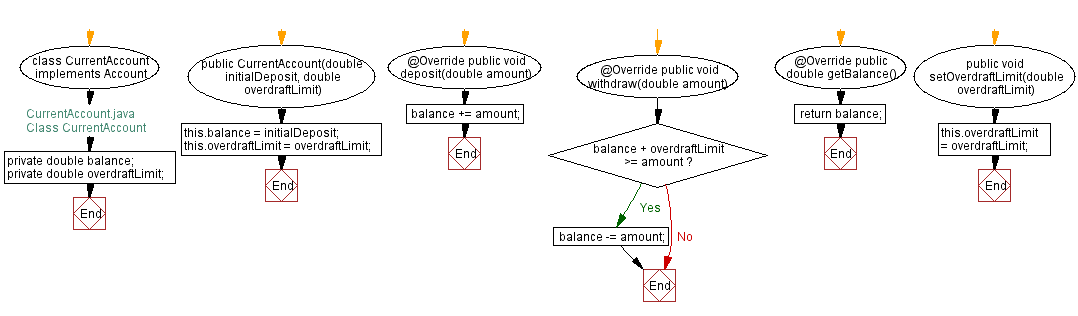
// CurrentAccount.java
// Class CurrentAccount
// Declare the CurrentAccount class, which implements the Account interface
class CurrentAccount implements Account {
// Declare private instance variables to store balance and overdraft limit
private double balance;
private double overdraftLimit;
// Constructor for initializing the balance and overdraft limit
public CurrentAccount(double initialDeposit, double overdraftLimit) {
this.balance = initialDeposit;
this.overdraftLimit = overdraftLimit;
}
// Implement the "deposit" method to add a specified amount to the balance
@Override
public void deposit(double amount) {
balance += amount;
}
// Implement the "withdraw" method to subtract a specified amount from the balance
@Override
public void withdraw(double amount) {
// Check if the balance plus overdraft limit is sufficient to cover the withdrawal
if (balance + overdraftLimit >= amount) {
balance -= amount;
}
}
// Implement the "getBalance" method to retrieve the current balance
@Override
public double getBalance() {
return balance;
}
// Method to set the overdraft limit for the current account
public void setOverdraftLimit(double overdraftLimit) {
this.overdraftLimit = overdraftLimit;
}
}
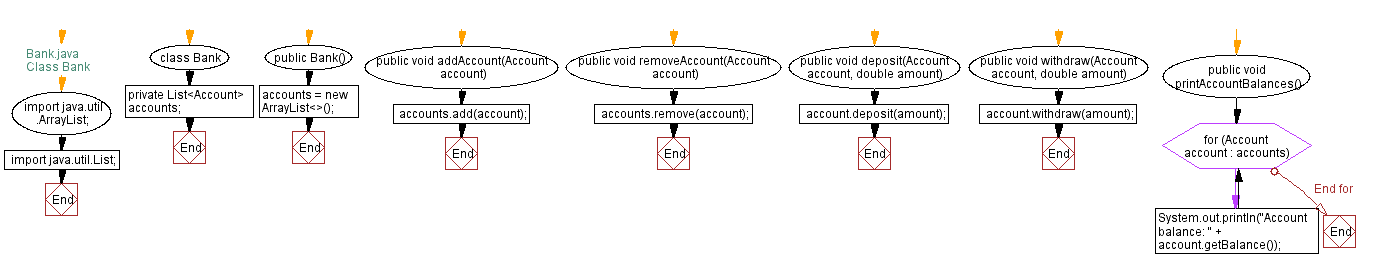
// Bank.java
// Class Bank
// Import required libraries for List and ArrayList
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
// Declare the Bank class
class Bank {
// Declare a private list to store accounts
private List accounts;
// Constructor for initializing the list of accounts
public Bank() {
accounts = new ArrayList<>();
}
// Method to add an account to the list of accounts
public void addAccount(Account account) {
accounts.add(account);
}
// Method to remove an account from the list of accounts
public void removeAccount(Account account) {
accounts.remove(account);
}
// Method to deposit a specified amount into an account
public void deposit(Account account, double amount) {
account.deposit(amount);
}
// Method to withdraw a specified amount from an account
public void withdraw(Account account, double amount) {
account.withdraw(amount);
}
// Method to print the balances of all accounts in the bank
public void printAccountBalances() {
for (Account account : accounts) {
System.out.println("Account balance: " + account.getBalance());
}
}
}
// Main.java
// Class Main
// Declare the Main class
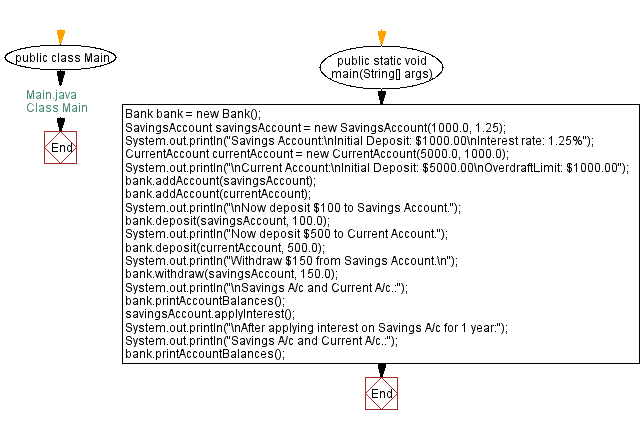
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create an instance of the Bank class
Bank bank = new Bank();
// Create a SavingsAccount with an initial deposit and interest rate
SavingsAccount savingsAccount = new SavingsAccount(1000.0, 1.25);
System.out.println("Savings Account:\nInitial Deposit: $1000.00\nInterest rate: 1.25%");
// Create a CurrentAccount with an initial deposit and overdraft limit
CurrentAccount currentAccount = new CurrentAccount(5000.0, 1000.0);
System.out.println("\nCurrent Account:\nInitial Deposit: $5000.00\nOverdraft Limit: $1000.00");
// Add the SavingsAccount and CurrentAccount to the bank
bank.addAccount(savingsAccount);
bank.addAccount(currentAccount);
System.out.println("\nNow deposit $100 to Savings Account.");
// Deposit $100 into the SavingsAccount
bank.deposit(savingsAccount, 100.0);
System.out.println("Now deposit $500 to Current Account.");
// Deposit $500 into the CurrentAccount
bank.deposit(currentAccount, 500.0);
System.out.println("Withdraw $150 from Savings Account.\n");
// Withdraw $150 from the SavingsAccount
bank.withdraw(savingsAccount, 150.0);
System.out.println("\nSavings A/c and Current A/c.:");
// Print the balances of all accounts in the bank
bank.printAccountBalances();
// Apply interest to the SavingsAccount
savingsAccount.applyInterest();
System.out.println("\nAfter applying interest on Savings A/c for 1 year:");
System.out.println("Savings A/c and Current A/c.:");
// Print the balances of all accounts in the bank after applying interest
bank.printAccountBalances();
}
}
Sample Output:
Savings Account: Initial Deposit: $1000.00 Interest rate: 1.25% Current Account: Initial Deposit: $5000.00 OverdraftLimit: $1000.00 Now deposit $100 to Savings Account. Now deposit $500 to Current Account. Withdraw $150 from Savings Account. Savings A/c and Current A/c.: Account balance: 950.0 Account balance: 5500.0 After applying interest on Savings A/c for 1 year: Savings A/c and Current A/c.: Account balance: 961.875 Account balance: 5500.0
Flowchart of Interface Account:
Flowchart of Class SavingsAccount:
Flowchart of Class CurrentAccount:
Flowchart of Class Bank:
Flowchart of Class Main:
For more Practice: Solve these Related Problems:
- Write a Java program to create an Account interface with methods deposit(), withdraw(), and transfer(), then implement it in SavingsAccount and CurrentAccount classes.
- Write a Java program to design a banking system using interfaces for both Customer and Account, incorporating transaction error handling.
- Write a Java program to implement a multi-tier banking system with interfaces for Account and Transaction, simulating concurrent transactions using threads.
- Write a Java program to implement an Account interface that also calculates compound interest, then simulate multiple account operations.
Java Code Editor:
Previous: Implement the Flyable interface.
Next: Resizable interface for object resizing with rectangle class implementation.
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
