C++ Linked List Exercises: Insert new node at the middle of a Doubly Linked List
21. Insert Node at the Middle of Doubly Linked List
Write a C++ program to insert a new node at the middle of a given Doubly Linked List.
Test Data:
Doubly linked list is as follows:
---------------------------------
Traversal in Forward direction: Orange White Green Red
Traversal in Reverse direction: Red Green White Orange
Insert a new node at the middle position of the said Doubly linked list:
-----------------------------------------------------------------------
Traversal in Forward direction: Orange White Pink Green Red
Traversal in Reverse direction: Red Green Pink White Orange
Insert another new node at the middle position of the said Doubly linked list:
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Traversal in Forward direction: Orange White Pink Black Green Red
Traversal in Reverse direction: Red Green Black Pink White Orange
Sample Solution:
C++ Code:
#include <iostream> // Including input-output stream header file
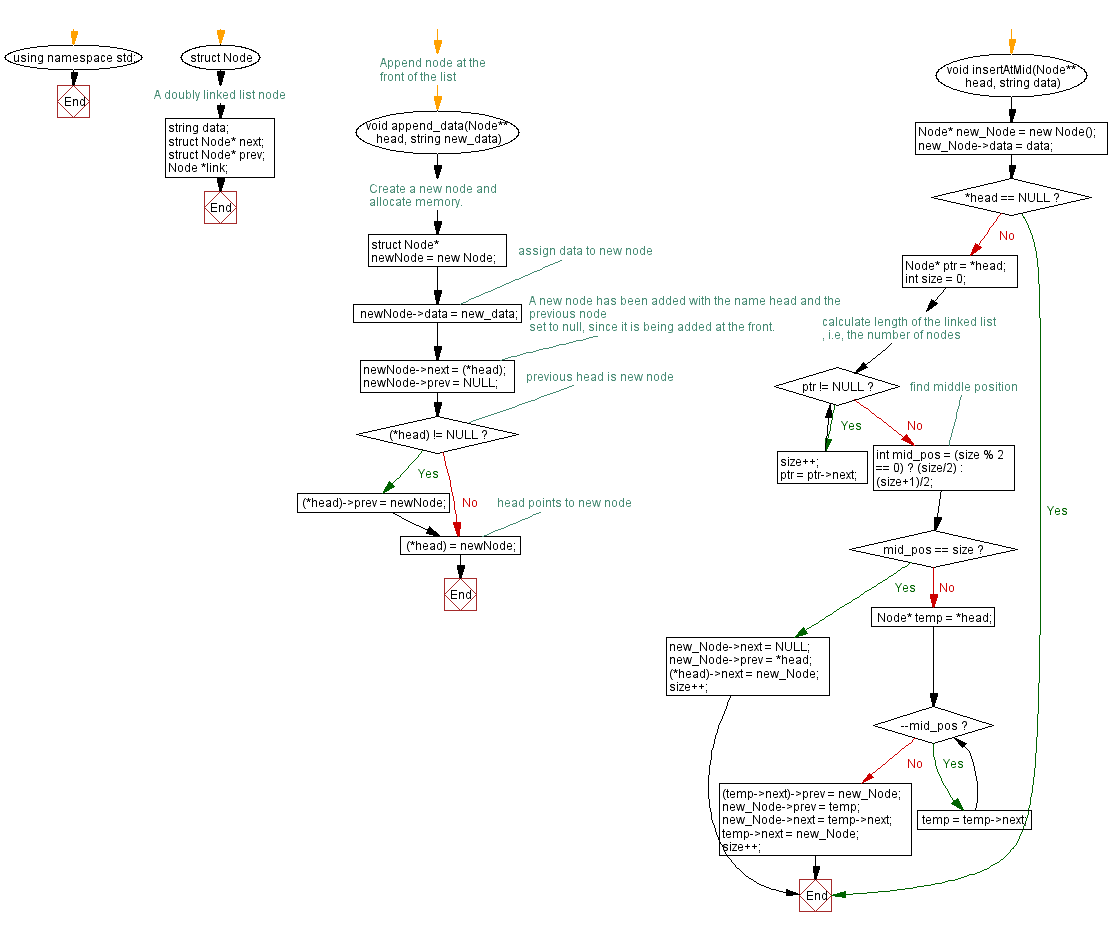
using namespace std; // Using standard namespace
// A doubly linked list node
struct Node {
string data; // Data field to store string data
struct Node* next; // Pointer to the next node
struct Node* prev; // Pointer to the previous node
Node *link; // Additional pointer, not used in the code
};
// Function to append data at the front of the doubly linked list
void append_data(Node** head, string new_data)
{
// Create a new node and allocate memory.
struct Node* newNode = new Node;
// Assign data to new node
newNode->data = new_data;
// A new node has been added with the name head and the previous node
// set to null, since it is being added at the front.
newNode->next = (*head);
newNode->prev = NULL;
// Previous head is the new node
if ((*head) != NULL)
(*head)->prev = newNode;
// Head points to the new node
(*head) = newNode;
}
// Function to insert a node at the middle position of the doubly linked list
void insertAtMid(Node** head, string data){
Node* new_Node = new Node(); // Creating a new node
new_Node->data = data; // Assigning data to the new node
if(*head == NULL){
return; // If the linked list is empty, return
}
Node* ptr = *head;
int size = 0;
// Calculate length of the linked list, i.e., the number of nodes
while (ptr != NULL) {
size++;
ptr = ptr->next;
}
// Find middle position
int mid_pos = (size % 2 == 0) ? (size/2) : (size+1)/2;
if(mid_pos == size){
new_Node->next = NULL;
new_Node->prev = *head;
(*head)->next = new_Node;
size++;
return;
}
Node* temp = *head;
while(--mid_pos){
temp = temp->next;
}
(temp->next)->prev = new_Node;
new_Node->prev = temp;
new_Node->next = temp->next;
temp->next = new_Node;
size++;
}
// Following function displays contents of the doubly linked list
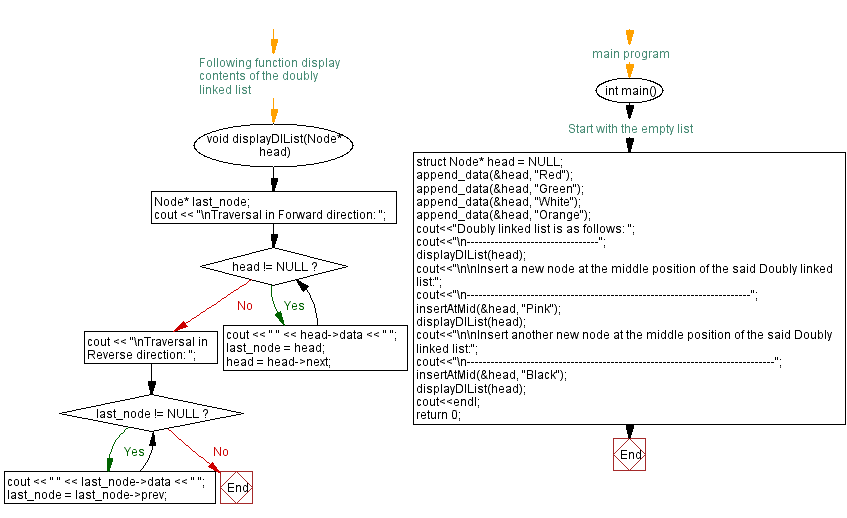
void displayDlList(Node* head)
{
Node* last_node;
cout << "\nTraversal in Forward direction: ";
while (head != NULL) {
cout << " " << head->data << " "; // Displaying data in forward direction
last_node = head;
head = head->next;
}
cout << "\nTraversal in Reverse direction: ";
while (last_node != NULL) {
cout << " " << last_node->data << " "; // Displaying data in reverse direction
last_node = last_node->prev;
}
}
// Main program
int main() {
/* Start with the empty list */
struct Node* head = NULL; // Initializing the head of the linked list as NULL
append_data(&head, "Red"); // Appending "Red" at the front of the list
append_data(&head, "Green"); // Appending "Green" at the front of the list
append_data(&head, "White"); // Appending "White" at the front of the list
append_data(&head, "Orange"); // Appending "Orange" at the front of the list
cout<<"Doubly linked list is as follows: ";
cout<<"\n---------------------------------";
displayDlList(head); // Displaying the doubly linked list
cout<<"\n\nInsert a new node at the middle position of the said Doubly linked list:";
cout<<"\n-----------------------------------------------------------------------";
insertAtMid(&head, "Pink"); // Inserting "Pink" node at the middle of the list
displayDlList(head); // Displaying the updated doubly linked list
cout<<"\n\nInsert another new node at the middle position of the said Doubly linked list:";
cout<<"\n-----------------------------------------------------------------------------";
insertAtMid(&head, "Black"); // Inserting "Black" node at the middle of the list
displayDlList(head); // Displaying the updated doubly linked list
cout<<endl;
return 0; // Returning from the main function
}
Sample Output:
Doubly linked list is as follows: --------------------------------- Traversal in Forward direction: Orange White Green Red Traversal in Reverse direction: Red Green White Orange Insert a new node at the middle position of the said Doubly linked list: ----------------------------------------------------------------------- Traversal in Forward direction: Orange White Pink Green Red Traversal in Reverse direction: Red Green Pink White Orange Insert another new node at the middle position of the said Doubly linked list: ----------------------------------------------------------------------------- Traversal in Forward direction: Orange White Pink Black Green Red Traversal in Reverse direction: Red Green Black Pink White Orange
Flowchart:
For more Practice: Solve these Related Problems:
- Write a C++ program to insert a node in the middle of a doubly linked list and then display the list in both directions.
- Develop a C++ program that computes the middle index of a doubly linked list and inserts a new node at that position.
- Design a C++ program to insert a node in the center of a doubly linked list while adjusting previous and next pointers accordingly.
- Implement a C++ program to add a node at the middle of a doubly linked list and validate the insertion by printing updated node connections.
Go to:
PREV : Find the Middle Element of a Doubly Linked List.
NEXT : C++ Stack Exercises Home.
C++ Code Editor:
Contribute your code and comments through Disqus.
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
