C Exercises: Find the maximum element in a stack
12. Maximum Element in Stack Variants
Write a C program to find the maximum element in a stack.
Sample Solution:
C Code:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <limits.h>
#define MAX_SIZE 100
// Arrays to maintain the main stack and the stack for tracking maximum elements
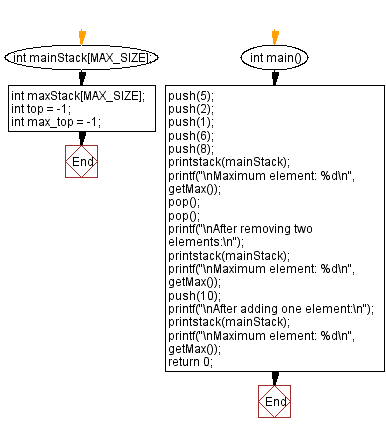
int mainStack[MAX_SIZE];
int maxStack[MAX_SIZE];
int top = -1; // Top index of the main stack
int max_top = -1; // Top index of the maximum stack
// Function to push an element onto the main stack
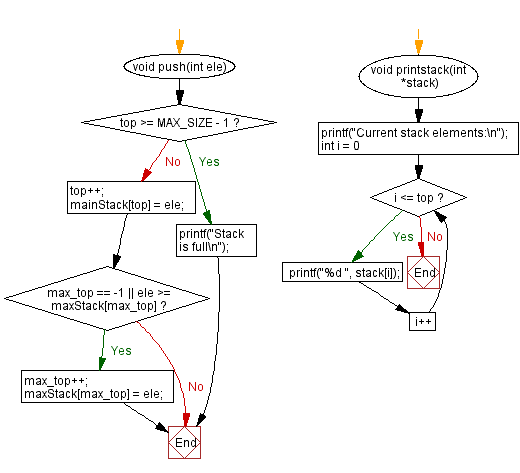
void push(int ele) {
if (top >= MAX_SIZE - 1) {
printf("Stack is full\n");
return;
}
// Push the element onto the main stack
top++;
mainStack[top] = ele;
// If the maxStack is empty or the element is greater than or equal to the top element in maxStack,
// push the element onto the maxStack to track maximum elements
if (max_top == -1 || ele >= maxStack[max_top]) {
max_top++;
maxStack[max_top] = ele;
}
}
// Function to pop an element from the main stack
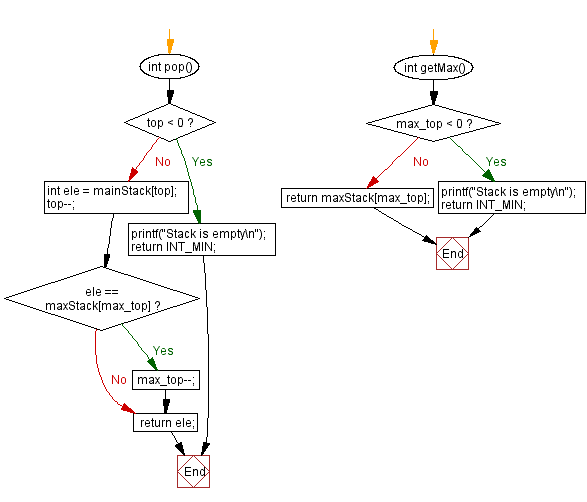
int pop() {
if (top < 0) {
printf("Stack is empty\n");
return INT_MIN;
}
// Pop the top element from the main stack
int ele = mainStack[top];
top--;
// If the popped element is the top element in maxStack, also pop it from maxStack
if (ele == maxStack[max_top]) {
max_top--;
}
return ele;
}
// Function to get the maximum element from the main stack
int getMax() {
if (max_top < 0) {
printf("Stack is empty\n");
return INT_MIN;
}
return maxStack[max_top];
}
// Function to print the elements of the stack
void printstack(int *stack) {
printf("Current stack elements:\n");
for (int i = 0; i <= top; i++) {
printf("%d ", stack[i]);
}
}
int main() {
// Example usage of the stack functions
push(5);
push(2);
push(1);
push(6);
push(8);
printstack(mainStack);
printf("\nMaximum element: %d\n", getMax());
pop();
pop();
printf("\nAfter removing two elements:\n");
printstack(mainStack);
printf("\nMaximum element: %d\n", getMax());
push(10);
printf("\nAfter adding one element:\n");
printstack(mainStack);
printf("\nMaximum element: %d\n", getMax());
return 0;
}
Output:
Current stack elements: 5 2 1 6 8 Maximum element: 8 After removing two elements: Current stack elements: 5 2 1 Maximum element: 5 After adding one element: Current stack elements: 5 2 1 10 Maximum element: 10
Flowchart:
For more Practice: Solve these Related Problems:
- Write a C program to find the second maximum element in a stack without fully sorting it.
- Write a C program to implement an auxiliary stack that retrieves the maximum element in O(1) time.
- Write a C program to remove the maximum element from a stack and maintain the order of the other elements.
- Write a C program to display the current maximum element in the stack after each push or pop operation.
Go to:
PREV : Minimum Element in Stack Variants.
NEXT : Middle Element Operations in Stack.
C Programming Code Editor:
Have another way to solve this solution? Contribute your code (and comments) through Disqus.
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
Test your Programming skills with w3resource's quiz.
