Python: Flatten a given nested list structure
Flatten Nested List Structure
Write a Python program to flatten a given nested list structure.
Sample Solution-1:
Python Code:
# Define a function 'flatten_list' that takes a nested list 'n_list' as input
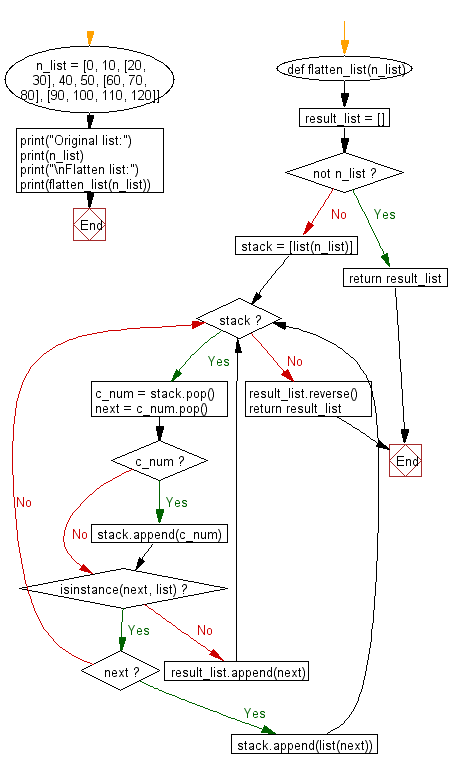
def flatten_list(n_list):
# Initialize an empty list 'result_list' to store the flattened elements
result_list = []
# Check if 'n_list' is empty; if so, return an empty result list
if not n_list:
return result_list
# Create a stack to keep track of nested lists; start with 'n_list' as the initial item in the stack
stack = [list(n_list)]
# Iterate while the stack is not empty
while stack:
# Pop the current list 'c_num' from the stack
c_num = stack.pop()
# Pop the next item from 'c_num'
next = c_num.pop()
# If 'c_num' is not empty, push it back onto the stack
if c_num:
stack.append(c_num)
# Check if 'next' is a list
if isinstance(next, list):
# If 'next' is a non-empty list, push it onto the stack
if next:
stack.append(list(next))
else:
# If 'next' is not a list, add it to 'result_list'
result_list.append(next)
# Reverse 'result_list' to maintain the original order of elements
result_list.reverse()
# Return the flattened list
return result_list
# Define a nested list 'n_list' with various sublists
n_list = [0, 10, [20, 30], 40, 50, [60, 70, 80], [90, 100, 110, 120]]
# Print a message indicating the purpose of the following output
print("Original list:")
# Print the original nested list 'n_list'
print(n_list)
# Print a message indicating the purpose of the following output
print("\nFlatten list:")
# Call the 'flatten_list' function with 'n_list' as an argument and print the flattened result
print(flatten_list(n_list))
Sample Output:
Original list: [0, 10, [20, 30], 40, 50, [60, 70, 80], [90, 100, 110, 120]] Flatten list: [0, 10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60, 70, 80, 90, 100, 110, 120]
Flowchart:
Sample Solution-2:
Loop over elements, use list.extend() if the element is a list, list.append() otherwise.
Python Code:
# Define a function 'flatten_list' that takes a nested list 'nums' as input
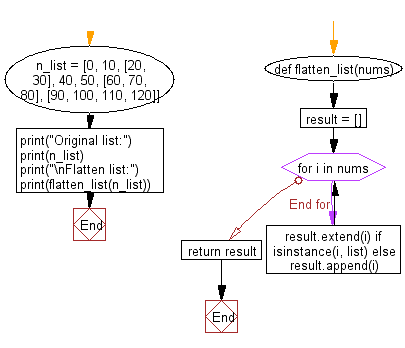
def flatten_list(nums):
# Initialize an empty list 'result' to store the flattened elements
result = []
# Iterate through each element 'i' in the input list 'nums'
for i in nums:
# Check if 'i' is a list; if so, extend 'result' with its elements, otherwise, append 'i' to 'result'
result.extend(i) if isinstance(i, list) else result.append(i)
# Return the flattened list
return result
# Define a nested list 'n_list' with various sublists
n_list = [0, 10, [20, 30], 40, 50, [60, 70, 80], [90, 100, 110, 120]]
# Print a message indicating the purpose of the following output
print("Original list:")
# Print the original nested list 'n_list'
print(n_list)
# Print a message indicating the purpose of the following output
print("\nFlatten list:")
# Call the 'flatten_list' function with 'n_list' as an argument and print the flattened result
print(flatten_list(n_list))
Sample Output:
Original list: [0, 10, [20, 30], 40, 50, [60, 70, 80], [90, 100, 110, 120]] Flatten list: [0, 10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60, 70, 80, 90, 100, 110, 120]
Flowchart:
For more Practice: Solve these Related Problems:
- Write a Python program to flatten a list containing nested lists and tuples.
- Write a Python program to flatten a nested list up to a specified depth.
- Write a Python program to flatten a list while preserving non-list elements as-is.
- Write a Python program to convert a nested list into a single-level dictionary.
Go to:
Previous: Write a Python program to check whether all dictionaries in a list are empty or not.
Next: Write a Python program to remove consecutive (following each other continuously) duplicates (elements) of a given list.
Python Code Editor:
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
Test your Programming skills with w3resource's quiz.
