C Exercises: Find the ceiling in a sorted array
40. Find Ceiling in Sorted Array
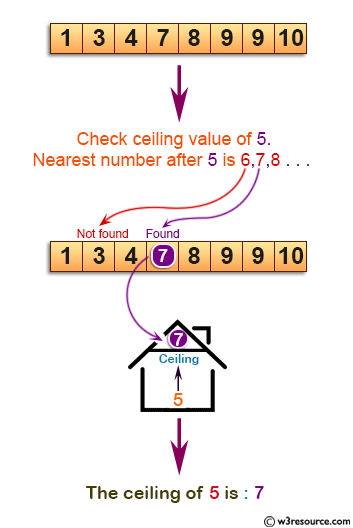
Write a program in C to find the ceiling in a sorted array.
N.B.: Given a sorted array in ascending order and a value x, the ceiling of x is the smallest element in array greater than or equal to x,
and the floor is the greatest element smaller than or equal to x.
This problem requires finding the smallest element in a sorted array that is greater than or equal to a given value x. The output displays the given array and identifies the ceiling value for x.
Visual Presentation:
Sample Solution:
C Code:
#include <stdio.h>
// Function to find the ceiling of a given element 'x' in the array
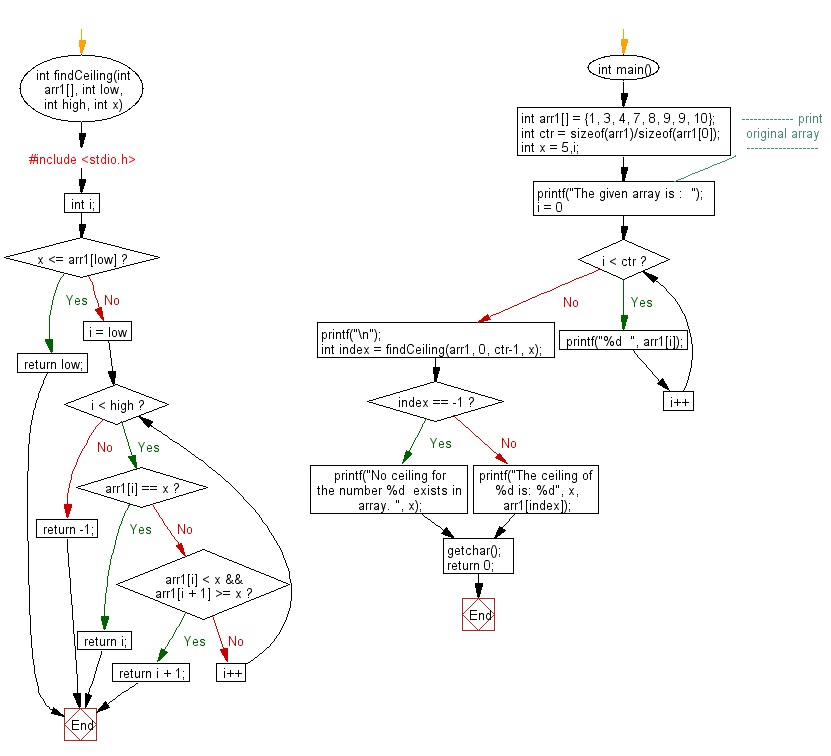
int findCeiling(int arr1[], int low, int high, int x) {
int i;
// If 'x' is smaller or equal to the first element, return the index of the first element
if (x <= arr1[low])
return low;
// Traverse the array
for (i = low; i < high; i++) {
// If 'x' is found in the array, return its index
if (arr1[i] == x)
return i;
// If 'x' is between two elements, return the index of the next greater element
if (arr1[i] < x && arr1[i + 1] >= x)
return i + 1;
}
return -1; // If no ceiling exists, return -1
}
int main() {
int arr1[] = {1, 3, 4, 7, 8, 9, 9, 10};
int ctr = sizeof(arr1) / sizeof(arr1[0]);
int x = 5, i;
// Print original array
printf("The given array is : ");
for (i = 0; i < ctr; i++) {
printf("%d ", arr1[i]);
}
printf("\n");
// Find the ceiling of 'x' in the array
int index = findCeiling(arr1, 0, ctr - 1, x);
// Display the result
if (index == -1)
printf("No ceiling for the number %d exists in the array. ", x);
else
printf("The ceiling of %d is: %d", x, arr1[index]);
getchar(); // To keep the console window open
return 0;
}
Sample Output:
The given array is : 1 3 4 7 8 9 9 10 The ceiling of 5 is: 7
Flowchart:
For more Practice: Solve these Related Problems:
- Write a C program to find the ceiling of a given number in a sorted array using binary search.
- Write a C program to determine both the floor and ceiling of a number in a sorted array.
- Write a C program to find the ceiling of a number and then compute the difference between the number and its ceiling.
- Write a C program to find the ceiling in a sorted array and display the next two higher elements.
Go to:
PREV : Rotate Array by N Positions.
NEXT : Floor & Ceiling from Sorted Array.
C Programming Code Editor:
Have another way to solve this solution? Contribute your code (and comments) through Disqus.
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
Test your Programming skills with w3resource's quiz.
