JavaScript Exercises: Head and Tail of a Doubly Linked Lists
JavaScript Data Structures: Exercise-4 with Solution
Get the head and tail of a DLL
Write a JavaScript program to get the head and tail of a Doubly Linked Lists.
Sample Solution:
JavaScript Code:
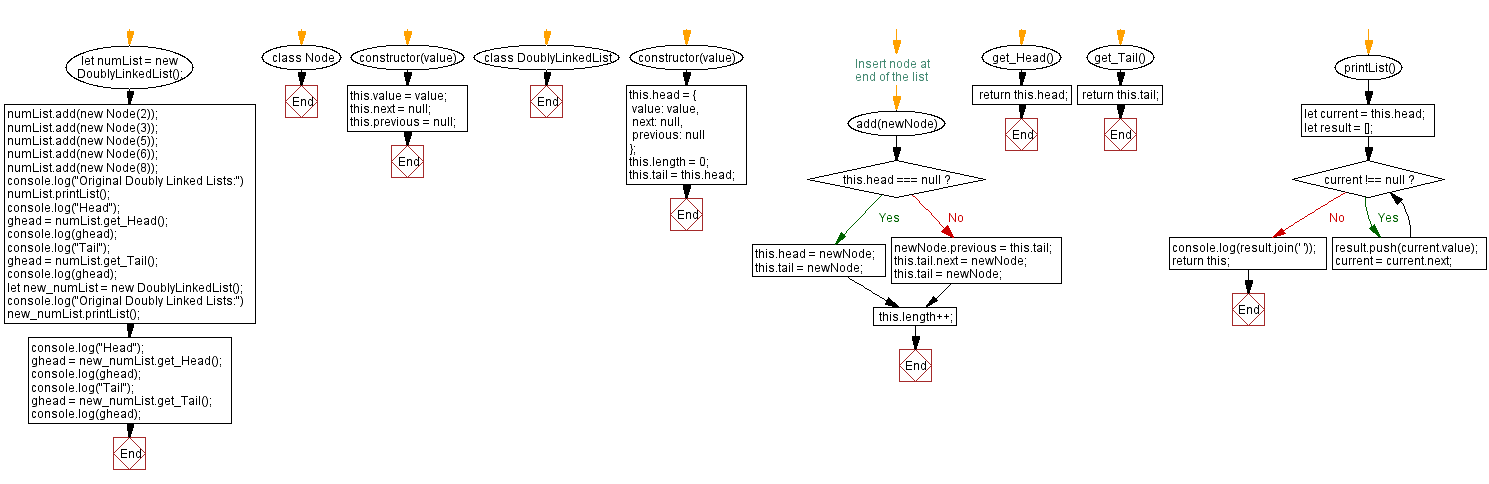
// Define a class for creating nodes of a doubly linked list
class Node {
constructor(value) {
this.value = value; // Store the value of the node
this.next = null; // Pointer to the next node in the list, initially set to null
this.previous = null; // Pointer to the previous node in the list, initially set to null
}
}
// Define a class for creating a doubly linked list
class DoublyLinkedList {
constructor(value) {
// Initialize the head node with the given value and no next or previous node
this.head = {
value: value, // Store the value of the head node
next: null, // Pointer to the next node in the list, initially set to null
previous: null // Pointer to the previous node in the list, initially set to null
};
this.length = 0; // Initialize the length of the list to 0
this.tail = this.head; // Set the tail node to the head node initially
}
// Method to add a new node at the end of the list
add(newNode) {
// Check if the head is null, indicating an empty list
if (this.head === null) {
this.head = newNode; // Set the head to the new node
this.tail = newNode; // Set the tail to the new node
} else {
newNode.previous = this.tail; // Set the previous pointer of the new node to the current tail
this.tail.next = newNode; // Set the next pointer of the current tail to the new node
this.tail = newNode; // Update the tail to the new node
}
this.length++; // Increment the length of the list
}
// Method to get the head node of the list
get_Head(){
return this.head; // Return the head node
}
// Method to get the tail node of the list
get_Tail(){
return this.tail; // Return the tail node
}
// Method to print the values of the nodes in the list
printList() {
let current = this.head; // Start from the head of the list
let result = []; // Array to store the values of the nodes
while (current !== null) { // Iterate through the list until reaching the end
result.push(current.value); // Push the value of the current node to the array
current = current.next; // Move to the next node
}
console.log(result.join(' ')); // Log the values of the nodes separated by space
return this; // Return the DoublyLinkedList object for chaining
}
}
// Create a new instance of the DoublyLinkedList class
let numList = new DoublyLinkedList();
// Add nodes to the list
numList.add(new Node(2));
numList.add(new Node(3));
numList.add(new Node(5));
numList.add(new Node(6));
numList.add(new Node(8));
// Display the original doubly linked list
console.log("Original Doubly Linked Lists:")
numList.printList();
// Get and display the head node of the list
console.log("Head");
let ghead = numList.get_Head();
console.log(ghead);
// Get and display the tail node of the list
console.log("Tail");
ghead = numList.get_Tail();
console.log(ghead);
// Create a new doubly linked list
let new_numList = new DoublyLinkedList();
console.log("Original Doubly Linked Lists:")
new_numList.printList();
// Get and display the head node of the new list
console.log("Head");
ghead = new_numList.get_Head();
console.log(ghead);
// Get and display the tail node of the new list
console.log("Tail");
ghead = new_numList.get_Tail();
console.log(ghead);
Output:
"Original Doubly Linked Lists:"
" 2 3 5 6 8"
"Head"
[object Object] {
next: [object Object] {
next: [object Object] { ... },
previous: [circular object Object],
value: 2
},
previous: null,
value: undefined
}
"Tail"
[object Object] {
next: null,
previous: [object Object] {
next: [circular object Object],
previous: [object Object] { ... },
value: 6
},
value: 8
}
"Original Doubly Linked Lists:"
""
"Head"
[object Object] {
next: null,
previous: null,
value: undefined
}
"Tail"
[object Object] {
next: null,
previous: null,
value: undefined
}
Flowchart:
Live Demo:
See the Pen javascript-doubly-linked-list-exercise-4 by w3resource (@w3resource) on CodePen.
For more Practice: Solve these Related Problems:
- Write a JavaScript function that retrieves the head and tail nodes of a doubly linked list and returns them as an object.
- Write a JavaScript function that logs the data of both the head and tail of a DLL after constructing it.
- Write a JavaScript function that traverses a DLL to confirm that the head's previous pointer is null and the tail's next pointer is null.
- Write a JavaScript function that creates a DLL and prints the values at the head and tail to verify correct pointer assignments.
Go to:
PREV : Check if a DLL is empty.
NEXT : Insert a new node at any position in a DLL.
Improve this sample solution and post your code through Disqus
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
Test your Programming skills with w3resource's quiz.
