C Exercises: Implement a queue using a linked list with insert, display
3. Queue Linked List Basic Operations
Write a C program to implement a queue using a linked list. Programs should contain functions for inserting elements into the queue, displaying queue elements, and checking whether the queue is empty or not.
Sample Solution:
C Code:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
// Define a structure for a node in the queue
struct Node {
int data;
struct Node *next;
};
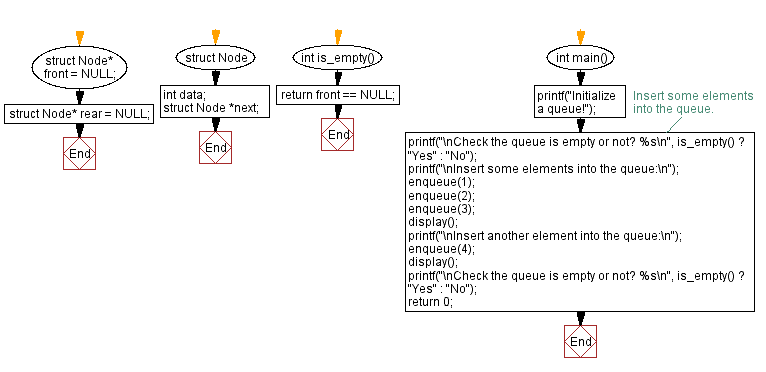
struct Node* front = NULL; // Declare a pointer to the front of the queue
struct Node* rear = NULL; // Declare a pointer to the rear of the queue
// Function to insert an element into the queue
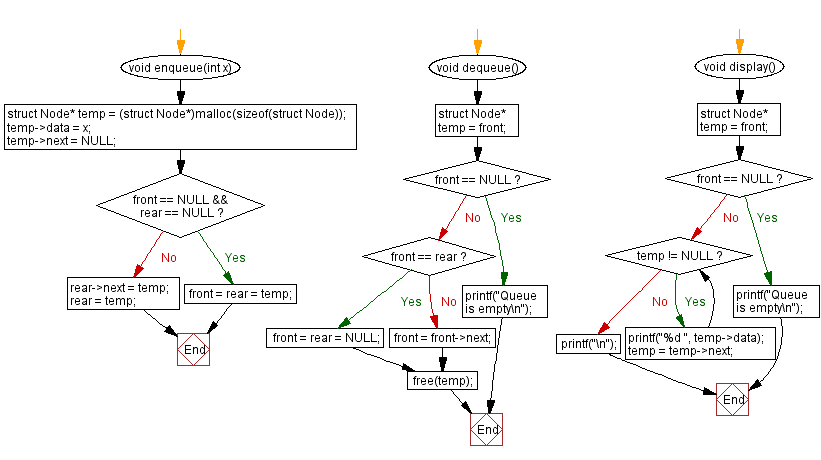
void enqueue(int x) {
// Allocate memory for a new node
struct Node* temp = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
temp->data = x; // Assign data to the new node
temp->next = NULL; // Set the next pointer of the new node to NULL
// Check if the queue is empty
if (front == NULL && rear == NULL) {
front = rear = temp; // If empty, set both front and rear to the new node
return;
}
rear->next = temp; // Otherwise, link the new node to the rear of the queue
rear = temp; // Update the rear pointer to the new node
}
// Function to remove an element from the queue
void dequeue() {
struct Node* temp = front; // Store the front node in a temporary variable
// Check if the queue is empty
if (front == NULL) {
printf("Queue is empty\n"); // Print error message if empty
return;
}
// Check if there's only one node in the queue
if (front == rear) {
front = rear = NULL; // If yes, set both front and rear to NULL
} else {
front = front->next; // Otherwise, move front to the next node
}
free(temp); // Free memory allocated for the removed node
}
// Function to display the elements in the queue
void display() {
struct Node* temp = front; // Initialize a temporary pointer to traverse the queue
// Check if the queue is empty
if (front == NULL) {
printf("Queue is empty\n"); // Print message if empty
return;
}
// Traverse the queue and print each element
while (temp != NULL) {
printf("%d ", temp->data); // Print the data of the current node
temp = temp->next; // Move to the next node
}
printf("\n"); // Print a newline after displaying all elements
}
// Function to check whether the queue is empty
int is_empty() {
return front == NULL; // Return 1 if front is NULL (indicating an empty queue), otherwise return 0
}
int main() {
printf("Initialize a queue!"); // Print message to indicate initializing a queue
// Insert some elements into the queue.
printf("\nCheck the queue is empty or not? %s\n", is_empty() ? "Yes" : "No"); // Check if the queue is empty
printf("\nInsert some elements into the queue:\n"); // Print message to indicate inserting elements into the queue
enqueue(1); // Insert element 1 into the queue
enqueue(2); // Insert element 2 into the queue
enqueue(3); // Insert element 3 into the queue
display(); // Display the elements of the queue
printf("\nInsert another element into the queue:\n"); // Print message to indicate inserting another element
enqueue(4); // Insert element 4 into the queue
display(); // Display the elements of the queue
printf("\nCheck the queue is empty or not? %s\n", is_empty() ? "Yes" : "No"); // Check if the queue is empty
return 0; // Return from the main function
}
Output:
Initialize a queue! Check the queue is empty or not? Yes Insert some elements into the queue: 1 2 3 Insert another element into the queue: 1 2 3 4 Check the queue is empty or not? No
Flowchart
For more Practice: Solve these Related Problems:
- Write a C program to implement a queue using a doubly linked list that supports both forward and reverse traversal.
- Write a C program to implement a linked list queue that prints its elements in reverse order using recursion.
- Write a C program to implement a queue with a linked list that recycles memory nodes to avoid memory leaks.
- Write a C program to implement a linked list queue where each node includes a timestamp, then display elapsed times.
Go to:
PREV : Array Queue Dequeue Operation.
NEXT : Array Queue Deletion Function.
C Programming Code Editor:
Have another way to solve this solution? Contribute your code (and comments) through Disqus.
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
Test your Programming skills with w3resource's quiz.
