Java Parameterized test with JUnit: MultiplyTest example
4. Parameterized Test for Multiple Inputs
Write a Java program that implements parameterized test to verify that a method behaves correctly for different input values.Sample Solution:
Java Code:
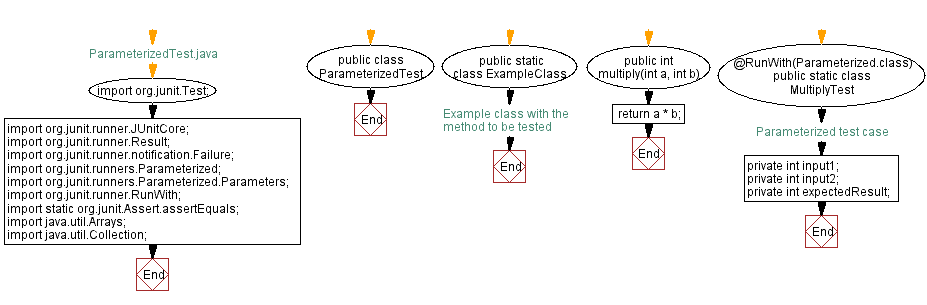
// ParameterizedTest.java
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.JUnitCore;
import org.junit.runner.Result;
import org.junit.runner.notification.Failure;
import org.junit.runners.Parameterized;
import org.junit.runners.Parameterized.Parameters;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import static org.junit.Assert.assertEquals;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Collection;
public class ParameterizedTest {
// Example class with the method to be tested
public static class ExampleClass {
public int multiply(int a, int b) {
return a * b;
}
}
// Parameterized test case
@RunWith(Parameterized.class)
public static class MultiplyTest {
private int input1;
private int input2;
private int expectedResult;
// Constructor with parameters
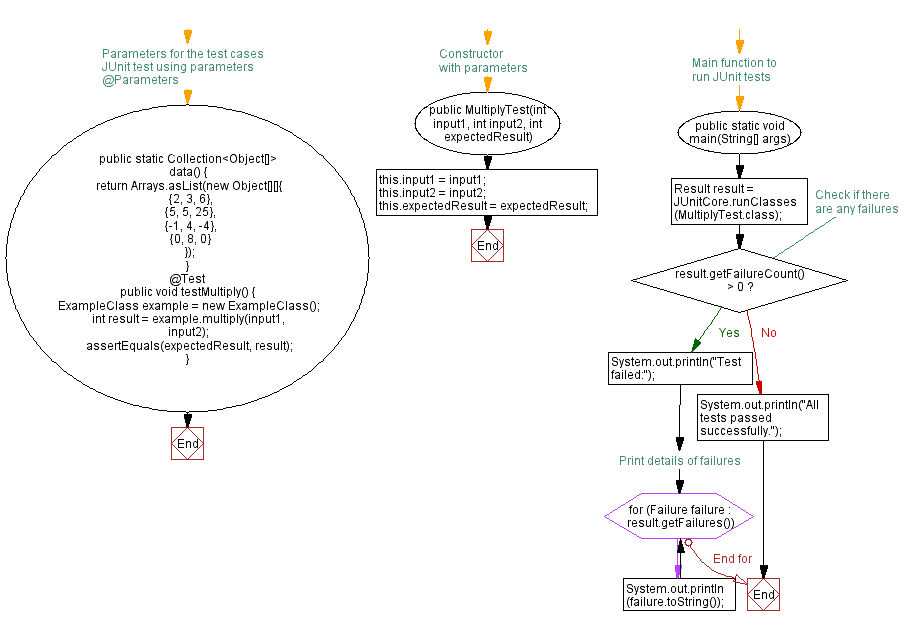
public MultiplyTest(int input1, int input2, int expectedResult) {
this.input1 = input1;
this.input2 = input2;
this.expectedResult = expectedResult;
}
// Parameters for the test cases
@Parameters
public static Collection data() {
return Arrays.asList(new Object[][]{
{2, 3, 6},
{5, 5, 25},
{-1, 4, -4},
{0, 8, 0}
});
}
// JUnit test using parameters
@Test
public void testMultiply() {
ExampleClass example = new ExampleClass();
int result = example.multiply(input1, input2);
assertEquals(expectedResult, result);
}
}
// Main function to run JUnit tests
public static void main(String[] args) {
Result result = JUnitCore.runClasses(MultiplyTest.class);
// Check if there are any failures
if (result.getFailureCount() > 0) {
System.out.println("Test failed:");
// Print details of failures
for (Failure failure : result.getFailures()) {
System.out.println(failure.toString());
}
} else {
System.out.println("All tests passed successfully.");
}
}
}
Sample Output:
All tests passed successfully.
Explanation:
The above Java code shows a parameterized JUnit test using the "Parameterized" runner. Here's a brief explanation:
- ExampleClass:
- Defines a simple class named "ExampleClass" with a method "multiply(int a, int b)" that multiplies two integers.
- MultiplyTest:
- A nested static class, "MultiplyTest", is marked with @RunWith(Parameterized.class). It signifies that this class will be run using the "Parameterized" runner.
- Constructor: It has a constructor with parameters (int input1, int input2, int expectedResult) that will be used to pass values for parameterized testing.
- @Parameters method: The "data()" method annotated with @Parameters provides a collection of parameter sets (arrays of inputs and expected results).
- Test Method: The "testMultiply()" method annotated with @Test is the actual JUnit test. It uses the provided parameters to perform the multiplication using the "ExampleClass" and asserts that the result matches the expected value.
- Main Function:
- The "main()" function is used to run the JUnit tests.
- JUnitCore.runClasses(MultiplyTest.class) runs the "MultiplyTest" class using the JUnitCore runner.
- The results are checked, and if there are any test failures, details are printed. Otherwise, a success message is displayed.
Flowchart:
For more Practice: Solve these Related Problems:
- Write a Java program to implement a parameterized JUnit test that validates method outputs for a range of input values.
- Write a Java program to create a parameterized test that reads test data from a CSV file and verifies the method behavior.
- Write a Java program to design a parameterized test that tests edge cases and normal cases using a collection of different inputs.
- Write a Java program to implement a parameterized test that uses a custom data provider to supply test parameters dynamically.
Go to:
PREV : JUnit Setup and Teardown Test.
NEXT : Fail Test on Timeout.
Java Code Editor:
Improve this sample solution and post your code through Disqus
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
Test your Programming skills with w3resource's quiz.
