Python: Takes two lists and returns True if they have at least one common member
Check Common Member Between Two Lists
Write a Python function that takes two lists and returns True if they have at least one common member.
Visual Presentation:
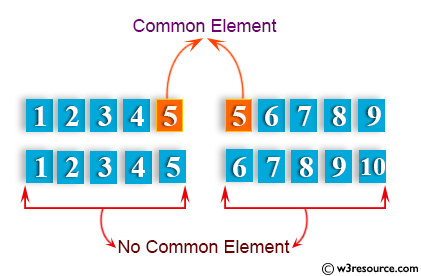
Sample Solution-1:
Python Code:
# Define a function called 'common_data' that takes two lists, 'list1' and 'list2', as input
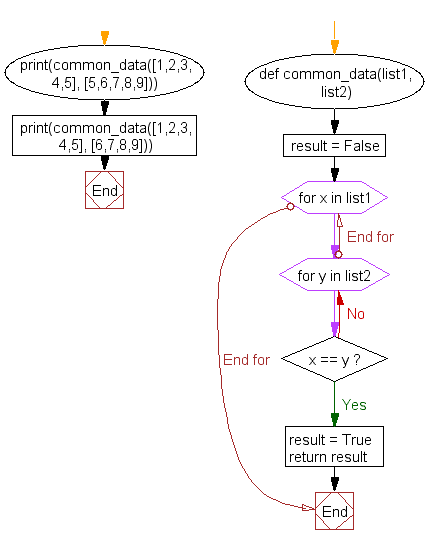
def common_data(list1, list2):
# Initialize a variable 'result' to False to indicate no common elements initially
result = False
# Iterate through each element 'x' in 'list1'
for x in list1:
# Iterate through each element 'y' in 'list2'
for y in list2:
# Check if the current elements 'x' and 'y' are equal
if x == y:
# If there's a common element, set 'result' to True and return it
result = True
return result
# Call the 'common_data' function with two lists and print the result
print(common_data([1, 2, 3, 4, 5], [5, 6, 7, 8, 9]))
# Call the 'common_data' function with two lists and print the result
print(common_data([1, 2, 3, 4, 5], [6, 7, 8, 9]))
Sample Output:
True None
Explanation:
The above code defines a function called "common_data" that takes two lists as arguments: list1 and list2. The function initializes a Boolean variable result to False.
The function then loops through each element in list1 and list2 using nested for loops. If the current element in list1 is equal to the current element in list2, the function sets result to True and immediately returns the result using the return statement. This means that the function will stop execution as soon as it finds a common element between the two lists.
print(common_data([1,2,3,4,5], [5,6,7,8,9])) print(common_data([1,2,3,4,5], [6,7,8,9]))
The above lines call the "common_data" function twice, with different sets of input lists.
The first call passes [1, 2, 3, 4, 5] and [5, 6, 7, 8, 9] as arguments. Since both lists have the element 5 in common, the function sets result to True and immediately returns it. Therefore, the first call to common_data will print True.
The second call passes [1, 2, 3, 4, 5] and [6, 7, 8, 9] as arguments. Since there are no elements that appear in both lists, the function will not set result to True and will not return a value. Therefore, the second call to common_data will print None.
Flowchart:
For more Practice: Solve these Related Problems:
- Write a Python program to find the number of common elements between two lists.
- Write a Python program to return a list of common elements, including duplicates, between two lists.
- Write a Python program to check if two lists have no elements in common.
- Write a Python program to find the common elements between multiple lists.
Go to:
Previous: Write a Python program to find the list of words that are longer than n from a given list of words.
Next: Write a Python program to print a specified list after removing the 0th, 4th and 5th elements.
Python Code Editor:
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
Test your Programming skills with w3resource's quiz.
