Java: Iterate through all elements in a array list
2. Iterate ArrayList Elements
Write a Java program to iterate through all elements in an array list..
Pictorial Presentation:
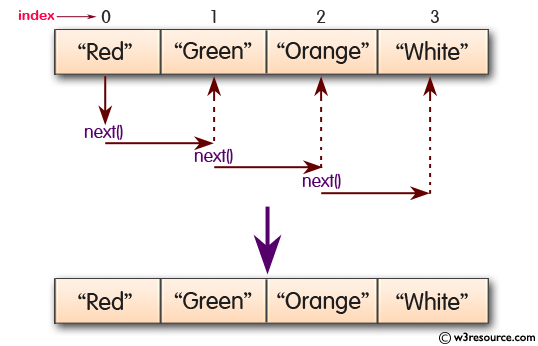
Sample Solution:-
Java Code:
import java.util.*;
public class Exercise2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Creae a list and add some colors to the list
List<String> list_Strings = new ArrayList<String>();
list_Strings.add("Red");
list_Strings.add("Green");
list_Strings.add("Orange");
list_Strings.add("White");
list_Strings.add("Black");
// Print the list
for (String element : list_Strings) {
System.out.println(element);
}
}
}
Sample Output:
Red Green Orange White Black
Flowchart:
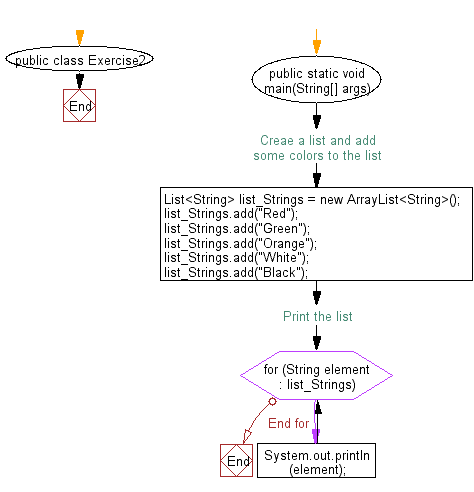
For more Practice: Solve these Related Problems:
- Write a Java program to iterate over an ArrayList of strings using a ListIterator and print elements in reverse order.
- Write a Java program to iterate through an ArrayList using Java streams and forEach(), and print each element with its index.
- Write a Java program to iterate over an ArrayList using a for-each loop and conditionally print only the elements that meet a specific pattern.
- Write a Java program to iterate through an ArrayList and simultaneously update each element by appending its length, then print the updated list.
Go to:
PREV : Create and Print ArrayList.
NEXT : Insert at First Position.
Java Code Editor:
Contribute your code and comments through Disqus.
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
Test your Programming skills with w3resource's quiz.
