C Exercises: Delete the nth element of a queue
11. Delete nth Element in Queue
Write a C program to delete the nth element of a queue.
Firstly, this code checks if the queue is empty or if the position to delete is invalid. If the position is valid, it deletes the first n-1 elements, then deletes the nth element by calling the dequeue() function.
Sample Solution:
C Code:
#include <stdio.h>
#define MAX_SIZE 100
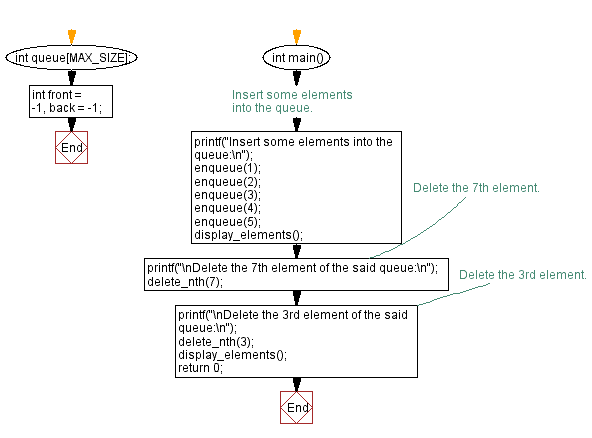
int queue[MAX_SIZE]; // Array to store elements of the queue
int front = -1, back = -1; // Initialize front and back pointers
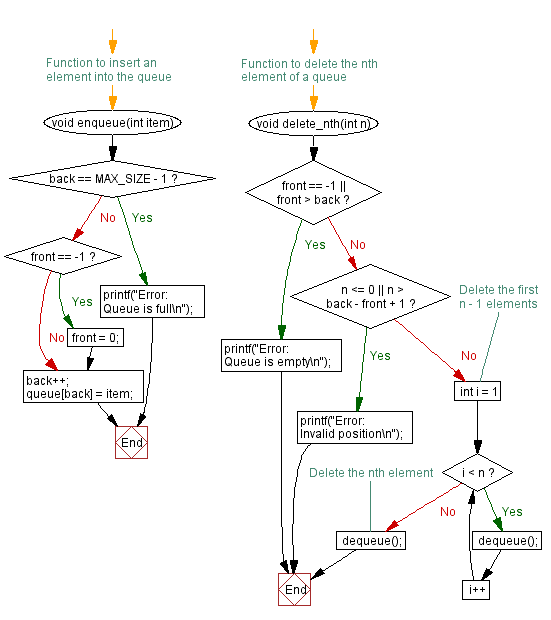
// Function to insert an element into the queue
void enqueue(int item) {
if (back == MAX_SIZE - 1) { // Check if the queue is full
printf("Error: Queue is full\n"); // Print error message if the queue is full
return;
}
if (front == -1) { // Check if the queue is empty
front = 0; // If empty, set front to 0
}
back++; // Increment the back pointer
queue[back] = item; // Add the item to the queue
}
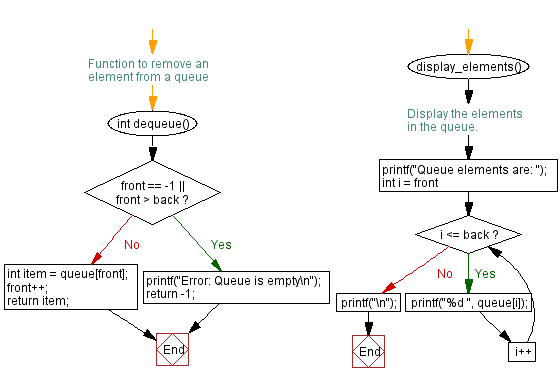
// Function to remove an element from a queue
int dequeue() {
if (front == -1 || front > back) { // Check if the queue is empty
printf("Error: Queue is empty\n"); // Print error message if the queue is empty
return -1; // Return -1 to indicate an empty queue
}
int item = queue[front]; // Get the front element of the queue
front++; // Move the front pointer to the next element
return item; // Return the removed element
}
// Function to delete the nth element of a queue
void delete_nth(int n) {
if (front == -1 || front > back) { // Check if the queue is empty
printf("Error: Queue is empty\n"); // Print error message if the queue is empty
return;
}
if (n <= 0 || n > back - front + 1) { // Check if the position is valid
printf("Error: Invalid position\n"); // Print error message if the position is invalid
return;
}
// Delete the first n - 1 elements
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
dequeue(); // Call dequeue to remove elements until reaching the nth position
}
// Delete the nth element
dequeue(); // Call dequeue to remove the nth element
}
// Function to display the elements in the queue
void display_elements() {
printf("Queue elements are: "); // Print message to indicate queue elements
for (int i = front; i <= back; i++) { // Loop through the elements of the queue
printf("%d ", queue[i]); // Print the current element
}
printf("\n"); // Print a newline after displaying all elements
}
int main() {
// Insert some elements into the queue.
printf("Insert some elements into the queue:\n");
enqueue(1);
enqueue(2);
enqueue(3);
enqueue(4);
enqueue(5);
display_elements(); // Display the elements in the queue
// Delete the 7th element.
printf("\nDelete the 7th element of the said queue:\n");
delete_nth(7); // Attempt to delete the 7th element
// Delete the 3rd element.
printf("\nDelete the 3rd element of the said queue:\n");
delete_nth(3); // Attempt to delete the 3rd element
display_elements(); // Display the elements in the queue after deletion
return 0; // Return 0 to indicate successful execution
}
Output:
Insert some elements into the queue: Queue elements are: 1 2 3 4 5 Delete the 7th element of the said queue: Error: Invalid position Delete the 3rd element of the said queue: Queue elements are: 4 5
Flowchart
For more Practice: Solve these Related Problems:
- Write a C program to implement a queue and delete the nth element from the front without shifting all subsequent elements.
- Write a C program to implement a circular queue where deletion of the nth element adjusts the front pointer correctly.
- Write a C program to implement a queue that deletes an element based on a condition rather than its fixed position.
- Write a C program to delete every kth element from a queue repeatedly until the queue is empty (Josephus problem style).
Go to:
PREV : Queue Minimum Element.
NEXT : Queue Sorting in Ascending Order.
C Programming Code Editor:
Have another way to solve this solution? Contribute your code (and comments) through Disqus.
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
Test your Programming skills with w3resource's quiz.
