Java: Find all unique combinations from a collection of candidate numbers
Unique Combinations for Target Sum
Write a Java program to find all unique combinations from a collection of candidate numbers. The sum of the numbers will equal a given target number.
Visual Presentation:
Sample Solution:
Java Code:
import java.util.*;
class Main {
// Method to insert values into a Map with key as a generic type and value as a List of generic type
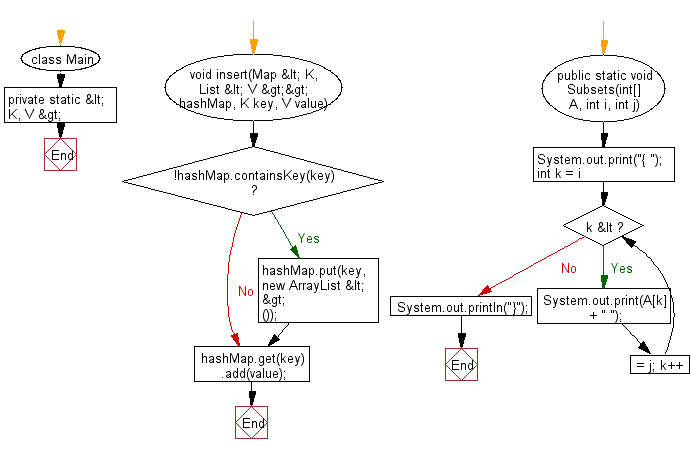
private static <K, V> void insert(Map<K, List<V>> hashMap, K key, V value) {
// If the key is not present in the map, create a new entry with an empty ArrayList
if (!hashMap.containsKey(key)) {
hashMap.put(key, new ArrayList<>());
}
// Add the value to the list corresponding to the key
hashMap.get(key).add(value);
}
// Method to print subsets of an array from index i to j
public static void Subsets(int[] A, int i, int j) {
System.out.print("{ ");
for (int k = i; k <= j; k++) {
System.out.print(A[k] + " ");
}
System.out.println("}");
}
// Method to find subsets with a given sum in the array
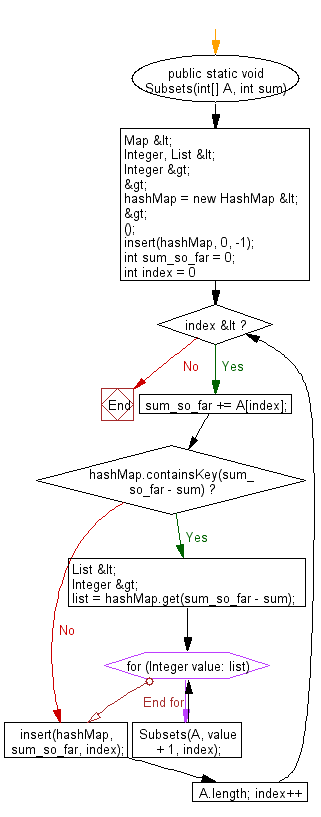
public static void Subsets(int[] A, int sum) {
// Create a HashMap to store the cumulative sum and corresponding indices
Map<Integer, List<Integer>> hashMap = new HashMap<>();
// Insert an initial entry with key 0 and value -1 (sum_so_far - sum = 0 - sum)
insert(hashMap, 0, -1);
int sum_so_far = 0;
for (int index = 0; index < A.length; index++) {
// Update the cumulative sum
sum_so_far += A[index];
// If the HashMap contains the key (cumulative sum - sum), print subsets
if (hashMap.containsKey(sum_so_far - sum)) {
List<Integer> list = hashMap.get(sum_so_far - sum);
for (Integer value : list) {
Subsets(A, value + 1, index);
}
}
// Insert the current cumulative sum and index into the HashMap
insert(hashMap, sum_so_far, index);
}
}
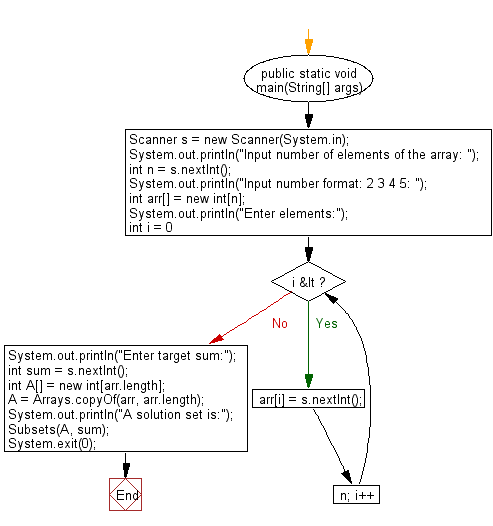
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Scanner for user input
Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in);
// Prompt for the number of elements in the array
System.out.println("Input number of elements of the array: ");
int n = s.nextInt();
// Prompt for entering array elements in number format
System.out.println("Input number format: 2 3 4 5: ");
int arr[] = new int[n];
// Prompt for entering array elements
System.out.println("Enter elements:");
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
arr[i] = s.nextInt();
// Prompt for entering the target sum
System.out.println("Enter target sum:");
int sum = s.nextInt();
// Create a copy of the original array
int A[] = Arrays.copyOf(arr, arr.length);
// Print the solution set (subsets with the given sum)
System.out.println("A solution set is:");
Subsets(A, sum);
// Exit the program
System.exit(0);
}
}
Sample Output:
Input number of elements of the array:
3
Input number format: 2 3 4 5:
Enter elements:
6 7 8
Enter target sum:
21
A solution set is:
{ 6 7 8 }
Flowchart:
For more Practice: Solve these Related Problems:
- Write a Java program to find all unique combinations that add up to a target sum when each candidate number can be used unlimited times.
- Write a Java program to determine unique combinations using exactly three numbers from an array that sum to a target value.
- Write a Java program to list unique combinations that sum to a target even when the input array contains duplicate numbers.
- Write a Java program to find all unique combinations summing to a target using a recursive backtracking approach with early pruning.
Go to:
PREV : String Compression with Repeated Counts.
NEXT : String Matching with Wildcards.
Java Code Editor:
Contribute your code and comments through Disqus.
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
Test your Programming skills with w3resource's quiz.
