C Exercises: Reverse alternate k nodes of a singly linked list
C Singly Linked List : Exercise-41 with Solution
Write a C program to reverse alternate k nodes of a given singly linked list.
Sample Solution:
C Code:
#include<stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
// Definition for singly-linked list
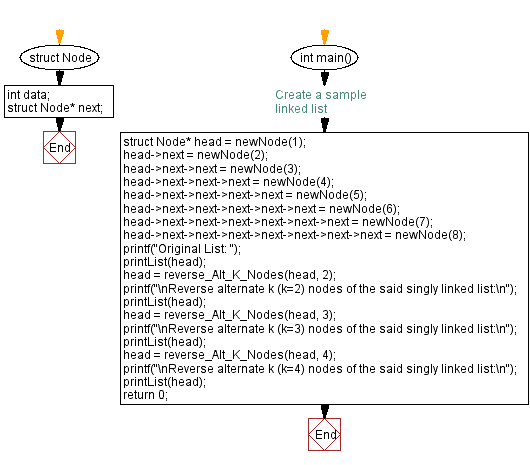
struct Node {
int data;
struct Node* next;
};
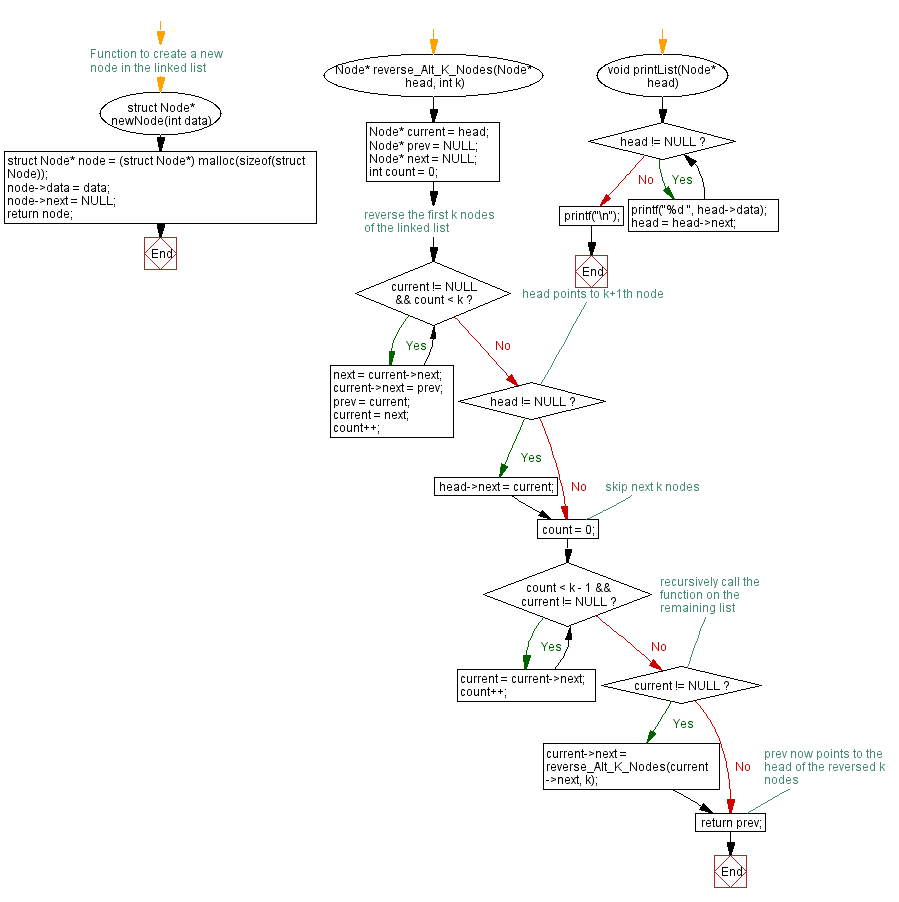
// Function to create a new node in the linked list
struct Node* newNode(int data) {
struct Node* node = (struct Node*) malloc(sizeof(struct Node)); // Allocate memory for a new node
node->data = data; // Assign data to the new node
node->next = NULL; // Initialize the next pointer as NULL
return node; // Return the newly created node
}
// Function to reverse alternate K nodes in a linked list
struct Node* reverse_Alt_K_Nodes(struct Node* head, int k) {
struct Node* current = head;
struct Node* prev = NULL;
struct Node* next = NULL;
int count = 0;
/* reverse the first k nodes of the linked list */
while (current != NULL && count < k) {
next = current->next;
current->next = prev;
prev = current;
current = next;
count++;
}
/* head points to k+1th node */
if (head != NULL) {
head->next = current;
}
/* skip next k nodes */
count = 0;
while (count < k - 1 && current != NULL) {
current = current->next;
count++;
}
/* recursively call the function on the remaining list */
if (current != NULL) {
current->next = reverse_Alt_K_Nodes(current->next, k);
}
/* prev now points to the head of the reversed k nodes */
return prev;
}
// Function to print the linked list
void printList(struct Node* head) {
while (head != NULL) {
printf("%d ", head->data);
head = head->next;
}
printf("\n");
}
// Main function to demonstrate reversing alternate K nodes in a linked list
int main() {
// Create a sample linked list
struct Node* head = newNode(1);
head->next = newNode(2);
head->next->next = newNode(3);
head->next->next->next = newNode(4);
head->next->next->next->next = newNode(5);
head->next->next->next->next->next = newNode(6);
head->next->next->next->next->next->next = newNode(7);
head->next->next->next->next->next->next->next = newNode(8);
printf("Original List: ");
printList(head);
head = reverse_Alt_K_Nodes(head, 2);
printf("\nReverse alternate k (k=2) nodes of the said singly linked list:\n");
printList(head);
head = reverse_Alt_K_Nodes(head, 3);
printf("\nReverse alternate k (k=3) nodes of the said singly linked list:\n");
printList(head);
head = reverse_Alt_K_Nodes(head, 4);
printf("\nReverse alternate k (k=4) nodes of the said singly linked list:\n");
printList(head);
return 0;
}
Sample Output:
Original List: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Reverse alternate k (k=2) nodes of the said singly linked list: 2 1 3 4 6 5 7 8 Reverse alternate k (k=3) nodes of the said singly linked list: 3 1 2 4 6 5 8 7 Reverse alternate k (k=4) nodes of the said singly linked list: 4 2 1 3 6 5 8 7
Flowchart :
C Programming Code Editor:
Previous: Swap every two adjacent nodes of a singly linked list.
Next: Find the point at which two singly linked lists intersect.
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
- Weekly Trends and Language Statistics
- Weekly Trends and Language Statistics