JavaScript: Find the Greatest Common Divisor or GCD of more than 2 integers
JavaScript Math: Exercise-9 with Solution
GCD of Multiple Numbers
Write a JavaScript function to find the GCD (greatest common divisor) of more than 2 integers.
Test Data:
console.log(gcd_more_than_two_numbers([3,15,27]));
console.log(gcd_more_than_two_numbers([5,10,15,25]));
Output :
3
5
Sample Solution:
JavaScript Code:
// Define a function named gcd_more_than_two_numbers that calculates the greatest common divisor (GCD) of an array of numbers.
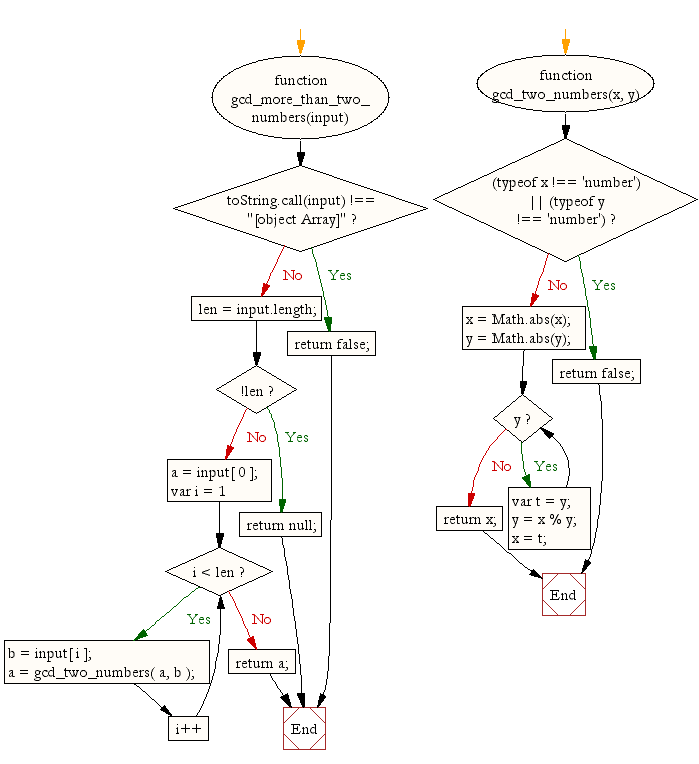
function gcd_more_than_two_numbers(input) {
// Check if the input is an array, if not, return false.
if (toString.call(input) !== "[object Array]")
return false;
var len, a, b;
len = input.length;
// If the array is empty, return null.
if (!len) {
return null;
}
// Set the initial value of a to the first element of the array.
a = input[0];
// Iterate through the array to find the GCD of all numbers.
for (var i = 1; i < len; i++) {
b = input[i];
// Call the gcd_two_numbers function to find the GCD of two numbers.
a = gcd_two_numbers(a, b);
}
// Return the final GCD.
return a;
}
// Define a function named gcd_two_numbers that calculates the GCD of two numbers.
function gcd_two_numbers(x, y) {
// Check if both x and y are of type number, if not, return false.
if ((typeof x !== 'number') || (typeof y !== 'number'))
return false;
// Take the absolute values of x and y to ensure positivity.
x = Math.abs(x);
y = Math.abs(y);
// Use the Euclidean algorithm to find the GCD.
while(y) {
var t = y;
y = x % y;
x = t;
}
// Return the GCD, which is stored in x after the loop.
return x;
}
// Output the GCD of the numbers 3, 15, and 27 to the console.
console.log(gcd_more_than_two_numbers([3, 15, 27]));
// Output the GCD of the numbers 5, 10, 15, and 25 to the console.
console.log(gcd_more_than_two_numbers([5, 10, 15, 25]));
Output:
3 5
Flowchart:
Live Demo:
See the Pen javascript-math-exercise-9 by w3resource (@w3resource) on CodePen.
For more Practice: Solve these Related Problems:
- Write a JavaScript function that calculates the GCD of an array of numbers by reducing them pairwise.
- Write a JavaScript function that recursively computes the GCD for more than two numbers using a helper function.
- Write a JavaScript function that iteratively finds the GCD of multiple numbers from a given array.
- Write a JavaScript function that handles non-integer values gracefully while computing the GCD of multiple numbers.
Go to:
PREV : GCD of Two Numbers.
NEXT : LCM of Two Numbers.
Improve this sample solution and post your code through Disqus.
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
Test your Programming skills with w3resource's quiz.
