SQL Subqueries
What is subquery in SQL?
A subquery is a SQL query nested inside a larger query.
- A subquery can be located in :
- - A SELECT clause
- - A FROM clause
- - A WHERE clause
- - A HAVING clause
- The subquery can be nested inside a SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, or DELETE statement or inside another subquery.
- A subquery is usually added within the WHERE Clause of another SQL SELECT statement.
- You can use the comparison operators, such as >, <, or =. The comparison operator can also be a multiple-row operator, such as IN, ANY, or ALL.
- A subquery is also called an inner query or inner select, while the statement containing a subquery is also called an outer query or outer select.
- The inner query executes first before its parent query so that the results of an inner query can be passed to the outer query.
You can use a subquery in a SELECT, INSERT, DELETE, or UPDATE statement to perform the following tasks:
- Compare an expression to the result of the query.
- Determine if an expression is included in the results of the query.
- Check whether the query selects any rows.
Syntax :

- The subquery (inner query) executes once before the main query (outer query) executes.
- The main query (outer query) use the subquery result.
SQL Subqueries Locations :
Sample table: employees
employee_id|first_name |last_name |email |phone_number |hire_date |job_id |salary |commission_pct|manager_id|department_id|
-----------+-----------+-----------+--------+------------------+----------+----------+--------+--------------+----------+-------------+
100|Steven |King |SKING |515.123.4567 |2003-06-17|AD_PRES |24000.00| 0.00| 0| 90|
101|Neena |Kochhar |NKOCHHAR|515.123.4568 |2005-09-21|AD_VP |17000.00| 0.00| 100| 90|
102|Lex |De Haan |LDEHAAN |515.123.4569 |2001-01-13|AD_VP |17000.00| 0.00| 100| 90|
103|Alexander |Hunold |AHUNOLD |590.423.4567 |2006-01-03|IT_PROG | 9000.00| 0.00| 102| 60|
104|Bruce |Ernst |BERNST |590.423.4568 |2007-05-21|IT_PROG | 6000.00| 0.00| 103| 60|
105|David |Austin |DAUSTIN |590.423.4569 |2005-06-25|IT_PROG | 4800.00| 0.00| 103| 60|
106|Valli |Pataballa |VPATABAL|590.423.4560 |2006-02-05|IT_PROG | 4800.00| 0.00| 103| 60|
107|Diana |Lorentz |DLORENTZ|590.423.5567 |2007-02-07|IT_PROG | 4200.00| 0.00| 103| 60|
108|Nancy |Greenberg |NGREENBE|515.124.4569 |2002-08-17|FI_MGR |12000.00| 0.00| 101| 100|
109|Daniel |Faviet |DFAVIET |515.124.4169 |2002-08-16|FI_ACCOUNT| 9000.00| 0.00| 108| 100|
..........
Sample table: departments
department_id|department_name |manager_id|location_id|
-------------+--------------------+----------+-----------+
10|Administration | 200| 1700|
20|Marketing | 201| 1800|
30|Purchasing | 114| 1700|
40|Human Resources | 203| 2400|
50|Shipping | 121| 1500|
60|IT | 103| 1400|
70|Public Relations | 204| 2700|
80|Sales | 145| 2500|
90|Executive | 100| 1700|
100|Finance | 108| 1700|
..........
SELECT first_name, (SELECT department_name FROM departments WHERE departments.department_id = employees.department_id) AS department_name
FROM employees;
SELECT *
FROM (SELECT first_name, salary FROM employees WHERE salary > 5000) AS "high_salaried"
SELECT first_name
FROM employees
WHERE department_id IN (SELECT department_id FROM departments WHERE location_id>1500);
SELECT department_id, AVG(salary)
FROM employees
GROUP BY department_id
HAVING AVG(salary) > (SELECT AVG(salary) FROM employees);
SQL Subqueries Example :
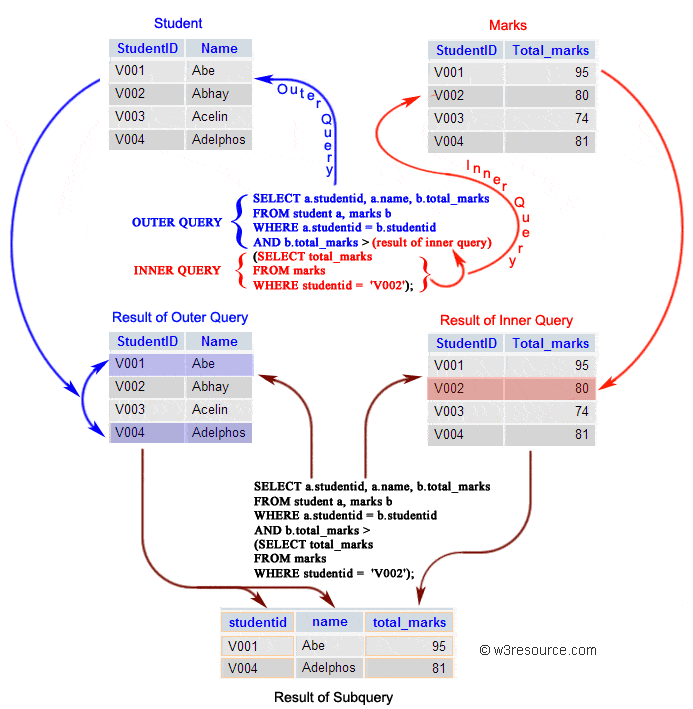
In this section, you will learn the requirements of using subqueries. We have the following two tables 'student' and 'marks' with common field 'StudentID'.
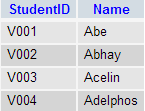
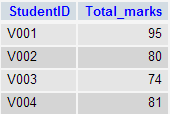
Now we want to write a query to identify all students who get better marks than that of the student who's StudentID is 'V002', but we do not know the marks of 'V002'.
- To solve the problem, we require two queries. One query returns the marks (stored in Total_marks field) of 'V002' and a second query identifies the students who get better marks than the result of the first query.
First query:
-- Selecting all columns from the 'marks' table
SELECT *
-- Specifying the table from which to retrieve data: 'marks'
FROM `marks`
-- Filtering the result set to include only rows where the value in the 'studentid' column is 'V002'
WHERE studentid = 'V002';
Explanation:
- This SQL query retrieves data from the 'marks' table.
- It selects all columns from the table using the asterisk (*) wildcard.
- The FROM clause specifies the table from which to retrieve data, which is 'marks'.
- The WHERE clause filters the result set to include only rows where the value in the 'studentid' column is equal to 'V002'.
- This query is useful for retrieving all marks records associated with a specific student, identified by their student ID ('V002' in this case).
Output:

The result of the query is 80.
-
Using the result of this query, here we have written another query to identify the students who get better marks than 80. Here is the query :
Second query:
-- Selecting specific columns: 'studentid' and 'name' from table 'a' (student), and 'total_marks' from table 'b' (marks)
SELECT a.studentid, a.name, b.total_marks
-- Performing a Cartesian product (cross join) between tables 'student' (aliased as 'a') and 'marks' (aliased as 'b') (implicit join)
FROM student a, marks b
-- Defining the join condition in the WHERE clause where 'a.studentid' equals 'b.studentid'
WHERE a.studentid = b.studentid
-- Filtering the result set to include only rows where 'total_marks' from 'marks' is greater than 80
AND b.total_marks > 80;
Explanation:
- This SQL query retrieves data from two tables: 'student' and 'marks'.
- It selects specific columns from these tables: 'studentid' and 'name' from the 'student' table (aliased as 'a'), and 'total_marks' from the 'marks' table (aliased as 'b').
- The query performs a Cartesian product (cross join) between the 'student' and 'marks' tables, implicitly joining every row from the 'student' table with every row from the 'marks' table.
- The join condition is specified in the WHERE clause, where 'a.studentid' (from 'student') must equal 'b.studentid' (from 'marks'). This links the two tables based on the student ID.
- Additionally, the WHERE clause includes a condition to filter the result set, ensuring that only rows where 'total_marks' from 'marks' are greater than 80 are included.
- This query retrieves data about students whose total marks are greater than 80, along with their student ID and name.
- Cartesian product may result in a large intermediate result set, and hence, it's essential to ensure that the join conditions are correctly specified to avoid unnecessary rows in the output.
Relational Algebra Expression:

Relational Algebra Tree:
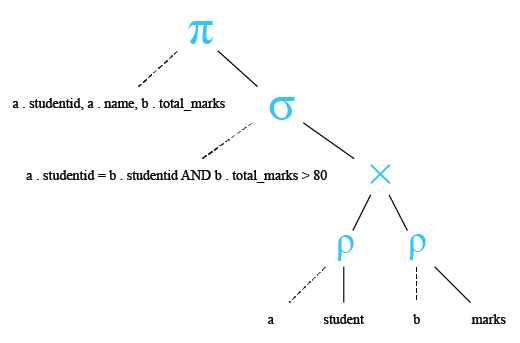
Output:
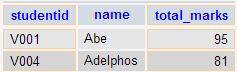
Above two queries identified students who get the better number than the student who's StudentID is 'V002' (Abhay).
You can combine the above two queries by placing one query inside the other. The subquery (also called the 'inner query') is the query inside the parentheses. See the following code and query result :
SQL Code:
-- Selecting specific columns: 'studentid' and 'name' from table 'a' (student), and 'total_marks' from table 'b' (marks)
SELECT a.studentid, a.name, b.total_marks
-- Performing a Cartesian product (cross join) between tables 'student' (aliased as 'a') and 'marks' (aliased as 'b') (implicit join)
FROM student a, marks b
-- Defining the join condition in the WHERE clause where 'a.studentid' equals 'b.studentid'
WHERE a.studentid = b.studentid
-- Filtering the result set to include only rows where 'total_marks' from 'marks' is greater than the total marks of student 'V002'
AND b.total_marks >
(SELECT total_marks
FROM marks
WHERE studentid = 'V002');
Explanation:
- This SQL query retrieves data from two tables: 'student' and 'marks'.
- It selects specific columns from these tables: 'studentid' and 'name' from the 'student' table (aliased as 'a'), and 'total_marks' from the 'marks' table (aliased as 'b').
- The query performs a Cartesian product (cross join) between the 'student' and 'marks' tables, implicitly joining every row from the 'student' table with every row from the 'marks' table.
- The join condition is specified in the WHERE clause, where 'a.studentid' (from 'student') must equal 'b.studentid' (from 'marks'). This links the two tables based on the student ID.
- Additionally, the WHERE clause includes a condition to filter the result set, ensuring that only rows where 'total_marks' from 'marks' are greater than the total marks of student 'V002' are included. This condition is obtained using a subquery.
- The subquery retrieves the total marks of student 'V002' from the 'marks' table, and the main query then compares the total marks of other students with this value.
- This query retrieves data about students whose total marks are greater than the total marks of student 'V002', along with their student ID and name.
- Using a subquery in the WHERE clause allows for dynamic filtering based on the result of another query.
Output:

Visual Presentation of SQL Subquery:
Subqueries: General Rules
A subquery SELECT statement is almost similar to the SELECT statement and it is used to begin a regular or outer query. Here is the syntax of a subquery:
Syntax:
(SELECT [DISTINCT] subquery_select_argument
FROM {table_name | view_name}
{table_name | view_name} ...
[WHERE search_conditions]
[GROUP BY aggregate_expression [, aggregate_expression] ...]
[HAVING search_conditions])
Subqueries: Guidelines
There are some guidelines to consider when using subqueries :
- A subquery must be enclosed in parentheses.
- A subquery must be placed on the right side of the comparison operator.
- Subqueries cannot manipulate their results internally, therefore ORDER BY clause cannot be added into a subquery. You can use an ORDER BY clause in the main SELECT statement (outer query) which will be the last clause.
- Use single-row operators with single-row subqueries.
- If a subquery (inner query) returns a null value to the outer query, the outer query will not return any rows when using certain comparison operators in a WHERE clause.
Type of Subqueries
- Scalar Subquery: Returns a single value.
- Column Subquery: Returns a single column of values
- Multiple column subqueries : Returns one or more columns.
- Single row subquery : Returns a single row of values.
- Multiple row subquery : Returns one or more rows.
- Table Subquery: Returns a result set that can be treated as a table
- Correlated subqueries : Reference one or more columns in the outer SQL statement. The subquery is known as a correlated subquery because the subquery is related to the outer SQL statement.
- Nested subqueries : Subqueries are placed within another subquery.
Scalar Subquery:
SELECT first_name
FROM employees
WHERE salary > (SELECT AVG(salary) FROM employees);
Column Subquery:
SELECT first_name
FROM employees
WHERE department_id IN (SELECT department_id FROM departments WHERE location_id > 1500);
Single Row Subquery:
SELECT first_name
FROM employees
WHERE salary = (SELECT MAX(salary) FROM employees);
Table Subquery:
SELECT first_name,last_name
FROM employees
WHERE department_id IN (SELECT department_id FROM departments);
Correlated vs. Non-Correlated Subqueries
Non-Correlated Subquery:
SELECT first_name
FROM employees
WHERE salary > (SELECT AVG(salary) FROM employees);
Correlated Subquery:
SELECT first_name
FROM employees e1
WHERE salary > (SELECT AVG(salary) FROM employees e2 WHERE e1.department_id = e2.department_id);
In the next session, we have thoroughly discussed the above topics. Apart from the above type of subqueries, you can use a subquery inside INSERT, UPDATE and DELETE statement. Here is a brief discussion :
Subqueries with INSERT statement
INSERT statement can be used with subqueries. Here are the syntax and an example of subqueries using INSERT statement.
Syntax:
INSERT INTO table_name [ (column1 [, column2 ]) ] SELECT [ *|column1 [, column2 ] FROM table1 [, table2 ] [ WHERE VALUE OPERATOR ];
If we want to insert those orders from 'orders' table which have the advance_amount 2000 or 5000 into 'neworder' table the following SQL can be used:
Sample table: orders
ORD_NUM ORD_AMOUNT ADVANCE_AMOUNT ORD_DATE CUST_CODE AGENT_CODE ORD_DESCRIPTION
---------- ---------- -------------- --------- --------------- --------------- -----------------
200114 3500 2000 15-AUG-08 C00002 A008
200122 2500 400 16-SEP-08 C00003 A004
200118 500 100 20-JUL-08 C00023 A006
200119 4000 700 16-SEP-08 C00007 A010
200121 1500 600 23-SEP-08 C00008 A004
200130 2500 400 30-JUL-08 C00025 A011
200134 4200 1800 25-SEP-08 C00004 A005
200108 4000 600 15-FEB-08 C00008 A004
200103 1500 700 15-MAY-08 C00021 A005
200105 2500 500 18-JUL-08 C00025 A011
.....
SQL Code:
-- Inserting data into the 'neworder' table
INSERT INTO neworder
-- Selecting all columns from the 'orders' table where 'advance_amount' is either 2000 or 5000
SELECT * FROM orders
WHERE advance_amount IN (2000, 5000);
Explanation:
- This SQL query inserts data into the 'neworder' table from the 'orders' table.
- The SELECT statement retrieves all columns from the 'orders' table where the 'advance_amount' column has values of either 2000 or 5000.
- The IN operator in the WHERE clause allows for specifying multiple values to filter rows based on those values.
- Only rows from the 'orders' table where the 'advance_amount' matches either 2000 or 5000 will be inserted into the 'neworder' table.
- This query is useful for copying specific rows from the 'orders' table to the 'neworder' table based on the advance amount. It helps in creating a subset of orders with certain criteria in a separate table.
Output:

To see more details of subqueries using INSERT statement click here.
Subqueries with UPDATE statement
In a UPDATE statement, you can set new column value equal to the result returned by a single row subquery. Here are the syntax and an example of subqueries using UPDATE statement.
Syntax:
UPDATE table SET column_name = new_value [ WHERE OPERATOR [ VALUE ] (SELECT COLUMN_NAME FROM TABLE_NAME) [ WHERE) ]
If we want to update that ord_date in 'neworder' table with '15-JAN-10' which have the difference of ord_amount and advance_amount is less than the minimum ord_amount of 'orders' table the following SQL can be used: Sample table: orders
ORD_NUM ORD_AMOUNT ADVANCE_AMOUNT ORD_DATE CUST_CODE AGENT_CODE ORD_DESCRIPTION
---------- ---------- -------------- --------- --------------- --------------- -----------------
200114 3500 2000 15-AUG-08 C00002 A008
200122 2500 400 16-SEP-08 C00003 A004
200118 500 100 20-JUL-08 C00023 A006
200119 4000 700 16-SEP-08 C00007 A010
200121 1500 600 23-SEP-08 C00008 A004
200130 2500 400 30-JUL-08 C00025 A011
200134 4200 1800 25-SEP-08 C00004 A005
200108 4000 600 15-FEB-08 C00008 A004
200103 1500 700 15-MAY-08 C00021 A005
200105 2500 500 18-JUL-08 C00025 A011
.....
SQL Code:
-- Update the 'neworder' table by setting the 'ord_date' column to '15-JAN-10'
-- for rows where the result of 'ord_amount' minus 'advance_amount' is less than
-- the minimum value of 'ord_amount' from the 'orders' table.
UPDATE neworder
-- Set the table to be updated to 'neworder'.
SET ord_date='15-JAN-10'
-- Set the value of the 'ord_date' column to '15-JAN-10' for the selected rows.
WHERE ord_amount-advance_amount<
-- Filter the rows based on the condition that the result of 'ord_amount' minus 'advance_amount'
(SELECT MIN(ord_amount) FROM orders);
-- Compare the result with the minimum value of 'ord_amount' from the 'orders' table.
Explanation:
- This SQL code is an UPDATE statement used to modify data in the 'neworder' table based on certain conditions.
- The purpose of this code seems to be updating the 'ord_date' column of the 'neworder' table under specific circumstances.
- The UPDATE statement specifies the table to be updated, which is 'neworder'.
- SET clause assigns the value '15-JAN-10' to the 'ord_date' column for the selected rows.
- The WHERE clause filters the rows based on a condition. In this case, it checks if the result of 'ord_amount' minus 'advance_amount' is less than the minimum value of 'ord_amount' from the 'orders' table.
- The subquery (SELECT MIN(ord_amount) FROM orders) retrieves the minimum value of 'ord_amount' from the 'orders' table, which is then used for comparison in the WHERE clause.
Output:

To see more details of subqueries using UPDATE statement click here.
Subqueries with DELETE statement
DELETE statement can be used with subqueries. Here are the syntax and an example of subqueries using DELETE statement.
Syntax:
DELETE FROM TABLE_NAME [ WHERE OPERATOR [ VALUE ] (SELECT COLUMN_NAME FROM TABLE_NAME) [ WHERE) ]
If we want to delete those orders from 'neworder' table which advance_amount are less than the maximum advance_amount of 'orders' table, the following SQL can be used:
Sample table: neworder
ORD_NUM ORD_AMOUNT ADVANCE_AMOUNT ORD_DATE CUST_CODE AGENT_CODE ORD_DESCRIPTION
---------- ---------- -------------- --------- --------------- --------------- -----------------
200114 3500 2000 15-AUG-08 C00002 A008
200122 2500 400 16-SEP-08 C00003 A004
200118 500 100 20-JUL-08 C00023 A006
200119 4000 700 16-SEP-08 C00007 A010
200121 1500 600 23-SEP-08 C00008 A004
200130 2500 400 30-JUL-08 C00025 A011
200134 4200 1800 25-SEP-08 C00004 A005
200108 4000 600 15-FEB-08 C00008 A004
200103 1500 700 15-MAY-08 C00021 A005
200105 2500 500 18-JUL-08 C00025 A011
.....
SQL Code:
-- Delete rows from the 'neworder' table where the 'advance_amount' column is less than
-- the maximum value of 'advance_amount' from the 'orders' table.
DELETE FROM neworder
-- Specify the table from which rows will be deleted, which is 'neworder'.
WHERE advance_amount <
-- Specify the condition for deletion: 'advance_amount' is less than
(SELECT MAX(advance_amount) FROM orders);
-- Compare 'advance_amount' from 'neworder' with the maximum value of 'advance_amount' from 'orders'.
Explanation:
- This SQL code is a DELETE statement used to remove rows from the 'neworder' table based on certain conditions.
- The purpose of this code seems to be deleting rows from the 'neworder' table where the 'advance_amount' is less than the maximum value of 'advance_amount' from the 'orders' table.
- The DELETE statement specifies the table from which rows will be deleted, which is 'neworder'.
- The WHERE clause filters the rows based on a condition. In this case, it checks if the 'advance_amount' in 'neworder' is less than the maximum value of 'advance_amount' from the 'orders' table.
- The subquery (SELECT MAX(advance_amount) FROM orders) retrieves the maximum value of 'advance_amount' from the 'orders' table, which is then used for comparison in the WHERE clause.
Output:

To see more details of subqueries using DELETE statement click here.
What Next?
- SQL Subqueries - Slide Presentation
- Single Row Subqueries
- Multiple Row and Column Subqueries
- Correlated subqueries using aliases
- Nested subqueries
Note: Outputs of the said SQL statement shown here is taken by using Oracle Database 10g Express Edition.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) - SQL Subqueries
1. What is a subquery in SQL?
A subquery is a SQL query nested inside a larger query.
2. Where can a subquery be located in SQL?
A subquery can be located in:
- A SELECT clause
- A FROM clause
- A WHERE clause
- A HAVING clause
3. In which SQL statements can a SQL subquery be nested?
A subquery can be nested inside SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, or DELETE statements or inside another subquery.
4. How does a SQL subquery operate within a query?
The inner query (subquery) executes first, and its result is passed to the outer query. This process allows the outer query to use the subquery's result for further operations.
5. What are the common uses of SQL subqueries?
Subqueries are used to:
- Compare an expression to the result of another SQL query.
- Determine if an expression is included in the results of another query.
- Check whether the query selects any rows.
6. What is the difference between an SQL inner query and an SQL outer query?
An inner query (subquery) is the query inside the parentheses, and it executes first. The outer query is the main query that uses the result of the inner query.
7. What are the general rules for using SQL subqueries?
- Subqueries must be enclosed in parentheses.
- A subquery must be placed on the right side of the comparison operator.
- Subqueries cannot include an ORDER BY clause. However, you can use an ORDER BY clause in the main (outer) query.
- Use single-row operators with single-row subqueries.
- If a subquery returns a null value to the outer query, the outer query will not return any rows when using certain comparison operators in a WHERE clause.
8. What are the types of SQL subqueries?
- Scalar Subquery: Returns a single value.
- Column Subquery: Returns a single column of values.
- Multiple Column Subquery: Returns one or more columns.
- Single Row Subquery: Returns a single row of values.
- Multiple Row Subquery: Returns one or more rows.
- Table Subquery: Returns a result set that can be treated as a table.
- Correlated Subquery: References one or more columns in the outer SQL statement and is related to the outer SQL statement.
- Nested Subquery: A subquery within another subquery.
9. Can SQL subqueries be used with INSERT statements?
Yes, subqueries can be used with INSERT statements to insert data based on the results of another query.
10. Can SQL subqueries be used with UPDATE statements?
Yes, subqueries can be used with UPDATE statements to set new column values based on the results of another query.
11. Can SQL subqueries be used with DELETE statements?
Yes, subqueries can be used with DELETE statements to delete data based on the results of another query.
Check out our 1000+ SQL Exercises with solution and explanation to improve your skills.
Previous: Using a where clause to join tables based on nonkey columns
Next: Single Row Subqueries