C Exercises: Remove the minimum value from a stack
15. Remove Minimum Element Variants
Write a C program to implement a stack and accept some numeric values. Remove the number whose value is the minimum on the stack.
Sample Solution:
C Code:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <limits.h>
// Define the Stack structure
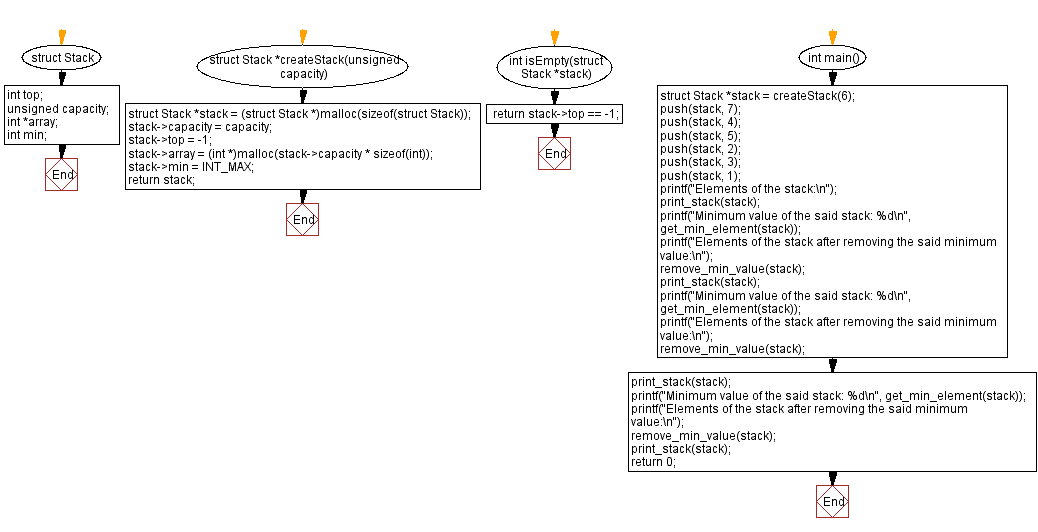
struct Stack {
int top; // Represents the top of the stack
unsigned capacity; // Represents the capacity of the stack
int *array; // Array to store stack elements
int min; // Variable to store the minimum value in the stack
};
// Function to create a stack with a given capacity
struct Stack *createStack(unsigned capacity) {
struct Stack *stack = (struct Stack *)malloc(sizeof(struct Stack)); // Allocate memory for the stack
stack->capacity = capacity; // Initialize stack capacity
stack->top = -1; // Initialize top of the stack
stack->array = (int *)malloc(stack->capacity * sizeof(int)); // Allocate memory for stack elements
stack->min = INT_MAX; // Initialize minimum value to the maximum possible integer value
return stack; // Return the created stack
}
// Function to check if the stack is full
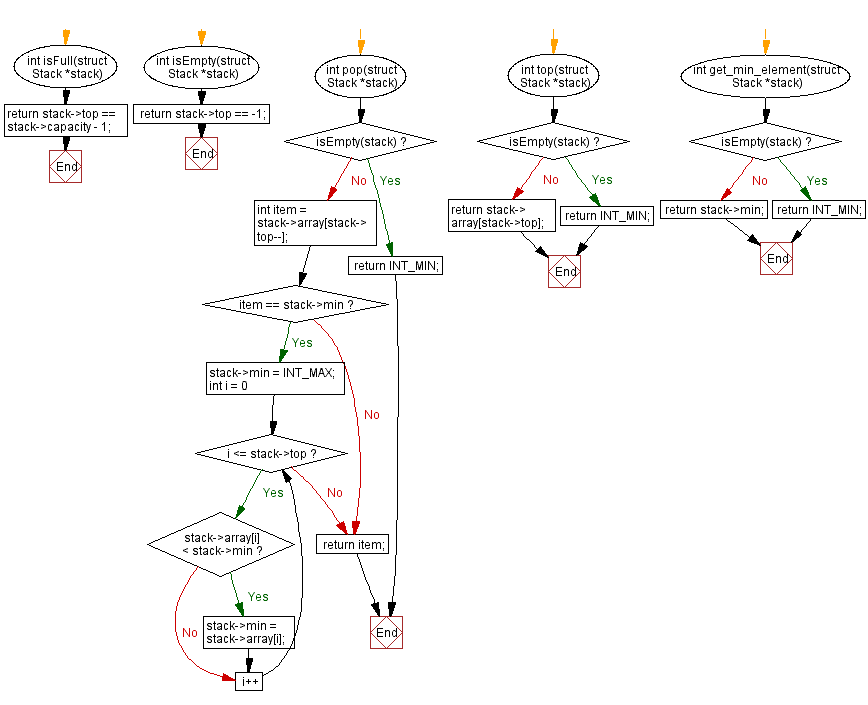
int isFull(struct Stack *stack) {
return stack->top == stack->capacity - 1; // Returns 1 if the stack is full, otherwise 0
}
// Function to check if the stack is empty
int isEmpty(struct Stack *stack) {
return stack->top == -1; // Returns 1 if the stack is empty, otherwise 0
}
// Function to push an element onto the stack
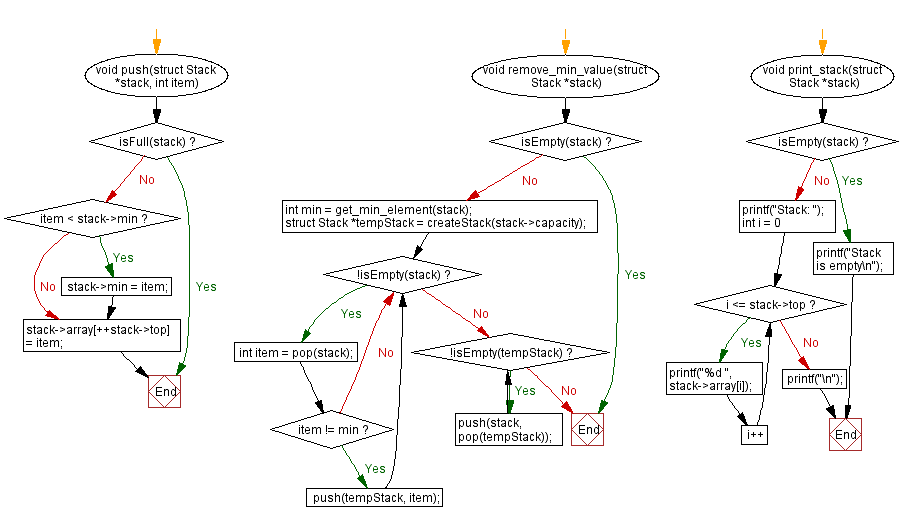
void push(struct Stack *stack, int item) {
if (isFull(stack)) {
return; // If the stack is full, return without pushing
}
if (item < stack->min) {
stack->min = item; // Update the minimum value if the new item is smaller
}
stack->array[++stack->top] = item; // Increment top and insert the item onto the stack
}
// Function to pop an element from the stack
int pop(struct Stack *stack) {
if (isEmpty(stack)) {
return INT_MIN; // If the stack is empty, return the minimum possible integer value
}
int item = stack->array[stack->top--]; // Get the top element and decrement top
// If the popped item was the minimum value, recalculate the minimum value in the stack
if (item == stack->min) {
stack->min = INT_MAX;
for (int i = 0; i <= stack->top; i++) {
if (stack->array[i] < stack->min) {
stack->min = stack->array[i];
}
}
}
return item; // Return the popped item
}
// Function to get the top element of the stack
int top(struct Stack *stack) {
if (isEmpty(stack)) {
return INT_MIN; // If the stack is empty, return the minimum possible integer value
}
return stack->array[stack->top]; // Return the top element of the stack
}
// Function to get the minimum value in the stack
int get_min_element(struct Stack *stack) {
if (isEmpty(stack)) {
return INT_MIN; // If the stack is empty, return the minimum possible integer value
}
return stack->min; // Return the minimum value in the stack
}
// Function to remove occurrences of the minimum value from the stack
void remove_min_value(struct Stack *stack) {
if (isEmpty(stack)) {
return; // If the stack is empty, return without removing
}
int min = get_min_element(stack); // Get the minimum value from the stack
struct Stack *tempStack = createStack(stack->capacity); // Create a temporary stack
// Transfer all non-minimum values to the temporary stack
while (!isEmpty(stack)) {
int item = pop(stack);
if (item != min) {
push(tempStack, item);
}
}
// Transfer elements back to the original stack from the temporary stack
while (!isEmpty(tempStack)) {
push(stack, pop(tempStack));
}
}
// Function to print the elements of the stack
void print_stack(struct Stack *stack) {
if (isEmpty(stack)) {
printf("Stack is empty\n");
return;
}
printf("Stack: ");
for (int i = 0; i <= stack->top; i++) {
printf("%d ", stack->array[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}
// Main function
int main() {
struct Stack *stack = createStack(6); // Create a stack with capacity 6
// Push elements onto the stack
push(stack, 7);
push(stack, 4);
push(stack, 5);
push(stack, 2);
push(stack, 3);
push(stack, 1);
printf("Elements of the stack:\n");
print_stack(stack); // Print the elements of the stack
printf("Minimum value of the said stack: %d\n", get_min_element(stack)); // Print the minimum value of the stack
printf("Elements of the stack after removing the said minimum value:\n");
remove_min_value(stack); // Remove occurrences of the minimum value from the stack
print_stack(stack); // Print the elements of the modified stack
printf("Minimum value of the said stack: %d\n", get_min_element(stack)); // Print the minimum value of the modified stack
printf("Elements of the stack after removing the said minimum value:\n");
remove_min_value(stack); // Remove occurrences of the minimum value from the stack
print_stack(stack); // Print the elements of the modified stack
printf("Minimum value of the said stack: %d\n", get_min_element(stack)); // Print the minimum value of the modified stack
printf("Elements of the stack after removing the said minimum value:\n");
remove_min_value(stack); // Remove occurrences of the minimum value from the stack
print_stack(stack); // Print the elements of the modified stack
return 0;
}
Output:
Elements of the stack: Stack: 7 4 5 2 3 1 Minimum value of the said stack: 1 Elements of the stack after removing the said minimum value: Stack: 7 4 5 2 3 Minimum value of the said stack: 2 Elements of the stack after removing the said minimum value: Stack: 7 4 5 3 Minimum value of the said stack: 3 Elements of the stack after removing the said minimum value: Stack: 7 4 5
Flowchart:
For more Practice: Solve these Related Problems:
- Write a C program to remove all occurrences of the minimum element from a stack.
- Write a C program to alternately remove the maximum and minimum elements from a stack until it is empty.
- Write a C program to repeatedly remove the minimum element until the remaining stack elements are in non-decreasing order.
- Write a C program to remove the minimum element and then insert a new element to maintain a sorted stack.
Go to:
PREV : Average and Statistical Measures of Stack.
NEXT : Kth Element Retrieval in Stack.
C Programming Code Editor:
Have another way to solve this solution? Contribute your code (and comments) through Disqus.
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
Test your Programming skills with w3resource's quiz.
