Java: Find the longest increasing continuous subsequence in a given array of integers
Longest Increasing Subsequence
Write a Java program to find the longest increasing continuous subsequence in a given array of integers.
Visual Presentation:
Sample Solution:
Java Code:
// Importing necessary Java utilities
import java.util.*;
// Main class Solution
public class Solution {
// Main method
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Initializing an array of integers
int[] nums = { 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 7, 8, 9, 1, 2, 3 };
// Printing the original array
System.out.println("Original array: " + Arrays.toString(nums));
// Finding the size of the longest increasing continuous subsequence and printing it
System.out.println("Size of longest increasing continuous subsequence: " + longest_seq(nums));
}
// Method to find the size of the longest increasing continuous subsequence
public static int longest_seq(int[] nums) {
int max_sequ = 0; // Initializing the variable to hold the maximum sequence length
// Handling the case when the array contains only one element
if (nums.length == 1)
return 1; // If only one element is present, the longest sequence is of length 1
// Looping through the array to find the longest increasing or decreasing sequence
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length - 1; i++) {
int ctr = 1; // Counter to track the sequence length
int j = i; // Initializing j to the current index i
// Checking for an increasing sequence
if (nums[i + 1] > nums[i]) {
while (j < nums.length - 1 && nums[j + 1] > nums[j]) {
ctr++; // Incrementing the counter for each increasing element
j++;
}
}
// Checking for a decreasing sequence
else if (nums[i + 1] < nums[i]) {
while (j < nums.length - 1 && nums[j + 1] < nums[j]) {
ctr++; // Incrementing the counter for each decreasing element
j++;
}
}
// Updating the maximum sequence length encountered so far
if (ctr > max_sequ) {
max_sequ = ctr;
}
// Moving the index i ahead by the sequence length minus 2 to avoid rechecking elements
i += ctr - 2;
}
return max_sequ; // Returning the size of the longest sequence found
}
}
Sample Output:
Original array: [10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 7, 8, 9, 1, 2, 3] Size of longest increasing continuous subsequence: 5
Flowchart:
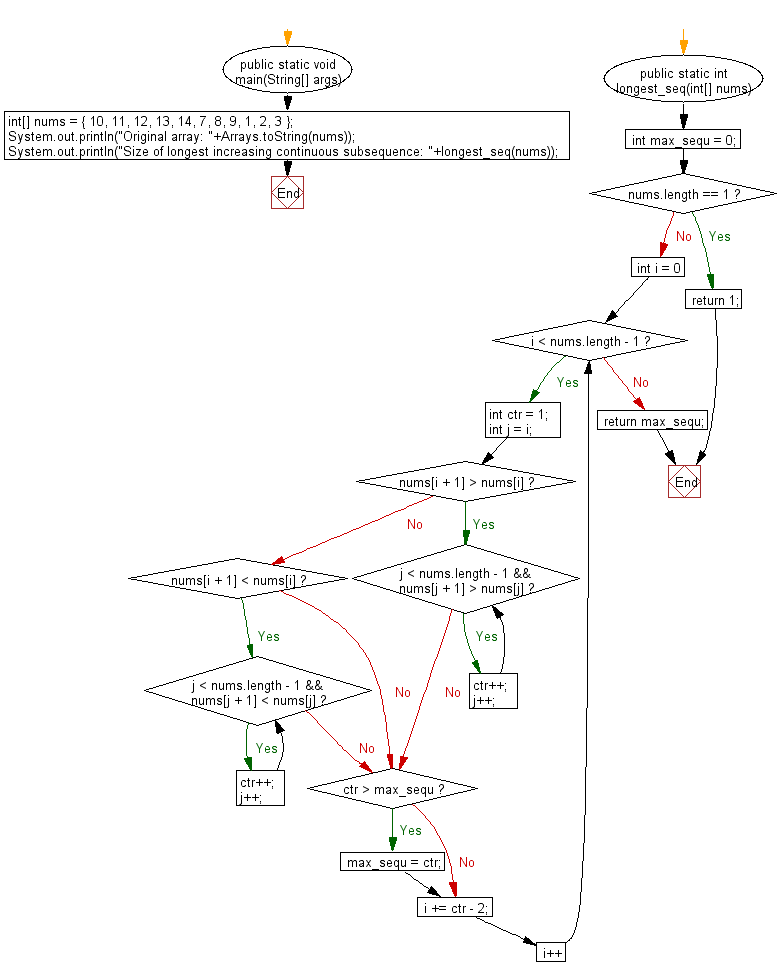
For more Practice: Solve these Related Problems:
- Write a Java program to find the longest increasing subsequence (not necessarily continuous) in an array.
- Write a Java program to determine the longest decreasing continuous subsequence in an array of integers.
- Write a Java program to find the longest subsequence in which elements alternate between increasing and decreasing.
- Write a Java program to compute the longest increasing continuous subsequence in an array that includes duplicate values.
Go to:
PREV : Clone Binary Tree.
NEXT : Add One to Array Number.
Java Code Editor:
Company: Facebook
Contribute your code and comments through Disqus.
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
Test your Programming skills with w3resource's quiz.
