SQL: Multiple Row and Column Subqueries
Multiple Row Subqueries
Multiple row subquery returns one or more rows to the outer SQL statement. You may use the IN, ANY, or ALL operator in outer query to handle a subquery that returns multiple rows.
Contents:
SQL: Using IN operator with a Multiple Row Subquery
IN operator is used to checking a value within a set of values. The list of values may come from the results returned by a subquery. See the following example :
To get 'ord_num', 'ord_amount', 'ord_date', 'cust_code' and 'agent_code' from the table 'orders' with following conditions:
Sample table : agents+------------+----------------------+--------------------+------------+-----------------+---------+ | AGENT_CODE | AGENT_NAME | WORKING_AREA | COMMISSION | PHONE_NO | COUNTRY | +------------+----------------------+--------------------+------------+-----------------+---------+ | A007 | Ramasundar | Bangalore | 0.15 | 077-25814763 | | | A003 | Alex | London | 0.13 | 075-12458969 | | | A008 | Alford | New York | 0.12 | 044-25874365 | | | A011 | Ravi Kumar | Bangalore | 0.15 | 077-45625874 | | | A010 | Santakumar | Chennai | 0.14 | 007-22388644 | | | A012 | Lucida | San Jose | 0.12 | 044-52981425 | | | A005 | Anderson | Brisban | 0.13 | 045-21447739 | | | A001 | Subbarao | Bangalore | 0.14 | 077-12346674 | | | A002 | Mukesh | Mumbai | 0.11 | 029-12358964 | | | A006 | McDen | London | 0.15 | 078-22255588 | | | A004 | Ivan | Torento | 0.15 | 008-22544166 | | | A009 | Benjamin | Hampshair | 0.11 | 008-22536178 | | +------------+----------------------+--------------------+------------+-----------------+---------+Sample table: orders
ORD_NUM ORD_AMOUNT ADVANCE_AMOUNT ORD_DATE CUST_CODE AGENT_CODE ORD_DESCRIPTION
---------- ---------- -------------- --------- --------------- --------------- -----------------
200114 3500 2000 15-AUG-08 C00002 A008
200122 2500 400 16-SEP-08 C00003 A004
200118 500 100 20-JUL-08 C00023 A006
200119 4000 700 16-SEP-08 C00007 A010
200121 1500 600 23-SEP-08 C00008 A004
200130 2500 400 30-JUL-08 C00025 A011
200134 4200 1800 25-SEP-08 C00004 A005
200108 4000 600 15-FEB-08 C00008 A004
200103 1500 700 15-MAY-08 C00021 A005
200105 2500 500 18-JUL-08 C00025 A011
200109 3500 800 30-JUL-08 C00011 A010
200101 3000 1000 15-JUL-08 C00001 A008
200111 1000 300 10-JUL-08 C00020 A008
200104 1500 500 13-MAR-08 C00006 A004
200106 2500 700 20-APR-08 C00005 A002
200125 2000 600 10-OCT-08 C00018 A005
200117 800 200 20-OCT-08 C00014 A001
200123 500 100 16-SEP-08 C00022 A002
200120 500 100 20-JUL-08 C00009 A002
200116 500 100 13-JUL-08 C00010 A009
200124 500 100 20-JUN-08 C00017 A007
200126 500 100 24-JUN-08 C00022 A002
200129 2500 500 20-JUL-08 C00024 A006
200127 2500 400 20-JUL-08 C00015 A003
200128 3500 1500 20-JUL-08 C00009 A002
200135 2000 800 16-SEP-08 C00007 A010
200131 900 150 26-AUG-08 C00012 A012
200133 1200 400 29-JUN-08 C00009 A002
200100 1000 600 08-JAN-08 C00015 A003
200110 3000 500 15-APR-08 C00019 A010
200107 4500 900 30-AUG-08 C00007 A010
200112 2000 400 30-MAY-08 C00016 A007
200113 4000 600 10-JUN-08 C00022 A002
200102 2000 300 25-MAY-08 C00012 A012
in the outer query:
'agent_code' of 'orders' table must be in the list within IN operator in inner query :
in inner query:
'working_area' of 'agents' table must be 'Bangalore',
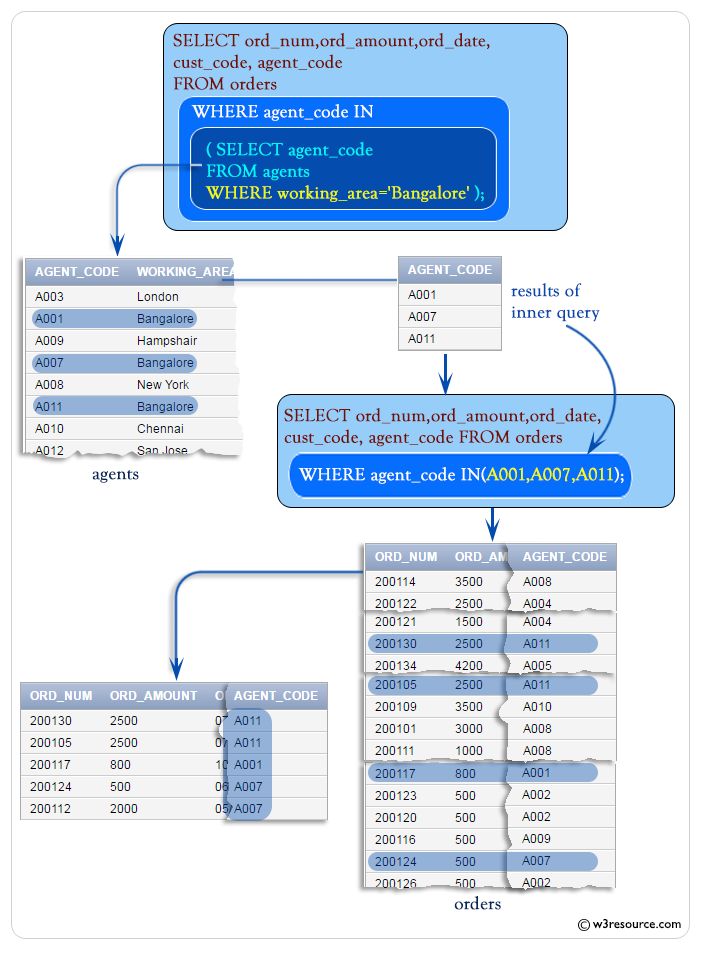
Here is the complete SQL statement :
SQL Code:
-- Selecting specific columns from the orders table
SELECT ord_num, ord_amount, ord_date,
cust_code, agent_code
-- Filtering orders based on agent_code
FROM orders
-- Subquery to find agent_codes working in Bangalore
WHERE agent_code IN (
-- Selecting agent_codes from agents table
SELECT agent_code
-- Filtering agents based on working_area
FROM agents
WHERE working_area='Bangalore'
);
Explanation:
- This SQL query retrieves specific columns from the "orders" table.
- It filters the orders based on the agent_code.
- The subquery is used to find agent_codes of agents who work in Bangalore.
- It first selects the agent_codes from the "agents" table.
- Then it filters these agents based on their working_area being 'Bangalore'.
- The main query then selects orders where the agent_code matches those found in the subquery, meaning it selects orders handled by agents working in Bangalore.
Output:
ORD_NUM ORD_AMOUNT ORD_DATE CUST_CODE AGENT_CODE
---------- ---------- --------- ---------- ----------
200130 2500 30-JUL-08 C00025 A011
200105 2500 18-JUL-08 C00025 A011
200117 800 20-OCT-08 C00014 A001
200124 500 20-JUN-08 C00017 A007
200112 2000 30-MAY-08 C00016 A007
Let's break the above query and analyze what's going on in inner query. Here is the code of inner query :
SQL Code:
-- Selecting the agent_code column from the agents table
SELECT agent_code
-- Filtering agents based on their working_area
FROM agents
-- Specifying the condition for filtering
WHERE working_area='Bangalore';
Explanation:
- This SQL query retrieves the agent_code from the "agents" table.
- It filters the agents based on their working_area.
- The condition specified in the WHERE clause restricts the results to only those agents whose working_area is 'Bangalore'.
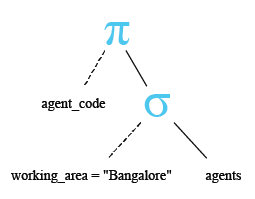
Relational Algebra Expression:
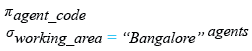
Relational Algebra Tree:
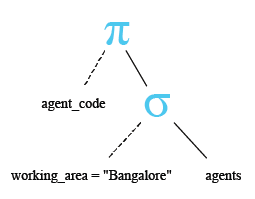
Output:
AGENT_CODE ---------- A001 A007 A011
The above query returns two agent codes 'A011' and 'A001'.
Visual Presentation:
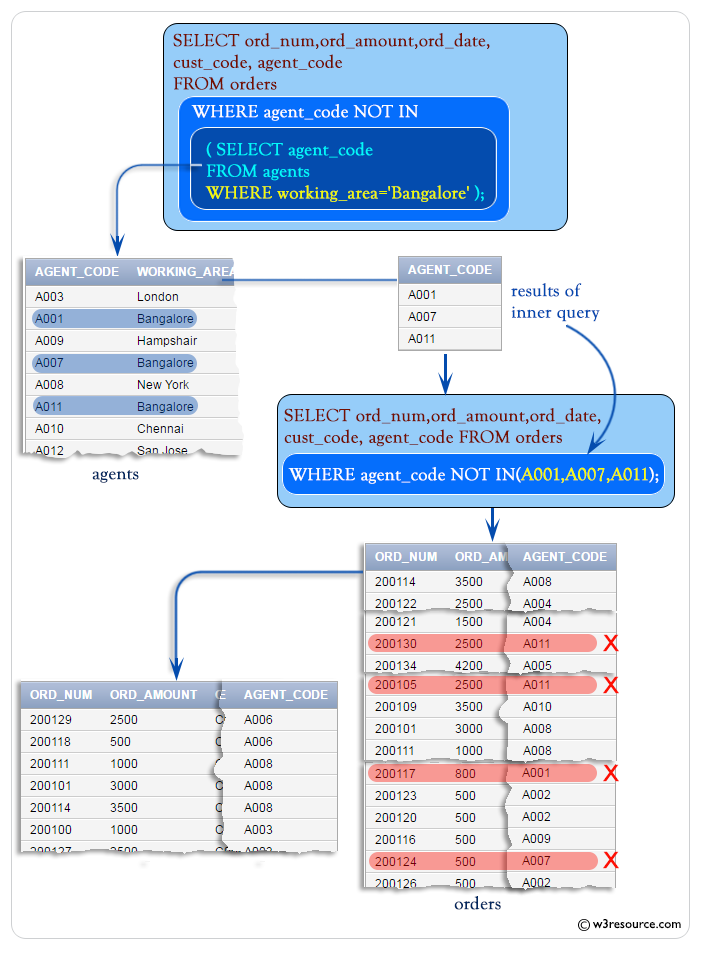
SQL: Using NOT IN operator with a Multiple Row Subquery
You can also use NOT IN operator to perform the logical opposite of IN operator. See the following example :
Sample table : agents+------------+----------------------+--------------------+------------+-----------------+---------+ | AGENT_CODE | AGENT_NAME | WORKING_AREA | COMMISSION | PHONE_NO | COUNTRY | +------------+----------------------+--------------------+------------+-----------------+---------+ | A007 | Ramasundar | Bangalore | 0.15 | 077-25814763 | | | A003 | Alex | London | 0.13 | 075-12458969 | | | A008 | Alford | New York | 0.12 | 044-25874365 | | | A011 | Ravi Kumar | Bangalore | 0.15 | 077-45625874 | | | A010 | Santakumar | Chennai | 0.14 | 007-22388644 | | | A012 | Lucida | San Jose | 0.12 | 044-52981425 | | | A005 | Anderson | Brisban | 0.13 | 045-21447739 | | | A001 | Subbarao | Bangalore | 0.14 | 077-12346674 | | | A002 | Mukesh | Mumbai | 0.11 | 029-12358964 | | | A006 | McDen | London | 0.15 | 078-22255588 | | | A004 | Ivan | Torento | 0.15 | 008-22544166 | | | A009 | Benjamin | Hampshair | 0.11 | 008-22536178 | | +------------+----------------------+--------------------+------------+-----------------+---------+Sample table: orders
ORD_NUM ORD_AMOUNT ADVANCE_AMOUNT ORD_DATE CUST_CODE AGENT_CODE ORD_DESCRIPTION
---------- ---------- -------------- --------- --------------- --------------- -----------------
200114 3500 2000 15-AUG-08 C00002 A008
200122 2500 400 16-SEP-08 C00003 A004
200118 500 100 20-JUL-08 C00023 A006
200119 4000 700 16-SEP-08 C00007 A010
200121 1500 600 23-SEP-08 C00008 A004
200130 2500 400 30-JUL-08 C00025 A011
200134 4200 1800 25-SEP-08 C00004 A005
200108 4000 600 15-FEB-08 C00008 A004
200103 1500 700 15-MAY-08 C00021 A005
200105 2500 500 18-JUL-08 C00025 A011
200109 3500 800 30-JUL-08 C00011 A010
200101 3000 1000 15-JUL-08 C00001 A008
200111 1000 300 10-JUL-08 C00020 A008
200104 1500 500 13-MAR-08 C00006 A004
200106 2500 700 20-APR-08 C00005 A002
200125 2000 600 10-OCT-08 C00018 A005
200117 800 200 20-OCT-08 C00014 A001
200123 500 100 16-SEP-08 C00022 A002
200120 500 100 20-JUL-08 C00009 A002
200116 500 100 13-JUL-08 C00010 A009
200124 500 100 20-JUN-08 C00017 A007
200126 500 100 24-JUN-08 C00022 A002
200129 2500 500 20-JUL-08 C00024 A006
200127 2500 400 20-JUL-08 C00015 A003
200128 3500 1500 20-JUL-08 C00009 A002
200135 2000 800 16-SEP-08 C00007 A010
200131 900 150 26-AUG-08 C00012 A012
200133 1200 400 29-JUN-08 C00009 A002
200100 1000 600 08-JAN-08 C00015 A003
200110 3000 500 15-APR-08 C00019 A010
200107 4500 900 30-AUG-08 C00007 A010
200112 2000 400 30-MAY-08 C00016 A007
200113 4000 600 10-JUN-08 C00022 A002
200102 2000 300 25-MAY-08 C00012 A012
To get 'ord_num', 'ord_amount', 'ord_date', 'cust_code' and 'agent_code' from the table 'orders' with following conditions :
in outer query:
'agent_code' of 'orders' table must be other than the list within IN operator.
in inner query :
'working_area' of 'agents' table must be 'Mumbai'
Here is the complete SQL statement :
SQL Code:
-- Selecting specific columns from the orders table
SELECT ord_num, ord_amount, ord_date,
cust_code, agent_code
-- Filtering orders based on agent_code
FROM orders
-- Filtering out orders handled by agents in Bangalore
WHERE agent_code NOT IN (
-- Selecting agent_codes from agents table
SELECT agent_code
-- Filtering agents based on working_area
FROM agents
WHERE working_area='Bangalore'
);
Explanation:
- This SQL query retrieves specific columns from the "orders" table.
- It filters the orders based on the agent_code.
- The subquery is used to find agent_codes of agents who work in Bangalore.
- It first selects the agent_codes from the "agents" table.
- Then it filters these agents based on their working_area being 'Bangalore'.
- The main query then selects orders where the agent_code does not match those found in the subquery, meaning it selects orders handled by agents who do not work in Bangalore.
Output:
ORD_NUM ORD_AMOUNT ORD_DATE CUST_CODE AGENT_CO --------- ---------- --------- ---------- -------- 200129 2500 20-JUL-08 C00024 A006 200118 500 20-JUL-08 C00023 A006 200111 1000 10-JUL-08 C00020 A008 200101 3000 15-JUL-08 C00001 A008 200114 3500 15-AUG-08 C00002 A008 200100 1000 08-JAN-08 C00015 A003 200127 2500 20-JUL-08 C00015 A003 200113 4000 10-JUN-08 C00022 A002 200133 1200 29-JUN-08 C00009 A002 200128 3500 20-JUL-08 C00009 A002 200126 500 24-JUN-08 C00022 A002 200120 500 20-JUL-08 C00009 A002 200123 500 16-SEP-08 C00022 A002 200106 2500 20-APR-08 C00005 A002 200116 500 13-JUL-08 C00010 A009 200132 4000 15-AUG-08 C00013 A013 200115 2000 08-FEB-08 C00013 A013 200125 2000 10-OCT-08 C00018 A005 200103 1500 15-MAY-08 C00021 A005 200134 4200 25-SEP-08 C00004 A005 ......... .........
Let's break the above query and analyze what's going on in inner query. Here is the code of inner query :
SQL Code:
SELECT agent_code FROM agents
WHERE working_area='Bangalore';
Relational Algebra Expression:
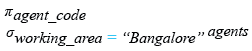
Relational Algebra Tree:
Output:
AGENT_CODE ---------- A001 A007 A011
Visual Presentation:
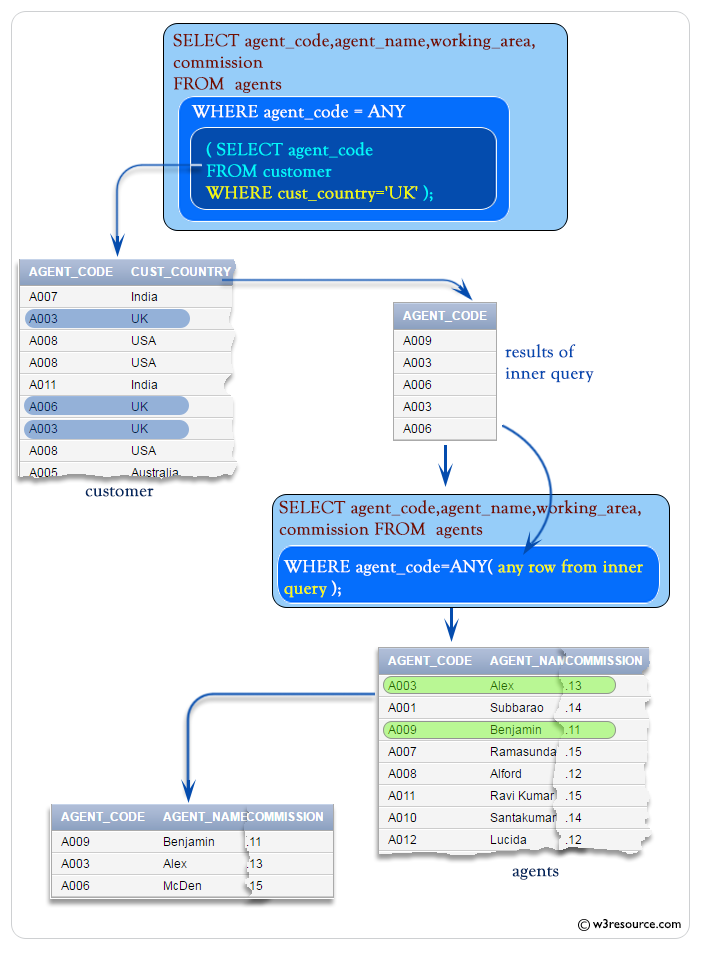
SQL: Using ANY with a Multiple Row Subquery
You can use the ANY operator to compare a value with any value in a list. You must place an =, <>, >, <, <= or >= operator before ANY in your query. The following example uses ANY to check if any of the agent who belongs to the country 'UK'.
Sample table : agents+------------+----------------------+--------------------+------------+-----------------+---------+ | AGENT_CODE | AGENT_NAME | WORKING_AREA | COMMISSION | PHONE_NO | COUNTRY | +------------+----------------------+--------------------+------------+-----------------+---------+ | A007 | Ramasundar | Bangalore | 0.15 | 077-25814763 | | | A003 | Alex | London | 0.13 | 075-12458969 | | | A008 | Alford | New York | 0.12 | 044-25874365 | | | A011 | Ravi Kumar | Bangalore | 0.15 | 077-45625874 | | | A010 | Santakumar | Chennai | 0.14 | 007-22388644 | | | A012 | Lucida | San Jose | 0.12 | 044-52981425 | | | A005 | Anderson | Brisban | 0.13 | 045-21447739 | | | A001 | Subbarao | Bangalore | 0.14 | 077-12346674 | | | A002 | Mukesh | Mumbai | 0.11 | 029-12358964 | | | A006 | McDen | London | 0.15 | 078-22255588 | | | A004 | Ivan | Torento | 0.15 | 008-22544166 | | | A009 | Benjamin | Hampshair | 0.11 | 008-22536178 | | +------------+----------------------+--------------------+------------+-----------------+---------+Sample table : customer
+-----------+-------------+-------------+--------------+--------------+-------+-------------+-------------+-------------+---------------+--------------+------------+ |CUST_CODE | CUST_NAME | CUST_CITY | WORKING_AREA | CUST_COUNTRY | GRADE | OPENING_AMT | RECEIVE_AMT | PAYMENT_AMT |OUTSTANDING_AMT| PHONE_NO | AGENT_CODE | +-----------+-------------+-------------+--------------+--------------+-------+-------------+-------------+-------------+---------------+--------------+------------+ | C00013 | Holmes | London | London | UK | 2 | 6000.00 | 5000.00 | 7000.00 | 4000.00 | BBBBBBB | A003 | | C00001 | Micheal | New York | New York | USA | 2 | 3000.00 | 5000.00 | 2000.00 | 6000.00 | CCCCCCC | A008 | | C00020 | Albert | New York | New York | USA | 3 | 5000.00 | 7000.00 | 6000.00 | 6000.00 | BBBBSBB | A008 | | C00025 | Ravindran | Bangalore | Bangalore | India | 2 | 5000.00 | 7000.00 | 4000.00 | 8000.00 | AVAVAVA | A011 | | C00024 | Cook | London | London | UK | 2 | 4000.00 | 9000.00 | 7000.00 | 6000.00 | FSDDSDF | A006 | | C00015 | Stuart | London | London | UK | 1 | 6000.00 | 8000.00 | 3000.00 | 11000.00 | GFSGERS | A003 | | C00002 | Bolt | New York | New York | USA | 3 | 5000.00 | 7000.00 | 9000.00 | 3000.00 | DDNRDRH | A008 | | C00018 | Fleming | Brisban | Brisban | Australia | 2 | 7000.00 | 7000.00 | 9000.00 | 5000.00 | NHBGVFC | A005 | | C00021 | Jacks | Brisban | Brisban | Australia | 1 | 7000.00 | 7000.00 | 7000.00 | 7000.00 | WERTGDF | A005 | | C00019 | Yearannaidu | Chennai | Chennai | India | 1 | 8000.00 | 7000.00 | 7000.00 | 8000.00 | ZZZZBFV | A010 | | C00005 | Sasikant | Mumbai | Mumbai | India | 1 | 7000.00 | 11000.00 | 7000.00 | 11000.00 | 147-25896312 | A002 | | C00007 | Ramanathan | Chennai | Chennai | India | 1 | 7000.00 | 11000.00 | 9000.00 | 9000.00 | GHRDWSD | A010 | | C00022 | Avinash | Mumbai | Mumbai | India | 2 | 7000.00 | 11000.00 | 9000.00 | 9000.00 | 113-12345678 | A002 | | C00004 | Winston | Brisban | Brisban | Australia | 1 | 5000.00 | 8000.00 | 7000.00 | 6000.00 | AAAAAAA | A005 | | C00023 | Karl | London | London | UK | 0 | 4000.00 | 6000.00 | 7000.00 | 3000.00 | AAAABAA | A006 | | C00006 | Shilton | Torento | Torento | Canada | 1 | 10000.00 | 7000.00 | 6000.00 | 11000.00 | DDDDDDD | A004 | | C00010 | Charles | Hampshair | Hampshair | UK | 3 | 6000.00 | 4000.00 | 5000.00 | 5000.00 | MMMMMMM | A009 | | C00017 | Srinivas | Bangalore | Bangalore | India | 2 | 8000.00 | 4000.00 | 3000.00 | 9000.00 | AAAAAAB | A007 | | C00012 | Steven | San Jose | San Jose | USA | 1 | 5000.00 | 7000.00 | 9000.00 | 3000.00 | KRFYGJK | A012 | | C00008 | Karolina | Torento | Torento | Canada | 1 | 7000.00 | 7000.00 | 9000.00 | 5000.00 | HJKORED | A004 | | C00003 | Martin | Torento | Torento | Canada | 2 | 8000.00 | 7000.00 | 7000.00 | 8000.00 | MJYURFD | A004 | | C00009 | Ramesh | Mumbai | Mumbai | India | 3 | 8000.00 | 7000.00 | 3000.00 | 12000.00 | Phone No | A002 | | C00014 | Rangarappa | Bangalore | Bangalore | India | 2 | 8000.00 | 11000.00 | 7000.00 | 12000.00 | AAAATGF | A001 | | C00016 | Venkatpati | Bangalore | Bangalore | India | 2 | 8000.00 | 11000.00 | 7000.00 | 12000.00 | JRTVFDD | A007 | | C00011 | Sundariya | Chennai | Chennai | India | 3 | 7000.00 | 11000.00 | 7000.00 | 11000.00 | PPHGRTS | A010 | +-----------+-------------+-------------+--------------+--------------+-------+-------------+-------------+-------------+---------------+--------------+------------+
To get 'agent_code', 'agent_name', 'working_area', 'commission' from 'agents' table with following conditions -
in outer query:
'agent_code' should be any 'agent_code' from 'customer' table
in inner query:
) 'cust_country' in the 'customer' table must be 'UK',
Here is the complete SQL statement :
SQL Code:
-- Selecting specific columns from the agents table
SELECT agent_code, agent_name, working_area, commission
-- Filtering agents based on agent_code
FROM agents
-- Filtering agents whose agent_code matches any in the subquery
WHERE agent_code = ANY (
-- Selecting agent_codes from customer table
SELECT agent_code
-- Filtering customers based on cust_country
FROM customer
WHERE cust_country='UK'
);
Explanation:
- This SQL query retrieves specific columns from the "agents" table.
- It filters the agents based on the agent_code.
- The subquery is used to find agent_codes of agents who have customers in the UK.
- It first selects the agent_codes from the "customer" table.
- Then it filters these customers based on their cust_country being 'UK'.
- The main query then selects agents whose agent_code matches any of those found in the subquery, meaning it selects agents who have customers in the UK.
Output:
AGENT_CODE AGENT_NAME WORKING_AREA COMMISSION ---------- ---------------------------------------- ----------------------------------- ---------- A009 Benjamin Hampshair .11 A003 Alex London .13 A006 McDen London .15
Visual Presentation:
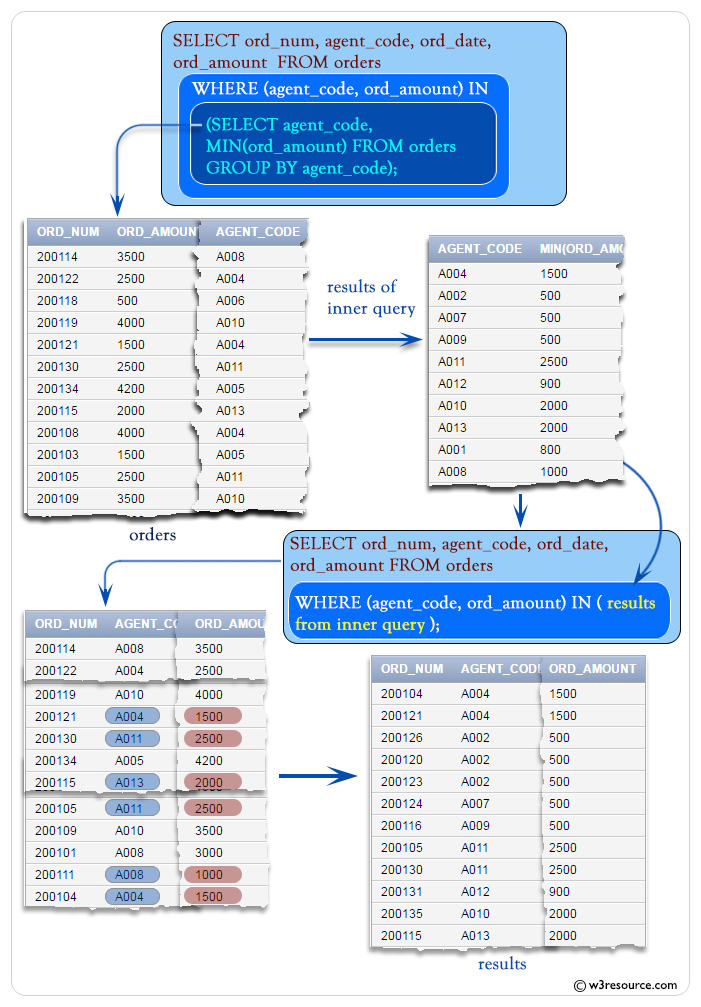
SQL: Multiple Column Subqueries
You can write subqueries that return multiple columns. The following example retrieves the order amount with the lowest price, group by agent code.
Sample table: orders
ORD_NUM ORD_AMOUNT ADVANCE_AMOUNT ORD_DATE CUST_CODE AGENT_CODE ORD_DESCRIPTION
---------- ---------- -------------- --------- --------------- --------------- -----------------
200114 3500 2000 15-AUG-08 C00002 A008
200122 2500 400 16-SEP-08 C00003 A004
200118 500 100 20-JUL-08 C00023 A006
200119 4000 700 16-SEP-08 C00007 A010
200121 1500 600 23-SEP-08 C00008 A004
200130 2500 400 30-JUL-08 C00025 A011
200134 4200 1800 25-SEP-08 C00004 A005
200108 4000 600 15-FEB-08 C00008 A004
200103 1500 700 15-MAY-08 C00021 A005
200105 2500 500 18-JUL-08 C00025 A011
200109 3500 800 30-JUL-08 C00011 A010
200101 3000 1000 15-JUL-08 C00001 A008
200111 1000 300 10-JUL-08 C00020 A008
200104 1500 500 13-MAR-08 C00006 A004
200106 2500 700 20-APR-08 C00005 A002
200125 2000 600 10-OCT-08 C00018 A005
200117 800 200 20-OCT-08 C00014 A001
200123 500 100 16-SEP-08 C00022 A002
200120 500 100 20-JUL-08 C00009 A002
200116 500 100 13-JUL-08 C00010 A009
200124 500 100 20-JUN-08 C00017 A007
200126 500 100 24-JUN-08 C00022 A002
200129 2500 500 20-JUL-08 C00024 A006
200127 2500 400 20-JUL-08 C00015 A003
200128 3500 1500 20-JUL-08 C00009 A002
200135 2000 800 16-SEP-08 C00007 A010
200131 900 150 26-AUG-08 C00012 A012
200133 1200 400 29-JUN-08 C00009 A002
200100 1000 600 08-JAN-08 C00015 A003
200110 3000 500 15-APR-08 C00019 A010
200107 4500 900 30-AUG-08 C00007 A010
200112 2000 400 30-MAY-08 C00016 A007
200113 4000 600 10-JUN-08 C00022 A002
200102 2000 300 25-MAY-08 C00012 A012
SQL Code:
-- Selecting specific columns from the agents table
SELECT agent_code, agent_name, working_area, commission
-- Filtering agents based on agent_code
FROM agents
-- Filtering agents whose agent_code matches any in the subquery
WHERE agent_code = ANY (
-- Selecting agent_codes from customer table
SELECT agent_code
-- Filtering customers based on cust_country
FROM customer
WHERE cust_country='UK'
);
Explanation:
- This SQL query retrieves specific columns from the "agents" table.
- It filters the agents based on the agent_code.
- The subquery is used to find agent_codes of agents who have customers in the UK.
- It first selects the agent_codes from the "customer" table.
- Then it filters these customers based on their cust_country being 'UK'.
- The main query then selects agents whose agent_code matches any of those found in the subquery, meaning it selects agents who have customers in the UK.
Output:
ORD_NUM AGENT_CODE ORD_DATE ORD_AMOUNT
---------- ---------- --------- ----------
200104 A004 13-MAR-08 1500
200121 A004 23-SEP-08 1500
200126 A002 24-JUN-08 500
200120 A002 20-JUL-08 500
200123 A002 16-SEP-08 500
200124 A007 20-JUN-08 500
200116 A009 13-JUL-08 500
200105 A011 18-JUL-08 2500
200130 A011 30-JUL-08 2500
200131 A012 26-AUG-08 900
200135 A010 16-SEP-08 2000
200115 A013 08-FEB-08 2000
200117 A001 20-OCT-08 800
200111 A008 10-JUL-08 1000
200118 A006 20-JUL-08 500
200103 A005 15-MAY-08 1500
200100 A003 08-JAN-08 1000
Visual Presentation:
SQL: Subqueries using DISTINCT
In this section, we are discussing the usage of DISTINCT clause in a subquery.
Example:
Sample table: orders
ORD_NUM ORD_AMOUNT ADVANCE_AMOUNT ORD_DATE CUST_CODE AGENT_CODE ORD_DESCRIPTION
---------- ---------- -------------- --------- --------------- --------------- -----------------
200114 3500 2000 15-AUG-08 C00002 A008
200122 2500 400 16-SEP-08 C00003 A004
200118 500 100 20-JUL-08 C00023 A006
200119 4000 700 16-SEP-08 C00007 A010
200121 1500 600 23-SEP-08 C00008 A004
200130 2500 400 30-JUL-08 C00025 A011
200134 4200 1800 25-SEP-08 C00004 A005
200108 4000 600 15-FEB-08 C00008 A004
200103 1500 700 15-MAY-08 C00021 A005
200105 2500 500 18-JUL-08 C00025 A011
200109 3500 800 30-JUL-08 C00011 A010
200101 3000 1000 15-JUL-08 C00001 A008
200111 1000 300 10-JUL-08 C00020 A008
200104 1500 500 13-MAR-08 C00006 A004
200106 2500 700 20-APR-08 C00005 A002
200125 2000 600 10-OCT-08 C00018 A005
200117 800 200 20-OCT-08 C00014 A001
200123 500 100 16-SEP-08 C00022 A002
200120 500 100 20-JUL-08 C00009 A002
200116 500 100 13-JUL-08 C00010 A009
200124 500 100 20-JUN-08 C00017 A007
200126 500 100 24-JUN-08 C00022 A002
200129 2500 500 20-JUL-08 C00024 A006
200127 2500 400 20-JUL-08 C00015 A003
200128 3500 1500 20-JUL-08 C00009 A002
200135 2000 800 16-SEP-08 C00007 A010
200131 900 150 26-AUG-08 C00012 A012
200133 1200 400 29-JUN-08 C00009 A002
200100 1000 600 08-JAN-08 C00015 A003
200110 3000 500 15-APR-08 C00019 A010
200107 4500 900 30-AUG-08 C00007 A010
200112 2000 400 30-MAY-08 C00016 A007
200113 4000 600 10-JUN-08 C00022 A002
200102 2000 300 25-MAY-08 C00012 A012
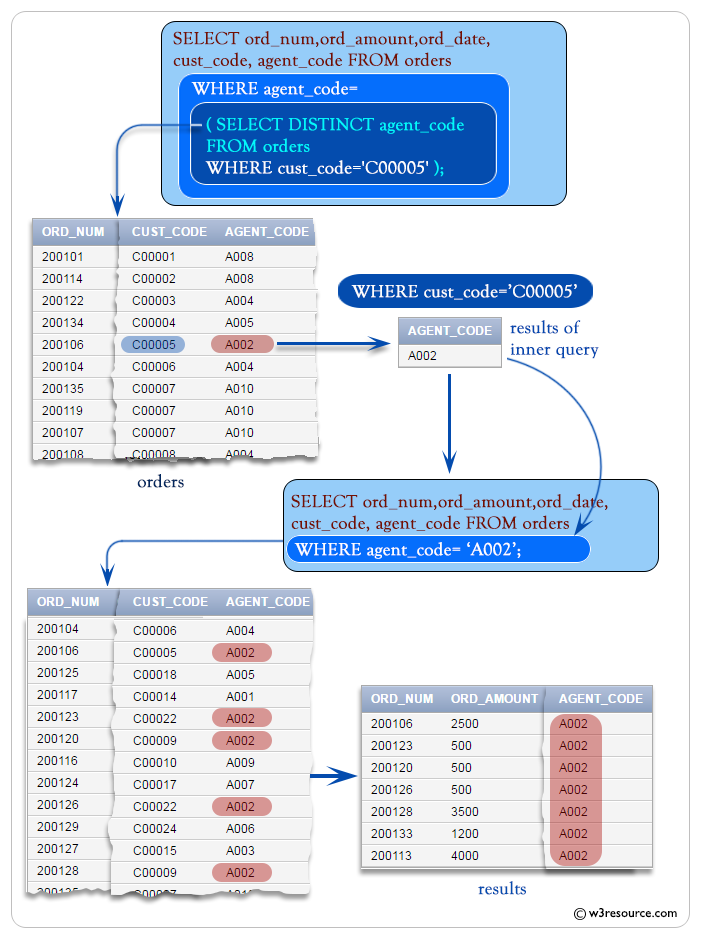
To get 'ord_num', 'ord_amount', 'ord_date', 'cust_code' and 'agent_code' from the table 'orders' with following conditions -
in outer query:
the 'agent_code' of 'orders' table must be the same 'agent_code' of 'orders' table with following conditions -
'agent_code' of 'orders' table should come distinctly with following
inner query:
;the 'cust_code' of 'orders' table must be 'C00005'
Here is the complete SQL statement :
SQL Code:
-- Selecting specific columns from the orders table
SELECT ord_num, ord_amount, ord_date,
cust_code, agent_code
-- Filtering orders based on agent_code
FROM orders
-- Filtering orders where the agent_code matches a subquery result
WHERE agent_code = (
-- Selecting distinct agent_code from orders table
SELECT DISTINCT agent_code
-- Filtering orders based on cust_code
FROM orders
WHERE cust_code='C00005'
);
Explanation:
- This SQL query retrieves specific columns from the "orders" table.
- It filters the orders based on the agent_code.
- The subquery selects distinct agent_codes from the "orders" table.
- It filters these agent_codes based on the cust_code being 'C00005'.
- The main query then selects orders where the agent_code matches the result of the subquery, meaning it selects orders handled by the agent(s) who have customers with the cust_code 'C00005'.
Output:
ORD_NUM ORD_AMOUNT ORD_DATE CUST_CODE AGENT_CODE
---------- ---------- --------- ---------- ----------
200106 2500 20-APR-08 C00005 A002
200123 500 16-SEP-08 C00022 A002
200120 500 20-JUL-08 C00009 A002
200126 500 24-JUN-08 C00022 A002
200128 3500 20-JUL-08 C00009 A002
200133 1200 29-JUN-08 C00009 A002
200113 4000 10-JUN-08 C00022 A002
The inner of the above query returns the 'agent_code' A002.
The simplified form of above code is :
SQL Code:
-- Selecting specific columns from the orders table
SELECT ord_num, ord_amount, ord_date,
cust_code, agent_code
-- Filtering orders based on agent_code
FROM orders
-- Specifying the condition for filtering
WHERE agent_code = 'A002';
Explanation:
- This SQL query retrieves specific columns from the "orders" table.
- It filters the orders based on the agent_code.
- The condition specified in the WHERE clause restricts the results to only those orders where the agent_code is 'A002', meaning it selects orders handled by the agent with the code 'A002'.
Relational Algebra Expression:
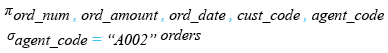
Relational Algebra Tree:
Check out our 1000+ SQL Exercises with solution and explanation to improve your skills.
Previous: Single Row Subqueries
Next: Correlated subqueries using aliases
