Graph Representation in C Using Adjacency Matrix
1. Graph Matrix Representation Extended Challenges
Write a C program to represent a graph using an adjacency matrix.
From Wikipedia -
In graph theory and computer science, an adjacency matrix is a square matrix used to represent a finite graph. The elements of the matrix indicate whether pairs of vertices are adjacent or not in the graph.
In the special case of a finite simple graph, the adjacency matrix is a (0,1)-matrix with zeros on its diagonal. If the graph is undirected (i.e. all of its edges are bidirectional), the adjacency matrix is symmetric. The relationship between a graph and the eigenvalues and eigenvectors of its adjacency matrix is studied in spectral graph theory.
The adjacency matrix of a graph should be distinguished from its incidence matrix, a different matrix representation whose elements indicate whether vertex–edge pairs are incident or not, and its degree matrix, which contains information about the degree of each vertex.
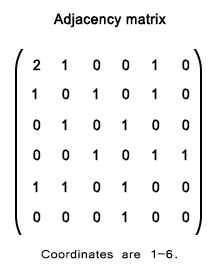
Sample Solution:
C Code:
#include <stdio.h>
#define MAX_VERTICES 100
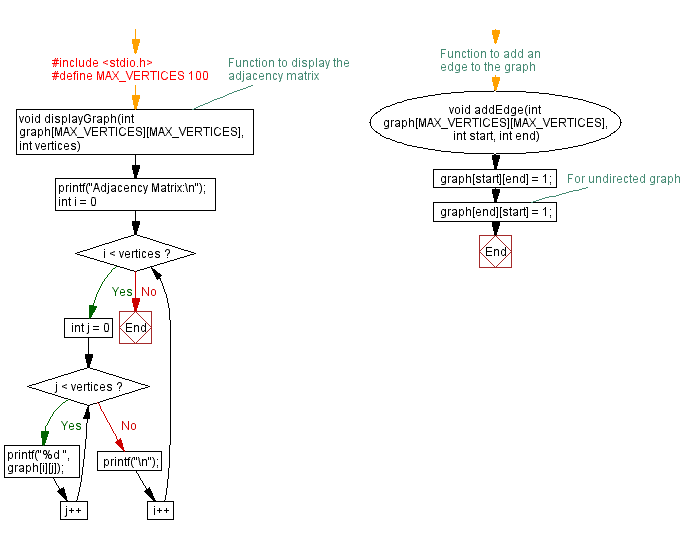
// Function to display the adjacency matrix
void displayGraph(int graph[MAX_VERTICES][MAX_VERTICES], int vertices) {
printf("Adjacency Matrix:\n");
for (int i = 0; i < vertices; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < vertices; j++) {
printf("%d ", graph[i][j]);
}
printf("\n");
}
}
// Function to add an edge to the graph
void addEdge(int graph[MAX_VERTICES][MAX_VERTICES], int start, int end) {
graph[start][end] = 1;
graph[end][start] = 1; // For undirected graph
}
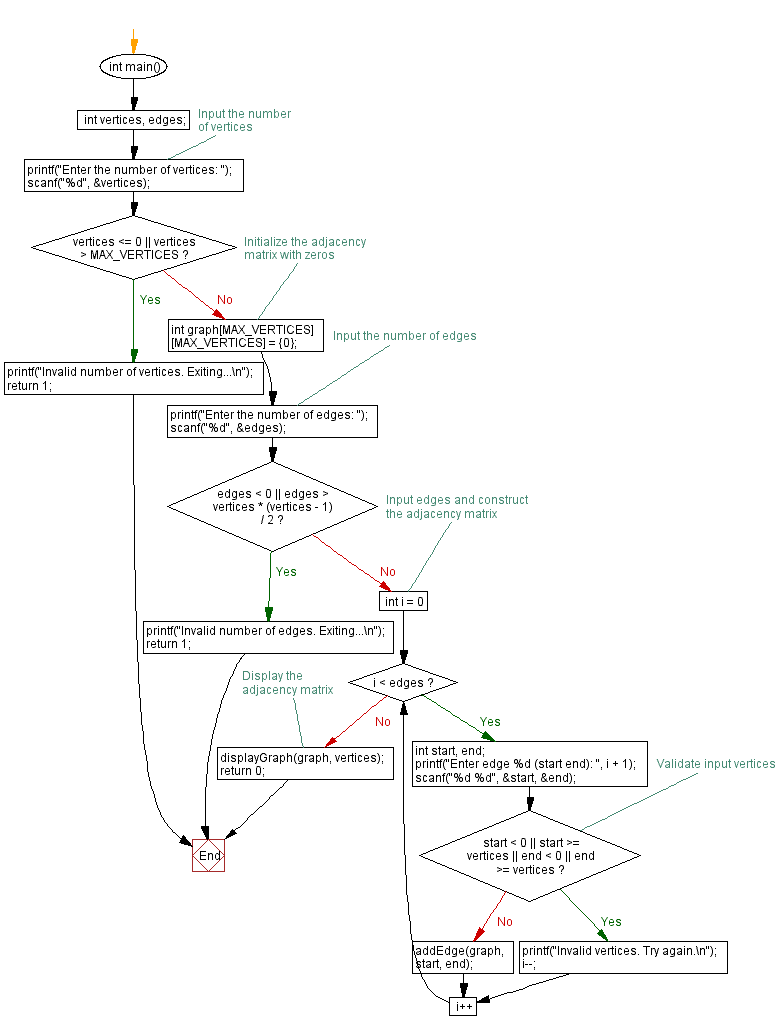
int main() {
int vertices, edges;
// Input the number of vertices
printf("Enter the number of vertices: ");
scanf("%d", &vertices);
if (vertices <= 0 || vertices > MAX_VERTICES) {
printf("Invalid number of vertices. Exiting...\n");
return 1;
}
int graph[MAX_VERTICES][MAX_VERTICES] = {0}; // Initialize the adjacency matrix with zeros
// Input the number of edges
printf("Enter the number of edges: ");
scanf("%d", &edges);
if (edges < 0 || edges > vertices * (vertices - 1) / 2) {
printf("Invalid number of edges. Exiting...\n");
return 1;
}
// Input edges and construct the adjacency matrix
for (int i = 0; i < edges; i++) {
int start, end;
printf("Enter edge %d (start end): ", i + 1);
scanf("%d %d", &start, &end);
// Validate input vertices
if (start < 0 || start >= vertices || end < 0 || end >= vertices) {
printf("Invalid vertices. Try again.\n");
i--;
continue;
}
addEdge(graph, start, end);
}
// Display the adjacency matrix
displayGraph(graph, vertices);
return 0;
}
Output:
Enter the number of vertices: 5 Enter the number of edges: 7 Enter edge 1 (start end): 0 1 Enter edge 2 (start end): 0 2 Enter edge 3 (start end): 1 2 Enter edge 4 (start end): 1 3 Enter edge 5 (start end): 2 4 Enter edge 6 (start end): 3 4 Enter edge 7 (start end): 4 0 Adjacency Matrix: 0 1 1 0 1 1 0 1 1 0 1 1 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 1 1 0 1 1 0
Explanation:
In the exercise above,
- Header and Definitions:
- #include <stdio.h>: Includes the standard input-output library.
- #define MAX_VERTICES 100: Defines the maximum number of vertices in the graph.
- Function Declarations:
- displayGraph: Displays the adjacency matrix of the graph.
- addEdge: Adds an undirected edge between two vertices in the graph.
- Main Function (main):
- Declares variables 'vertices' and 'edges' to store the number of vertices and edges, respectively.
- Inputs the number of vertices from the user, checks for validity, and exits if invalid.
- Initializes a 2D array 'graph' (adjacency matrix) with zeros.
- Inputs the number of edges, checks for validity, and exits if invalid.
- Loops to input edges, validates vertices, and adds edges to the graph using "addEdge()" function.
- Displays the adjacency matrix using the "displayGraph()" function.
- Function Definitions (displayGraph and addEdge):
- displayGraph: Prints the adjacency matrix using nested loops.
- addEdge: Sets the corresponding matrix entries to 1 for an undirected edge.
- Input and Validation:
- Ensure that the user inputs are within valid ranges.
- Validates that edge vertices are within the range of vertices.
- Adjacency Matrix Initialization:
- Initializes the adjacency matrix with zeros.
- Graph Construction:
- Accepts edges from the user and adds them to the graph.
- Display:
- Prints the final adjacency matrix representing the graph.
Flowchart:
For more Practice: Solve these Related Problems:
- Write a C program to represent a weighted graph using an adjacency matrix and implement a function to update edge weights dynamically.
- Write a C program to detect isolated vertices in a graph represented by an adjacency matrix.
- Write a C program to compute the transitive closure of a graph using its adjacency matrix representation.
- Write a C program to determine the number of connected components in a graph represented by an adjacency matrix.
Go to:
PREV : C Programming Exercises: Graph Structure and Algorithms Home.
NEXT : Add Vertex to Graph Extended Challenges.
C Programming Code Editor:
Have another way to solve this solution? Contribute your code (and comments) through Disqus.
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
Test your Programming skills with w3resource's quiz.
