Java Lambda expression - Check if string is empty
2. Check if a string is empty using lambda
Write a Java program to implement a lambda expression to check if a given string is empty.
Sample Solution:
Java Code:
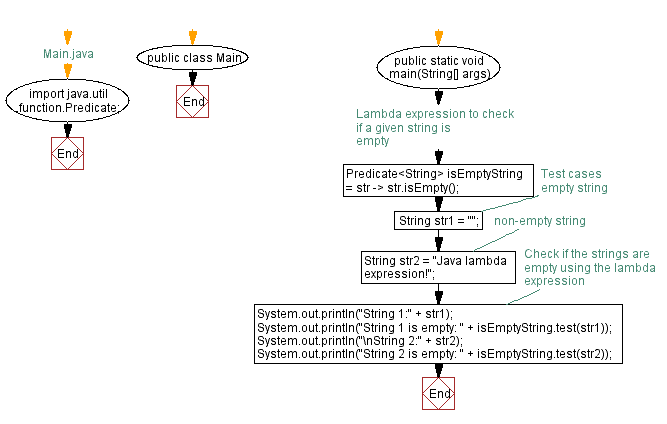
// Main.java
import java.util.function.Predicate;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Lambda expression to check if a given string is empty
Predicate isEmptyString = str -> str.isEmpty();
// Test cases
String str1 = ""; // empty string
String str2 = "Java lambda expression!"; // non-empty string
// Check if the strings are empty using the lambda expression
System.out.println("String 1:" + str1);
System.out.println("String 1 is empty: " + isEmptyString.test(str1));
System.out.println("\nString 2:" + str2);
System.out.println("String 2 is empty: " + isEmptyString.test(str2));
}
}
Sample Output:
String 1: String 1 is empty: true String 2:Java lambda expression! String 2 is empty: false
Explanation:
In the above exercise, we define a Predicate functional interface with a lambda expression to check if a given string is empty. The lambda expression uses the isEmpty() method of the String class to determine if the string is empty.
To check if the strings are empty, we create two test cases, str1 and str2, and use the test() method of the Predicate interface. On the console, the results are displayed.
Flowchart:
For more Practice: Solve these Related Problems:
- Write a Java program to implement a lambda expression that checks if a trimmed string is empty or contains only whitespace.
- Write a Java program to create a lambda that validates a list of strings, returning true only if all are empty.
- Write a Java program to implement a lambda expression that checks if a string is empty and, if so, returns a default message.
- Write a Java program to compose a lambda that verifies a string’s emptiness and logs an error if it is.
Go to:
PREV : Sum two integers using lambda expression.
NEXT : Convert strings to upper/lowercase using lambda.
Live Demo:
Java Code Editor:
Improve this sample solution and post your code through Disqus
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
Test your Programming skills with w3resource's quiz.
