C Exercises: Interleave elements of two linked lists alternatively
C Singly Linked List : Exercise-39 with Solution
Write a C program to interleave elements of two singly linked lists alternatively.
Sample Solution:
C Code:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
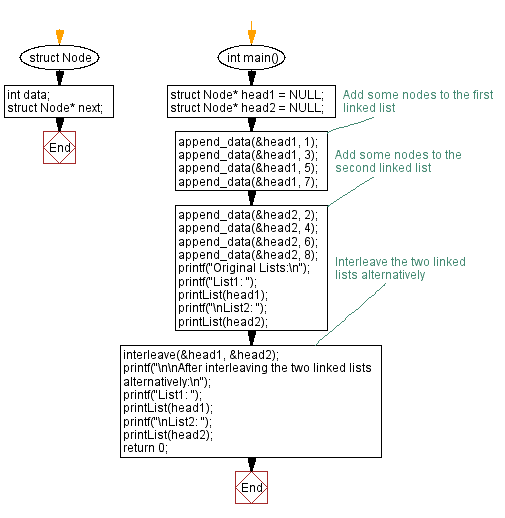
// Structure defining a node in a singly linked list
struct Node {
int data; // Data stored in the node
struct Node* next; // Pointer to the next node
};
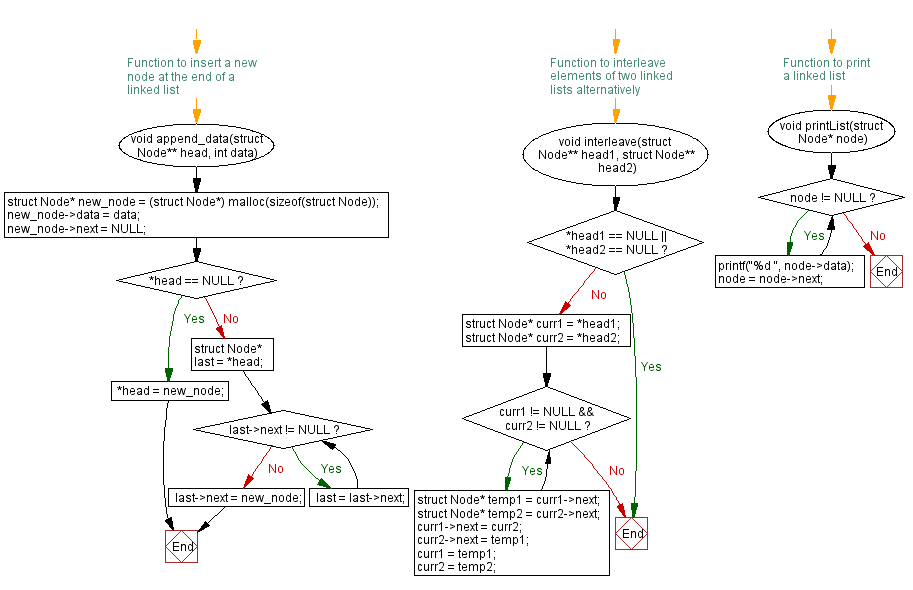
// Function to insert a new node at the end of a linked list
void append_data(struct Node** head, int data) {
struct Node* new_node = (struct Node*) malloc(sizeof(struct Node)); // Allocate memory for a new node
new_node->data = data; // Assign data to the new node
new_node->next = NULL; // Initialize the next pointer as NULL
// Check if the linked list is empty
if (*head == NULL) {
*head = new_node; // If empty, make the new node as the head
} else {
struct Node* last = *head;
while (last->next != NULL) {
last = last->next; // Traverse to the last node of the list
}
last->next = new_node; // Append the new node to the end of the list
}
}
// Function to interleave elements of two linked lists alternatively
void interleave(struct Node** head1, struct Node** head2) {
if (*head1 == NULL || *head2 == NULL) {
return; // If either list is empty, return
}
struct Node* curr1 = *head1; // Pointer for the first list
struct Node* curr2 = *head2; // Pointer for the second list
// Loop to interleave the nodes of the two lists alternatively
while (curr1 != NULL && curr2 != NULL) {
struct Node* temp1 = curr1->next; // Store next nodes to maintain continuity
struct Node* temp2 = curr2->next;
curr1->next = curr2; // Interleave the nodes
curr2->next = temp1;
curr1 = temp1; // Move to the next nodes
curr2 = temp2;
}
}
// Function to print elements of a linked list
void printList(struct Node* node) {
while (node != NULL) {
printf("%d ", node->data); // Print the data of the current node
node = node->next; // Move to the next node
}
}
// Main function to demonstrate interleaving two linked lists alternatively
int main() {
struct Node* head1 = NULL; // Initialize the first linked list
struct Node* head2 = NULL; // Initialize the second linked list
// Add nodes to the first linked list
append_data(&head1, 1);
append_data(&head1, 3);
append_data(&head1, 5);
append_data(&head1, 7);
// Add nodes to the second linked list
append_data(&head2, 2);
append_data(&head2, 4);
append_data(&head2, 6);
append_data(&head2, 8);
printf("Original Lists:\n");
printf("List1: ");
printList(head1); // Display the elements of the first list
printf("\nList2: ");
printList(head2); // Display the elements of the second list
interleave(&head1, &head2); // Interleave the two lists alternatively
printf("\n\nAfter interleaving the two linked lists alternatively:\n");
printf("List1: ");
printList(head1); // Display the modified first list after interleaving
printf("\nList2: ");
printList(head2); // Display the modified second list after interleaving
return 0;
}
Sample Output:
Original Lists: List1: 1 3 5 7 List2: 2 4 6 8 After interleaving the two linked lists alternatively: List1: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 List2: 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
Flowchart :
C Programming Code Editor:
Previous: Pair in a linked list whose sum is equal to a given value.
Next: Swap every two adjacent nodes of a singly linked list.
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
- Weekly Trends and Language Statistics
- Weekly Trends and Language Statistics