C Exercises: Create a singly linked list and count the number of nodes
3. Linked List Node Counter Variants
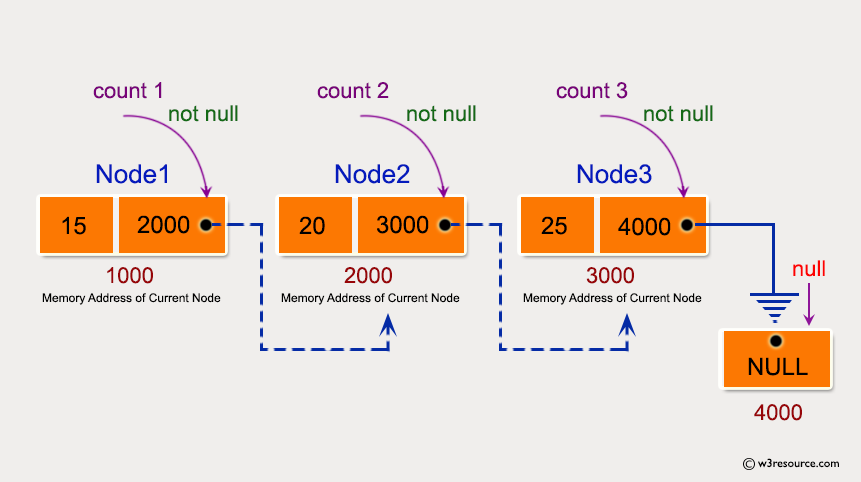
Write a program in C to create a singly linked list of n nodes and count the number of nodes.
Visual Presentation:
Sample Solution:
C Code:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
// Structure for a node in a linked list
struct node {
int num; // Data of the node
struct node *nextptr; // Address of the next node
} *stnode; // Pointer to the starting node
// Function prototypes
void createNodeList(int n); // Function to create the linked list
int NodeCount(); // Function to count the nodes
void displayList(); // Function to display the linked list
// Main function
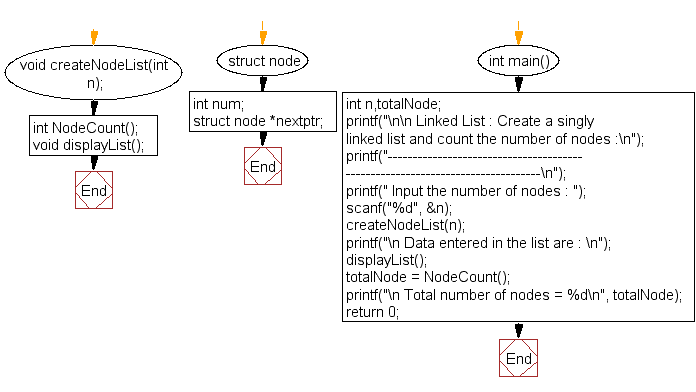
int main() {
int n, totalNode;
// Displaying the purpose of the program
printf("\n\n Linked List : Create a singly linked list and count the number of nodes :\n");
printf("------------------------------------------------------------------------------\n");
// Inputting the number of nodes for the linked list
printf(" Input the number of nodes : ");
scanf("%d", &n);
// Creating the linked list with n nodes
createNodeList(n);
printf("\n Data entered in the list are : \n");
// Displaying the data entered in the linked list
displayList();
// Counting the number of nodes in the linked list
totalNode = NodeCount();
printf("\n Total number of nodes = %d\n", totalNode);
return 0;
}
// Function to create a linked list with n nodes
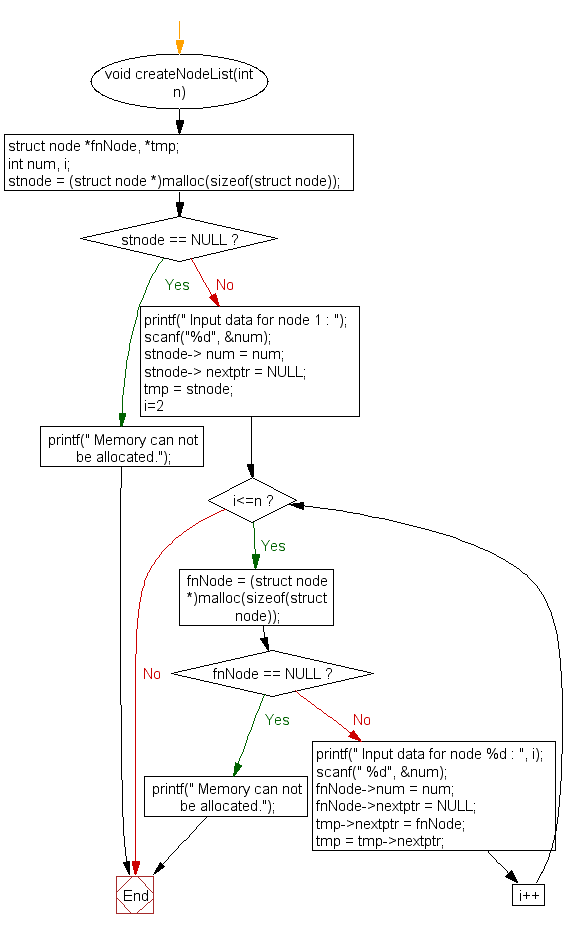
void createNodeList(int n) {
struct node *fnNode, *tmp;
int num, i;
// Allocating memory for the starting node
stnode = (struct node *)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
// Checking if memory allocation is successful
if(stnode == NULL) {
printf(" Memory can not be allocated.");
} else {
// Reading data for the starting node from user input
printf(" Input data for node 1 : ");
scanf("%d", &num);
stnode->num = num;
stnode->nextptr = NULL; // Setting the next pointer to NULL
tmp = stnode;
// Creating n nodes and adding them to the linked list
for(i = 2; i <= n; i++) {
fnNode = (struct node *)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
// Checking if memory allocation is successful
if(fnNode == NULL) {
printf(" Memory can not be allocated.");
break;
} else {
// Reading data for each node from user input
printf(" Input data for node %d : ", i);
scanf(" %d", &num);
fnNode->num = num; // Setting the data for fnNode
fnNode->nextptr = NULL; // Setting the next pointer to NULL
tmp->nextptr = fnNode; // Linking the current node to fnNode
tmp = tmp->nextptr; // Moving tmp to the next node
}
}
}
}
// Function to count the number of nodes in the linked list
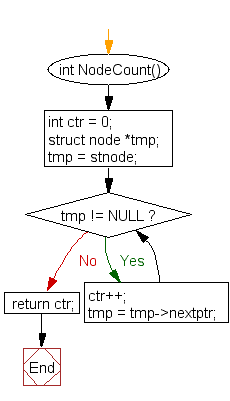
int NodeCount() {
int ctr = 0;
struct node *tmp;
tmp = stnode;
// Counting the nodes by traversing the linked list
while(tmp != NULL) {
ctr++;
tmp = tmp->nextptr;
}
return ctr;
}
// Function to display the linked list
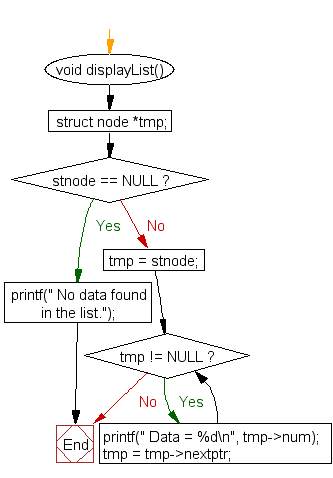
void displayList() {
struct node *tmp;
if(stnode == NULL) {
printf(" No data found in the list.");
} else {
tmp = stnode;
while(tmp != NULL) {
printf(" Data = %d\n", tmp->num); // Printing the data of current node
tmp = tmp->nextptr; // Advancing the position of current node
}
}
}
Sample Output:
Linked List : Create a singly linked list and count the number of nodes :
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Input the number of nodes : 3
Input data for node 1 : 5
Input data for node 2 : 6
Input data for node 3 : 7
Data entered in the list are :
Data = 5
Data = 6
Data = 7
Total number of nodes = 3
Flowchart:
createNodeList() :
NodeCount() :
displayList() :
For more Practice: Solve these Related Problems:
- Write a C program to count the nodes in a singly linked list using a recursive approach.
- Write a C program to traverse a linked list iteratively and count its nodes without using an explicit counter variable.
- Write a C program to count only the nodes with even values in a singly linked list.
- Write a C program to verify the node count by comparing iterative and recursive counting methods in a linked list.
Go to:
PREV : Linked List Reverse Display.
NEXT : Prepend Node Challenges.
C Programming Code Editor:
Have another way to solve this solution? Contribute your code (and comments) through Disqus.
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
Test your Programming skills with w3resource's quiz.
