C Exercises: Show a pointer to an array which contents are pointer to structure
20. Pointer to an Array of Pointers to Structures
Write a program in C to show a pointer to an array whose contents are pointers to structures.
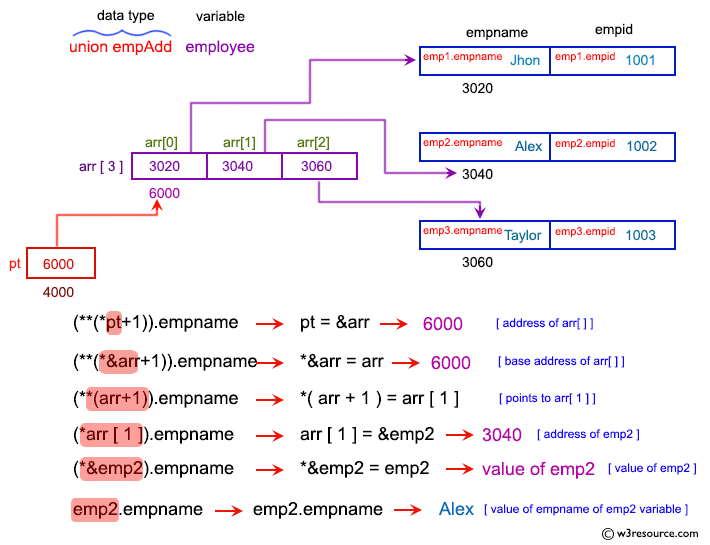
Visual Presentation:
Sample Solution:
C Code:
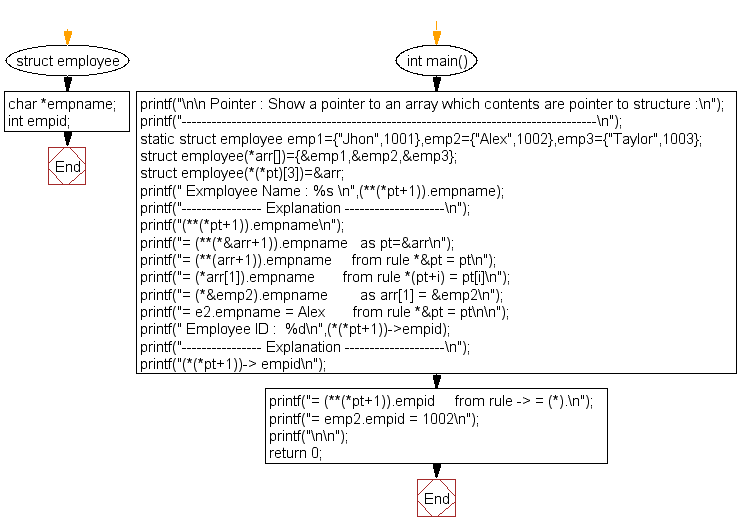
#include <stdio.h>
// Defining a structure for employee details
struct employee {
char *empname; // Employee name (string pointer)
int empid; // Employee ID (integer)
};
// Main function
int main() {
// Displaying the purpose of the program
printf("\n\n Pointer : Show a pointer to an array which contents are pointer to structure :\n");
printf("-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------\n");
// Initializing employee structures with values
static struct employee emp1 = {"John", 1001}, emp2 = {"Alex", 1002}, emp3 = {"Taylor", 1003};
// Creating an array of pointers to struct employee
struct employee (*arr[]) = {&emp1, &emp2, &emp3};
// Creating a pointer to an array of pointers to struct employee
struct employee (*(*pt)[3]) = &arr; // pt stores the address of the array of pointers
// Printing employee name using pointer to an array of pointers to structure
printf(" Employee Name : %s \n", (**(*pt + 1)).empname);
// Explanation for the printed employee name
printf("---------------- Explanation --------------------\n");
printf("(**(*pt+1)).empname\n");
printf("= (**(*&arr+1)).empname as pt=&arr\n");
printf("= (**(arr+1)).empname from rule *&pt = pt\n");
printf("= (*arr[1]).empname from rule *(pt+i) = pt[i]\n");
printf("= (*&emp2).empname as arr[1] = &emp2\n");
printf("= emp2.empname = Alex from rule *&pt = pt\n\n");
// Printing employee ID using pointer to an array of pointers to structure
printf(" Employee ID : %d\n", (*(*pt + 1))->empid);
// Explanation for the printed employee ID
printf("---------------- Explanation --------------------\n");
printf("(*(*pt+1))-> empid\n");
printf("= (**(*pt+1)).empid from rule -> = (*).\n");
printf("= emp2.empid = 1002\n");
printf("\n\n");
return 0;
}
Sample Output:
Pointer : Show a pointer to an array which contents are pointer to structure :
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Exmployee Name : Alex
---------------- Explanation --------------------
(**(*pt+1)).empname
= (**(*&arr+1)).empname as pt=&arr
= (**(arr+1)).empname from rule *&pt = pt
= (*arr[1]).empname from rule *(pt+i) = pt[i]
= (*&emp2).empname as arr[1] = &emp2
= emp2.empname = Alex from rule *&pt = pt
Employee ID : 1002
---------------- Explanation --------------------
(*(*pt+1))-> empid
= (**(*pt+1)).empid from rule -> = (*).
= emp2.empid = 1002
Flowchart:
For more Practice: Solve these Related Problems:
- Write a C program to create an array of pointers to structures, initialize them, and print the structure members.
- Write a C program to dynamically allocate an array of pointers to structures and then sort the structures by a member value.
- Write a C program to pass an array of pointers to structures to a function that modifies a member of each structure.
- Write a C program to implement a menu-driven program that manipulates an array of pointers to structures and displays the results.
Go to:
PREV : Pointer to a Union.
NEXT : Print Alphabets Using Pointer.
C Programming Code Editor:
Have another way to solve this solution? Contribute your code (and comments) through Disqus.
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
Test your Programming skills with w3resource's quiz.
