Java Program: Lambda expression to convert integer to binary
25. Convert integer to binary using lambda
Write a Java program to implement a lambda expression to convert an integer to their corresponding binary representation.
Sample Solution:
Java Code:
import java.util.function.Function;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int n = 33;
System.out.println("Number: " + n);
Function < Integer, String > convertToBinary = num -> Integer.toBinaryString(num);
String binaryRepresentation = convertToBinary.apply(n);
System.out.println("Binary representation: " + binaryRepresentation);
n = 747;
System.out.println("\nNumber: " + n);
convertToBinary = num -> Integer.toBinaryString(num);
binaryRepresentation = convertToBinary.apply(n);
System.out.println("Binary representation: " + binaryRepresentation);
}
}
Sample Output:
Number: 33 Binary representation: 100001 Number: 747 Binary representation: 1011101011
Explanation:
In the above exercise the program uses the Integer.toBinaryString() method to convert an integer to its binary representation. The lambda expression allows you to encapsulate this conversion logic and use it as a function.
The lambda expression:
- It takes an integer as input (num).
- It uses the Integer.toBinaryString() method to convert the integer to its binary representation.
- It returns the binary representation as a string.
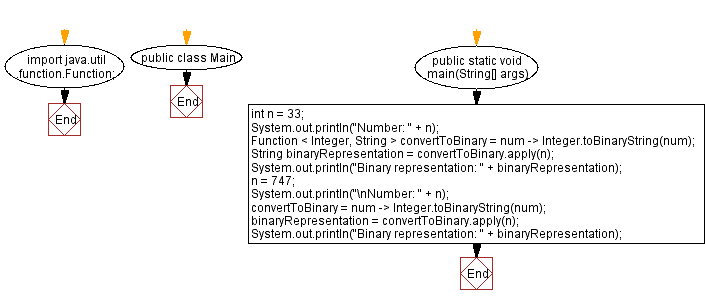
Flowchart:
For more Practice: Solve these Related Problems:
- Write a Java program to implement a lambda expression that converts an integer to a binary string using recursion.
- Write a Java program to create a lambda that converts a list of integers to their binary representations and collects them into a list.
- Write a Java program to implement a lambda expression that pads the binary representation of an integer to a fixed length.
- Write a Java program to chain lambda expressions to convert an integer to binary and then count the number of ones in the result.
Go to:
Improve this sample solution and post your code through Disqus
PREV : Find largest prime factor using lambda.
Live Demo:
Java Code Editor:
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
Test your Programming skills with w3resource's quiz.
