JavaScript: Display the current day and time in a specific format
JavaScript Basic: Exercise-1 with Solution
Display Current Day and Time
Write a JavaScript program to display the current day and time in the following format.
Today is : Tuesday.
Current time is : 10 PM : 30 : 38
This JavaScript program retrieves the current date and time, determines the day of the week, and formats the current hour, minute, and second in 12-hour format with AM/PM notation. It then prints the day of the week and the formatted current time to the console. The program also handles special cases for "Noon" and "Midnight" to ensure an accurate representation.
Visual Presentation:

Sample Solution:
JavaScript Code:
// Get the current date and time
var today = new Date();
// Get the day of the week (0-6, where 0 is Sunday and 6 is Saturday)
var day = today.getDay();
// Array of day names
var daylist = ["Sunday", "Monday", "Tuesday", "Wednesday", "Thursday", "Friday", "Saturday"];
// Display the current day
console.log("Today is: " + daylist[day] + ".");
// Get the current hour, minute, and second
var hour = today.getHours();
var minute = today.getMinutes();
var second = today.getSeconds();
// Determine if it's AM or PM
var prepand = (hour >= 12) ? " PM " : " AM ";
// Convert 24-hour format to 12-hour format
hour = (hour >= 12) ? hour - 12 : hour;
// Check for special cases when hour is 0
if (hour === 0 && prepand === ' PM ') {
if (minute === 0 && second === 0) {
hour = 12;
prepand = ' Noon';
} else {
hour = 12;
prepand = ' PM';
}
}
// Check for special cases when hour is 0
if (hour === 0 && prepand === ' AM ') {
if (minute === 0 && second === 0) {
hour = 12;
prepand = ' Midnight';
} else {
hour = 12;
prepand = ' AM';
}
}
// Display the current time
console.log("Current Time: " + hour + prepand + " : " + minute + " : " + second);
Output:
Today is : Tuesday. Current Time : 10 PM : 30 : 38
Live Demo:
See the Pen JavaScript current day and time - basic-ex-2 by w3resource (@w3resource) on CodePen.
Explanations:
Declaring a JavaScript date : In JavaScript Date objects are based on a time value that is the number of milliseconds since 1 January, 1970 UTC. You can declare a date in the following ways :
new Date(); new Date(value); new Date(dateString); new Date(year, month[, day[, hour[, minutes[, seconds[, milliseconds]]]]]);
The getDay() method is used to get the day of the week for the specified date according to local time, where 0 represents Sunday. The value returned by getDay() is an integer corresponding to the day of the week: 0 for Sunday, 1 for Monday, 2 for Tuesday, and so on.
The getHours() method is used to get the hour for a given date, according to local time. The value returned by getHours() is an integer between 0 and 23.
The getMinutes() method is used to get the minutes in the specified date according to local time. The value returned by getMinutes() is an integer between 0 and 59.
The getSeconds() method is used to get the seconds in the specified date according to local time. The value returned by getSeconds() is an integer between 0 and 59.
AM and PM : AM stands for 'ante meridiem', which means 'before noon' in Latin, while PM stands for 'post meridiem', which means 'after noon' in Latin.
12-Hour Periods : Nowadays most clocks are 12-hour clocks – they divide the 24 hours in a day into two 12-hour periods.
Ante meridiem: Before noon - Between midnight (0:00) & noon (12:00)
Post meridiem: After noon Between noon (12:00) & midnight (0:00)
Flowchart:
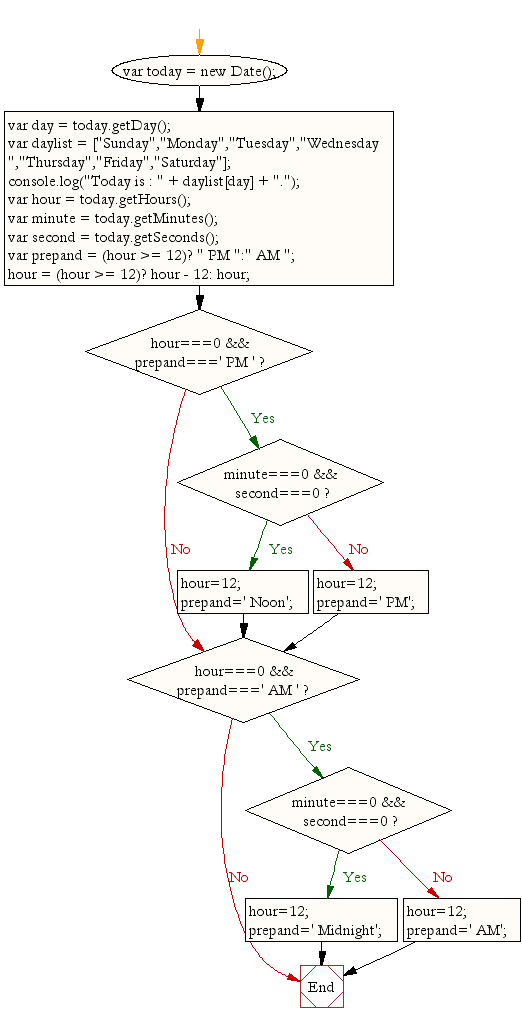
ES6 Version:
// Get the current date and time
const today = new Date();
// Get the day of the week (0-6, where 0 is Sunday and 6 is Saturday)
const day = today.getDay();
// Array of day names
const daylist = ["Sunday", "Monday", "Tuesday", "Wednesday", "Thursday", "Friday", "Saturday"];
// Display the current day
console.log(`Today is: ${daylist[day]}.`);
// Get the current hour, minute, and second
let hour = today.getHours();
const minute = today.getMinutes();
const second = today.getSeconds();
// Determine if it's AM or PM
let prepand = (hour >= 12) ? " PM " : " AM ";
// Convert 24-hour format to 12-hour format
hour = (hour >= 12) ? hour - 12 : hour;
// Check for special cases when hour is 0 and it's PM
if (hour === 0 && prepand === ' PM ') {
// Check if minute and second are also 0
if (minute === 0 && second === 0) {
hour = 12;
prepand = ' Noon';
} else {
hour = 12;
prepand = ' PM';
}
}
// Check for special cases when hour is 0 and it's AM
if (hour === 0 && prepand === ' AM ') {
// Check if minute and second are also 0
if (minute === 0 && second === 0) {
hour = 12;
prepand = ' Midnight';
} else {
hour = 12;
prepand = ' AM';
}
}
// Display the current time
console.log(`Current Time: ${hour}${prepand} : ${minute} : ${second}`);
For more Practice: Solve these Related Problems:
- Write a JavaScript program to display the current day, time, and time zone offset in a custom format.
- Write a JavaScript program that updates the displayed current day and time every second without using setInterval.
- Write a JavaScript program that displays the current day, time, and a special message if it's a weekend.
Go to:
PREV : JavaScript Basic Exercises Home
NEXT :Print Current Window Contents.
Improve this sample solution and post your code through Disqus.
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
Test your Programming skills with w3resource's quiz.
