C++ String Exercises: Reverse the words of three or more lengths in a string
32. Reverse Words of Length Three or More in a String
Write a C++ program that takes a string and reverses the words of three or more lengths in a string. Return the updated string. As input characters, only spaces and letters are permitted.
Sample Data:
("The quick brown fox jumps over the lazy dog") -> “ehT kciuq nworb xof spmuj revo eht yzal god”
("Reverse the words of three or more") -> “esreveR eht sdrow of eerht or erom”
("ABcDef") -> “feDcBA”
Sample Solution:
C++ Code:
#include <bits/stdc++.h> // Include all standard libraries
using namespace std; // Using the standard namespace
// Function to reverse words of three or more lengths in a string
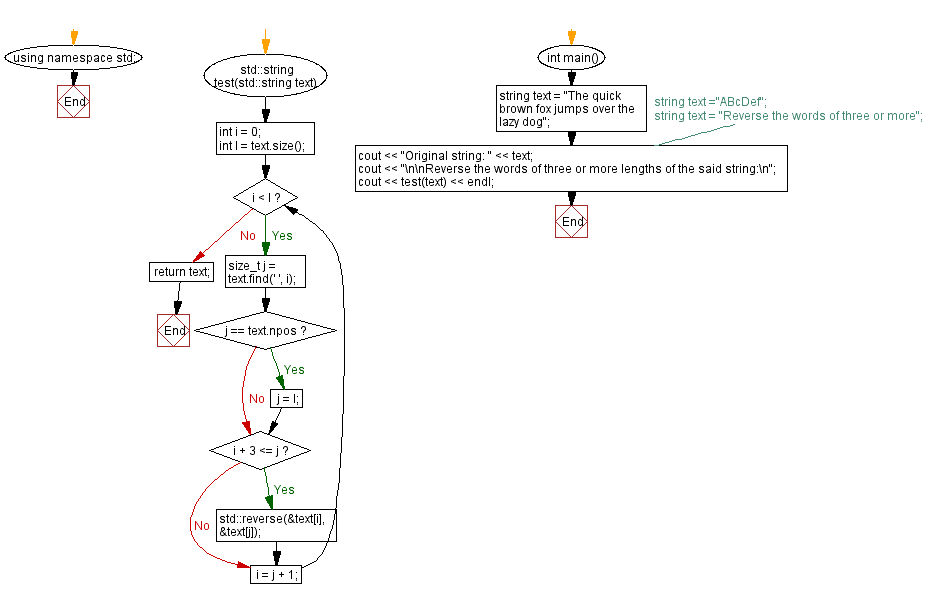
string test(string text) {
int i = 0; // Initializing variable i to 0
int l = text.size(); // Getting the size of the input string
// Loop through the string
while (i < l) {
// Find the position of the space character starting from index i
size_t j = text.find(' ', i);
// If space character is not found, assign j as the end of string index
if (j == text.npos) j = l;
// If the length of the word is three or more, reverse the characters in the word
if (i + 3 <= j)
std::reverse(&text[i], &text[j]);
i = j + 1; // Move to the next word by updating the starting index i
}
return text; // Return the modified string
}
int main() {
//string text = "The quick brown fox jumps over the lazy dog"; // Test string 1
//string text ="ABcDef"; // Test string 2
string text = "Reverse the words of three or more"; // Test string 3
cout << "Original string: " << text; // Display the original string
cout << "\n\nReverse the words of three or more lengths of the said string:\n";
cout << test(text) << endl; // Call the function to reverse words of three or more lengths and display the modified string
}
Sample Output:
Original string: The quick brown fox jumps over the lazy dog Reverse the words of three or more lengths of the said string: ehT kciuq nworb xof spmuj revo eht yzal god
Flowchart:
For more Practice: Solve these Related Problems:
- Write a C++ program to reverse only the words in a string that are three or more characters long.
- Write a C++ program that reads a sentence and reverses words exceeding a specified length while preserving short words.
- Write a C++ program to output a string where each word with three or more letters is reversed, leaving others intact.
- Write a C++ program that processes a sentence and alternates the order of letters for words with length greater than or equal to three.
Go to:
PREV : Check if a String Contains Only Uppercase or Lowercase Letters.
NEXT : Check if Letters of One String Appear in Another.
C++ Code Editor:
Contribute your code and comments through Disqus.
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
