SQL MAX() with COUNT()
MAX() with Count function
Sample table: orders
ORD_NUM ORD_AMOUNT ADVANCE_AMOUNT ORD_DATE CUST_CODE AGENT_CODE ORD_DESCRIPTION
---------- ---------- -------------- --------- --------------- --------------- -----------------
200114 3500 2000 15-AUG-08 C00002 A008
200122 2500 400 16-SEP-08 C00003 A004
200118 500 100 20-JUL-08 C00023 A006
200119 4000 700 16-SEP-08 C00007 A010
200121 1500 600 23-SEP-08 C00008 A004
200130 2500 400 30-JUL-08 C00025 A011
200134 4200 1800 25-SEP-08 C00004 A005
200108 4000 600 15-FEB-08 C00008 A004
200103 1500 700 15-MAY-08 C00021 A005
200105 2500 500 18-JUL-08 C00025 A011
200109 3500 800 30-JUL-08 C00011 A010
200101 3000 1000 15-JUL-08 C00001 A008
200111 1000 300 10-JUL-08 C00020 A008
200104 1500 500 13-MAR-08 C00006 A004
200106 2500 700 20-APR-08 C00005 A002
200125 2000 600 10-OCT-08 C00018 A005
200117 800 200 20-OCT-08 C00014 A001
200123 500 100 16-SEP-08 C00022 A002
200120 500 100 20-JUL-08 C00009 A002
200116 500 100 13-JUL-08 C00010 A009
200124 500 100 20-JUN-08 C00017 A007
200126 500 100 24-JUN-08 C00022 A002
200129 2500 500 20-JUL-08 C00024 A006
200127 2500 400 20-JUL-08 C00015 A003
200128 3500 1500 20-JUL-08 C00009 A002
200135 2000 800 16-SEP-08 C00007 A010
200131 900 150 26-AUG-08 C00012 A012
200133 1200 400 29-JUN-08 C00009 A002
200100 1000 600 08-JAN-08 C00015 A003
200110 3000 500 15-APR-08 C00019 A010
200107 4500 900 30-AUG-08 C00007 A010
200112 2000 400 30-MAY-08 C00016 A007
200113 4000 600 10-JUN-08 C00022 A002
200102 2000 300 25-MAY-08 C00012 A012
In this part, you will see the usage of SQL COUNT() along with the SQL MAX().
Example:
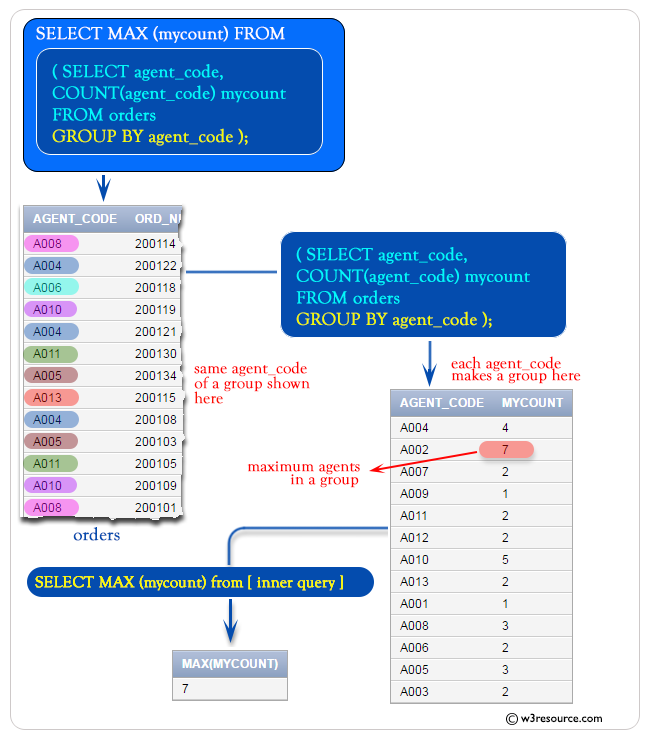
To get the maximum number of agents as column alias 'mycount' from the 'orders' table with the following condition -
1. 'agent_code' should be in a group,
the following SQL statement can be used :
SELECT MAX(mycount) -- Selecting the maximum value of the column 'mycount'
FROM ( -- Subquery: Creating a derived table
SELECT agent_code, COUNT(agent_code) AS mycount -- Selecting 'agent_code' and its count, aliased as 'mycount'
FROM orders -- From the 'orders' table
GROUP BY agent_code -- Grouping the results by 'agent_code'
);
Explanation:
- SELECT MAX(mycount): This line selects the maximum value of the column mycount from the result set returned by the subquery.
- (SELECT agent_code, COUNT(agent_code) AS mycount FROM orders GROUP BY agent_code): This is a subquery that generates a derived table. It selects the agent_code column and counts the occurrences of each agent_code in the orders table. The COUNT(agent_code) function is used to count the occurrences of each agent_code. The results are grouped by agent_code.
- SELECT agent_code, COUNT(agent_code) AS mycount: This line within the subquery selects the agent_code column and counts the occurrences of each agent_code in the orders table. The COUNT(agent_code) function is used to count the occurrences of each agent_code, and it is aliased as mycount.
- FROM orders: This specifies the table from which the subquery is selecting data, which is the orders table.
- GROUP BY agent_code: This line groups the results of the subquery by the agent_code column. This is necessary because we're using an aggregate function (COUNT) in conjunction with a non-aggregated column (agent_code). Grouping allows us to count the occurrences of each agent_code separately.
Output:
MAX(MYCOUNT)
------------
7
Visual Presentation :
SQL MAX() and COUNT() with HAVING
Sample table: orders
ORD_NUM ORD_AMOUNT ADVANCE_AMOUNT ORD_DATE CUST_CODE AGENT_CODE ORD_DESCRIPTION
---------- ---------- -------------- --------- --------------- --------------- -----------------
200114 3500 2000 15-AUG-08 C00002 A008
200122 2500 400 16-SEP-08 C00003 A004
200118 500 100 20-JUL-08 C00023 A006
200119 4000 700 16-SEP-08 C00007 A010
200121 1500 600 23-SEP-08 C00008 A004
200130 2500 400 30-JUL-08 C00025 A011
200134 4200 1800 25-SEP-08 C00004 A005
200108 4000 600 15-FEB-08 C00008 A004
200103 1500 700 15-MAY-08 C00021 A005
200105 2500 500 18-JUL-08 C00025 A011
200109 3500 800 30-JUL-08 C00011 A010
200101 3000 1000 15-JUL-08 C00001 A008
200111 1000 300 10-JUL-08 C00020 A008
200104 1500 500 13-MAR-08 C00006 A004
200106 2500 700 20-APR-08 C00005 A002
200125 2000 600 10-OCT-08 C00018 A005
200117 800 200 20-OCT-08 C00014 A001
200123 500 100 16-SEP-08 C00022 A002
200120 500 100 20-JUL-08 C00009 A002
200116 500 100 13-JUL-08 C00010 A009
200124 500 100 20-JUN-08 C00017 A007
200126 500 100 24-JUN-08 C00022 A002
200129 2500 500 20-JUL-08 C00024 A006
200127 2500 400 20-JUL-08 C00015 A003
200128 3500 1500 20-JUL-08 C00009 A002
200135 2000 800 16-SEP-08 C00007 A010
200131 900 150 26-AUG-08 C00012 A012
200133 1200 400 29-JUN-08 C00009 A002
200100 1000 600 08-JAN-08 C00015 A003
200110 3000 500 15-APR-08 C00019 A010
200107 4500 900 30-AUG-08 C00007 A010
200112 2000 400 30-MAY-08 C00016 A007
200113 4000 600 10-JUN-08 C00022 A002
200102 2000 300 25-MAY-08 C00012 A012
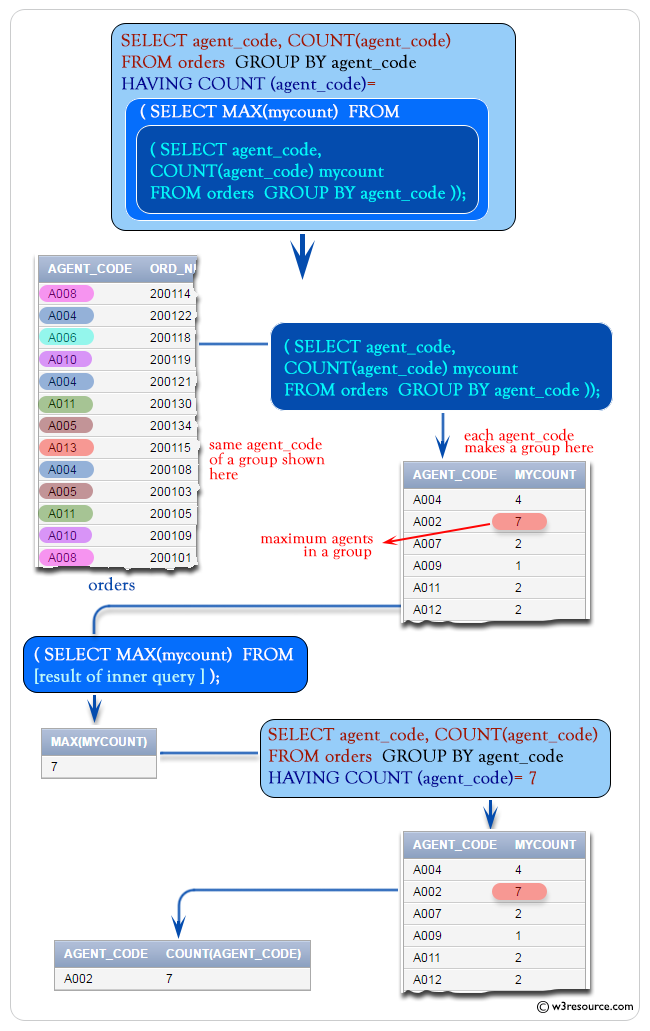
To get data of 'agent_code', and number of agents for each group of 'agent_code' from the orders table with the following conditions -
'agent_code' for a group will be equal to the result of an outer query [SELECT MAX(agent_code).......] with following condition -
the outer query produce the maximum number of agents mentioned as
'mycount' from an inner query [SELECT agent_code,
COUNT(agent_code) mycount FROM orders GROUP BY agent_code]
with following condition -
the inner query produced the data 'agent_code' number of agents as column alias 'mycount' from the 'orders' table with the following condition -
'agent_code' should be in a group,
the following SQL statement can be used :
SELECT agent_code, COUNT(agent_code) -- Selecting 'agent_code' and its count
FROM orders -- From the 'orders' table
GROUP BY agent_code -- Grouping the results by 'agent_code'
HAVING COUNT(agent_code) = ( -- Applying a condition on the grouped counts
SELECT MAX(mycount) -- Selecting the maximum count from a subquery
FROM ( -- Subquery: Creating a derived table
SELECT agent_code, COUNT(agent_code) AS mycount -- Selecting 'agent_code' and its count, aliased as 'mycount'
FROM orders -- From the 'orders' table
GROUP BY agent_code -- Grouping the results by 'agent_code'
)
);
Explanation:
- SELECT agent_code, COUNT(agent_code): This line selects the agent_code column and counts the occurrences of each agent_code in the orders table.
- FROM orders: This specifies the table from which data is being selected, which is the orders table.
- GROUP BY agent_code: This line groups the results by the agent_code column. This is necessary because we're using an aggregate function (COUNT) in conjunction with a non-aggregated column (agent_code). Grouping allows us to count the occurrences of each agent_code separately.
- HAVING COUNT(agent_code) = (...): This line filters the grouped results based on a condition. It selects groups where the count of agent_code matches the result of the subquery.
- SELECT MAX(mycount): This subquery selects the maximum value of the column mycount.
- (SELECT agent_code, COUNT(agent_code) AS mycount ... ): This is a subquery that generates a derived table. It calculates the count of occurrences of each agent_code in the orders table and aliases it as mycount.
- SELECT agent_code, COUNT(agent_code) AS mycount: This line within the subquery selects the agent_code column and counts the occurrences of each agent_code in the orders table. The COUNT(agent_code) function is used to count the occurrences of each agent_code, and it is aliased as mycount.
- FROM orders: This specifies the table from which the subquery is selecting data, which is the orders table.
- GROUP BY agent_code: This line groups the results of the subquery by the agent_code column. This is necessary because we're using an aggregate function (COUNT) in conjunction with a non-aggregated column (agent_code). Grouping allows us to count the occurrences of each agent_code separately.
Output:
AGENT_CODE COUNT(AGENT_CODE) ---------- ----------------- A002 7
Note: Outputs of the said SQL statement shown here is taken by using Oracle Database 10g Express Edition
Here is a slide presentation of all aggregate functions.
Check out our 1000+ SQL Exercises with solution and explanation to improve your skills.
Previous: Max Date
Next: Min function
- Weekly Trends and Language Statistics
- Weekly Trends and Language Statistics