C++ Linked List Exercises: Get Nth node in a Singly Linked List
8. Get Nth Node in a Singly Linked List
Write a C++ program to get Nth node in a given Singly Linked List.
Test Data:
Original list:
7 5 3 1
Position: 1
Value: 7
Position: 2
Value: 5
Position: 3
Value: 3
Position: 4
Value: 1
Sample Solution:
C++ Code:
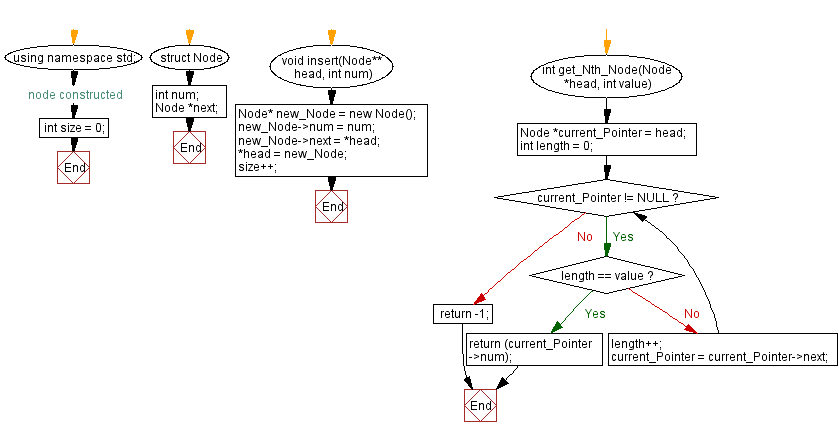
#include <iostream> // Including input-output stream header file
using namespace std; // Using standard namespace
// Structure for defining a Node
struct Node {
int num; // Data field to store a number
Node *next; // Pointer to the next node
}; // Node constructed
int sz = 0; // Initializing variable to keep track of the size of the linked list
// Function to insert a node at the beginning of the linked list
void insert(Node** head, int num) {
Node* new_Node = new Node(); // Creating a new node
new_Node->num = num; // Assigning data to the new node
new_Node->next = *head; // Pointing the new node to the current head
*head = new_Node; // Making the new node as the head
sz++; // Increasing the size of the linked list
}
// Function to get the value of the node at a specific position in the linked list
int get_Nth_Node(Node *head, int value) {
Node *current_Pointer = head; // Pointer to traverse the list
int length = 0; // Initializing length to zero
while (current_Pointer != NULL) { // Loop through the list until the end is reached
if (length == value) // If the position matches the desired value
return (current_Pointer->num); // Return the value of the node at that position
length++; // Incrementing the length
current_Pointer = current_Pointer->next; // Moving to the next node
}
return -1; // If the position is not found, return -1
}
// Display all nodes in the linked list
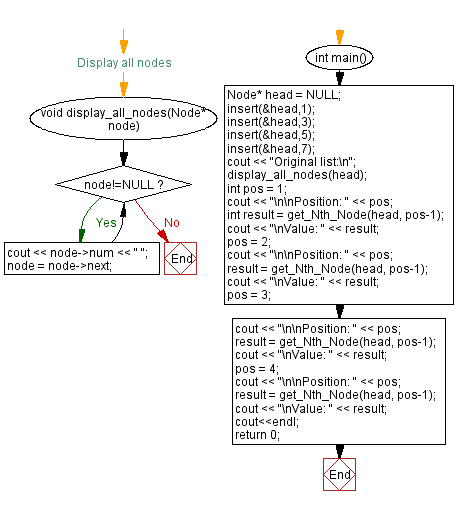
void display_all_nodes(Node* node) {
while (node != NULL) {
cout << node->num << " "; // Displaying the data in the current node
node = node->next; // Move to the next node
}
}
int main() {
Node* head = NULL; // Initializing the head of the linked list as NULL
insert(&head, 1); // Inserting a node with value 1
insert(&head, 3); // Inserting a node with value 3
insert(&head, 5); // Inserting a node with value 5
insert(&head, 7); // Inserting a node with value 7
cout << "Original list:\n"; // Displaying message for the original list
display_all_nodes(head); // Displaying all nodes in the original list
int pos = 1;
cout << "\n\nPosition: " << pos; // Displaying the position
int result = get_Nth_Node(head, pos - 1); // Getting the value at the specified position
cout << "\nValue: " << result; // Displaying the value
pos = 2;
cout << "\n\nPosition: " << pos; // Displaying the position
result = get_Nth_Node(head, pos - 1); // Getting the value at the specified position
cout << "\nValue: " << result; // Displaying the value
pos = 3;
cout << "\n\nPosition: " << pos; // Displaying the position
result = get_Nth_Node(head, pos - 1); // Getting the value at the specified position
cout << "\nValue: " << result; // Displaying the value
pos = 4;
cout << "\n\nPosition: " << pos; // Displaying the position
result = get_Nth_Node(head, pos - 1); // Getting the value at the specified position
cout << "\nValue: " << result; // Displaying the value
cout << endl; // Displaying newline
return 0; // Returning from the main function
}
Sample Output:
Original list: 7 5 3 1 Position: 1 Value: 7 Position: 2 Value: 5 Position: 3 Value: 3 Position: 4 Value: 1
Flowchart:
For more Practice: Solve these Related Problems:
- Write a C++ program to retrieve and display the nth node from a singly linked list using iterative traversal.
- Develop a C++ program to get the nth node from a singly linked list and handle out-of-bound indices gracefully.
- Design a C++ program that finds the nth node from a singly linked list using recursion and then displays its value.
- Implement a C++ program to fetch the nth node from a singly linked list and then update its value before printing the list.
Go to:
PREV : Insert Node in the Middle of Singly Linked List.
NEXT : Insert Node at Any Position in Singly Linked List.
C++ Code Editor:
Contribute your code and comments through Disqus.
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
