SQL MIN() function
MIN() function
The aggregate function SQL MIN() is used to find the minimum value or lowest value of a column or expression. This function is useful to determine the smallest of all selected values of a column.
Syntax:
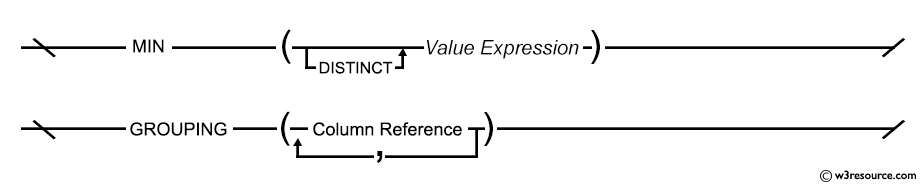
MIN ([ALL | DISTINCT] expression )
MySQL, PostgreSQL, and SQL Server
All the above platforms support the SQL syntax of MIN.
DB2 and Oracle Syntax:
MIN ([ALL | DISTINCT] expression ) OVER (window_clause)
Parameters:
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| ALL | Applies to all values. |
| DISTINCT | Consider each unique value. DISTINCT is not meaningful with MIN function. |
| expression | Expression made up of a single constant, variable, scalar function, or column name or any combination of arithmetic, bitwise, and string operators. MIN can be used with numeric, character, and datetime columns, but not with bit columns. Aggregate functions and subqueries are not permitted. |
Syntax diagram - MIN() function
SQL MIN() on specific column
Sample table: orders
ORD_NUM ORD_AMOUNT ADVANCE_AMOUNT ORD_DATE CUST_CODE AGENT_CODE ORD_DESCRIPTION
---------- ---------- -------------- --------- --------------- --------------- -----------------
200114 3500 2000 15-AUG-08 C00002 A008
200122 2500 400 16-SEP-08 C00003 A004
200118 500 100 20-JUL-08 C00023 A006
200119 4000 700 16-SEP-08 C00007 A010
200121 1500 600 23-SEP-08 C00008 A004
200130 2500 400 30-JUL-08 C00025 A011
200134 4200 1800 25-SEP-08 C00004 A005
200108 4000 600 15-FEB-08 C00008 A004
200103 1500 700 15-MAY-08 C00021 A005
200105 2500 500 18-JUL-08 C00025 A011
200109 3500 800 30-JUL-08 C00011 A010
200101 3000 1000 15-JUL-08 C00001 A008
200111 1000 300 10-JUL-08 C00020 A008
200104 1500 500 13-MAR-08 C00006 A004
200106 2500 700 20-APR-08 C00005 A002
200125 2000 600 10-OCT-08 C00018 A005
200117 800 200 20-OCT-08 C00014 A001
200123 500 100 16-SEP-08 C00022 A002
200120 500 100 20-JUL-08 C00009 A002
200116 500 100 13-JUL-08 C00010 A009
200124 500 100 20-JUN-08 C00017 A007
200126 500 100 24-JUN-08 C00022 A002
200129 2500 500 20-JUL-08 C00024 A006
200127 2500 400 20-JUL-08 C00015 A003
200128 3500 1500 20-JUL-08 C00009 A002
200135 2000 800 16-SEP-08 C00007 A010
200131 900 150 26-AUG-08 C00012 A012
200133 1200 400 29-JUN-08 C00009 A002
200100 1000 600 08-JAN-08 C00015 A003
200110 3000 500 15-APR-08 C00019 A010
200107 4500 900 30-AUG-08 C00007 A010
200112 2000 400 30-MAY-08 C00016 A007
200113 4000 600 10-JUN-08 C00022 A002
200102 2000 300 25-MAY-08 C00012 A012
To get the minimum or lowest value of 'ord_amout' from the orders table, the following SQL statement can be used:
SELECT MIN(ord_amount) -- Selects the minimum value of the 'ord_amount' column
FROM orders; -- Specifies the 'orders' table as the source of data
Explanation:
- SELECT MIN(ord_amount): This is the main part of the SQL query. It uses the MIN() function to calculate the minimum value of the 'ord_amount' column in the 'orders' table. The result will be a single value representing the minimum value found in the 'ord_amount' column.
- FROM orders: This specifies the source of the data for the query, which is the 'orders' table. The FROM keyword is used to indicate the table from which the data will be selected. In this case, it selects data from the 'orders' table.
Output:
MIN(ORD_AMOUNT)
---------------
500
SQL MIN() with addition of two columns
Sample table: customer+-----------+-------------+-------------+--------------+--------------+-------+-------------+-------------+-------------+---------------+--------------+------------+ |CUST_CODE | CUST_NAME | CUST_CITY | WORKING_AREA | CUST_COUNTRY | GRADE | OPENING_AMT | RECEIVE_AMT | PAYMENT_AMT |OUTSTANDING_AMT| PHONE_NO | AGENT_CODE | +-----------+-------------+-------------+--------------+--------------+-------+-------------+-------------+-------------+---------------+--------------+------------+ | C00013 | Holmes | London | London | UK | 2 | 6000.00 | 5000.00 | 7000.00 | 4000.00 | BBBBBBB | A003 | | C00001 | Micheal | New York | New York | USA | 2 | 3000.00 | 5000.00 | 2000.00 | 6000.00 | CCCCCCC | A008 | | C00020 | Albert | New York | New York | USA | 3 | 5000.00 | 7000.00 | 6000.00 | 6000.00 | BBBBSBB | A008 | | C00025 | Ravindran | Bangalore | Bangalore | India | 2 | 5000.00 | 7000.00 | 4000.00 | 8000.00 | AVAVAVA | A011 | | C00024 | Cook | London | London | UK | 2 | 4000.00 | 9000.00 | 7000.00 | 6000.00 | FSDDSDF | A006 | | C00015 | Stuart | London | London | UK | 1 | 6000.00 | 8000.00 | 3000.00 | 11000.00 | GFSGERS | A003 | | C00002 | Bolt | New York | New York | USA | 3 | 5000.00 | 7000.00 | 9000.00 | 3000.00 | DDNRDRH | A008 | | C00018 | Fleming | Brisban | Brisban | Australia | 2 | 7000.00 | 7000.00 | 9000.00 | 5000.00 | NHBGVFC | A005 | | C00021 | Jacks | Brisban | Brisban | Australia | 1 | 7000.00 | 7000.00 | 7000.00 | 7000.00 | WERTGDF | A005 | | C00019 | Yearannaidu | Chennai | Chennai | India | 1 | 8000.00 | 7000.00 | 7000.00 | 8000.00 | ZZZZBFV | A010 | | C00005 | Sasikant | Mumbai | Mumbai | India | 1 | 7000.00 | 11000.00 | 7000.00 | 11000.00 | 147-25896312 | A002 | | C00007 | Ramanathan | Chennai | Chennai | India | 1 | 7000.00 | 11000.00 | 9000.00 | 9000.00 | GHRDWSD | A010 | | C00022 | Avinash | Mumbai | Mumbai | India | 2 | 7000.00 | 11000.00 | 9000.00 | 9000.00 | 113-12345678 | A002 | | C00004 | Winston | Brisban | Brisban | Australia | 1 | 5000.00 | 8000.00 | 7000.00 | 6000.00 | AAAAAAA | A005 | | C00023 | Karl | London | London | UK | 0 | 4000.00 | 6000.00 | 7000.00 | 3000.00 | AAAABAA | A006 | | C00006 | Shilton | Torento | Torento | Canada | 1 | 10000.00 | 7000.00 | 6000.00 | 11000.00 | DDDDDDD | A004 | | C00010 | Charles | Hampshair | Hampshair | UK | 3 | 6000.00 | 4000.00 | 5000.00 | 5000.00 | MMMMMMM | A009 | | C00017 | Srinivas | Bangalore | Bangalore | India | 2 | 8000.00 | 4000.00 | 3000.00 | 9000.00 | AAAAAAB | A007 | | C00012 | Steven | San Jose | San Jose | USA | 1 | 5000.00 | 7000.00 | 9000.00 | 3000.00 | KRFYGJK | A012 | | C00008 | Karolina | Torento | Torento | Canada | 1 | 7000.00 | 7000.00 | 9000.00 | 5000.00 | HJKORED | A004 | | C00003 | Martin | Torento | Torento | Canada | 2 | 8000.00 | 7000.00 | 7000.00 | 8000.00 | MJYURFD | A004 | | C00009 | Ramesh | Mumbai | Mumbai | India | 3 | 8000.00 | 7000.00 | 3000.00 | 12000.00 | Phone No | A002 | | C00014 | Rangarappa | Bangalore | Bangalore | India | 2 | 8000.00 | 11000.00 | 7000.00 | 12000.00 | AAAATGF | A001 | | C00016 | Venkatpati | Bangalore | Bangalore | India | 2 | 8000.00 | 11000.00 | 7000.00 | 12000.00 | JRTVFDD | A007 | | C00011 | Sundariya | Chennai | Chennai | India | 3 | 7000.00 | 11000.00 | 7000.00 | 11000.00 | PPHGRTS | A010 | +-----------+-------------+-------------+--------------+--------------+-------+-------------+-------------+-------------+---------------+--------------+------------+
To get minimum or lowest values of (opening_amt+receive_amt) from the customer table, the following SQL statement can be used:
SELECT MIN(opening_amt + receive_amt) -- Selects the minimum value of the sum of 'opening_amt' and 'receive_amt'
FROM customer; -- Specifies the 'customer' table as the source of data
Explanation:
- SELECT MIN(opening_amt + receive_amt): This is the main part of the SQL query. It calculates the sum of the 'opening_amt' and 'receive_amt' columns for each row in the 'customer' table and then selects the minimum value among these sums. The MIN() function is used to find the minimum value.
- FROM customer: This specifies the source of the data for the query, which is the 'customer' table. The FROM keyword is used to indicate the table from which the data will be selected. In this case, it selects data from the 'customer' table.
Output:
MIN(OPENING_AMT+RECEIVE_AMT)
----------------------------
8000
SQL MIN() on date value
Sample table: orders
ORD_NUM ORD_AMOUNT ADVANCE_AMOUNT ORD_DATE CUST_CODE AGENT_CODE ORD_DESCRIPTION
---------- ---------- -------------- --------- --------------- --------------- -----------------
200114 3500 2000 15-AUG-08 C00002 A008
200122 2500 400 16-SEP-08 C00003 A004
200118 500 100 20-JUL-08 C00023 A006
200119 4000 700 16-SEP-08 C00007 A010
200121 1500 600 23-SEP-08 C00008 A004
200130 2500 400 30-JUL-08 C00025 A011
200134 4200 1800 25-SEP-08 C00004 A005
200108 4000 600 15-FEB-08 C00008 A004
200103 1500 700 15-MAY-08 C00021 A005
200105 2500 500 18-JUL-08 C00025 A011
200109 3500 800 30-JUL-08 C00011 A010
200101 3000 1000 15-JUL-08 C00001 A008
200111 1000 300 10-JUL-08 C00020 A008
200104 1500 500 13-MAR-08 C00006 A004
200106 2500 700 20-APR-08 C00005 A002
200125 2000 600 10-OCT-08 C00018 A005
200117 800 200 20-OCT-08 C00014 A001
200123 500 100 16-SEP-08 C00022 A002
200120 500 100 20-JUL-08 C00009 A002
200116 500 100 13-JUL-08 C00010 A009
200124 500 100 20-JUN-08 C00017 A007
200126 500 100 24-JUN-08 C00022 A002
200129 2500 500 20-JUL-08 C00024 A006
200127 2500 400 20-JUL-08 C00015 A003
200128 3500 1500 20-JUL-08 C00009 A002
200135 2000 800 16-SEP-08 C00007 A010
200131 900 150 26-AUG-08 C00012 A012
200133 1200 400 29-JUN-08 C00009 A002
200100 1000 600 08-JAN-08 C00015 A003
200110 3000 500 15-APR-08 C00019 A010
200107 4500 900 30-AUG-08 C00007 A010
200112 2000 400 30-MAY-08 C00016 A007
200113 4000 600 10-JUN-08 C00022 A002
200102 2000 300 25-MAY-08 C00012 A012
To get minimum or smallest value of 'ord_date' from the 'orders' table, the following SQL statement can be used:
SELECT MIN(ord_date) AS "Min Date" -- Selects the minimum value of the 'ord_date' column and renames the result column as "Min Date"
FROM orders; -- Specifies the 'orders' table as the source of data
Explanation:
- SELECT MIN(ord_date) AS "Min Date": This is the main part of the SQL query. It uses the MIN() function to calculate the minimum value of the 'ord_date' column in the 'orders' table. The result will be a single value representing the minimum date. The AS keyword is used to rename the result column as "Min Date".
- FROM orders: This specifies the source of the data for the query, which is the 'orders' table. The FROM keyword is used to indicate the table from which the data will be selected. In this case, it selects data from the 'orders' table.
Output:
Min Date --------- 08-JAN-08
All Aggregate Functions

Here is a new document which is a collection of questions with short and simple answers, useful for learning SQL as well as for interviews.
Check out our 1000+ SQL Exercises with solution and explanation to improve your skills.
Previous: Max Count, Having
Next: Min group by, order by
