JavaScript Exercises: Insert a new node at the end of a Singly Linked List
JavaScript Singly Linked List: Exercise-6 with Solution
Insert a node at the end of a SLL
Write a JavaScript program to insert a node at the end of a Singly Linked List.
Sample Solution:
JavaScript Code:
// Define a class representing a node in a singly linked list
class Node {
constructor(data) {
// Initialize the node with provided data
this.data = data
// Initialize the next pointer to null
this.next = null
}
}
// Define a class representing a singly linked list
class SinglyLinkedList {
constructor(Head = null) {
// Initialize the head of the list
this.Head = Head
}
// Method to add a new node to the end of the list
add(newNode){
// Start traversal from the head node
let node = this.Head;
// If the list is empty, set the new node as the head and return
if(node == null){
this.Head = newNode;
return;
}
// Traverse the list until the last node
while (node.next) {
node = node.next;
}
// Set the next pointer of the last node to the new node
node.next = newNode;
}
// Method to insert a new node at a specified index in the list
insertAt(index, newNode){
// Start traversal from the head node
let node = this.Head;
// If the specified index is 0, insert the new node at the beginning of the list
if(index == 0) {
newNode.next = node;
this.Head = newNode;
return;
}
// Traverse the list until the node just before the specified index
while(--index){
// If the next node exists, move to the next node
if(node.next !== null)
node = node.next;
// If the next node does not exist and the index is not reached, throw an error
else
throw Error("Index Out of Bound");
}
// Store the next node of the current node in a temporary variable
let tempVal = node.next;
// Set the next pointer of the current node to the new node
node.next = newNode;
// Set the next pointer of the new node to the previously stored next node
newNode.next = tempVal;
}
// Method to insert a new node at the last position of the list
insertLast(value) {
// Call the insertAt method with the size of the list as the index to insert the node at the last position
this.insertAt(this.size(), value);
}
// Method to get the size of the list
size() {
let ctr = 0;
let node = this.Head;
// Traverse the list and increment the counter for each node
while (node) {
ctr++;
node = node.next;
}
return ctr;
}
// Method to display the elements of the list
displayList(){
// Start traversal from the head node
let node = this.Head;
// Initialize an empty string to store the elements of the list
var str = ""
// Traverse the list and concatenate each element to the string
while (node) {
str += node.data + "->";
node = node.next;
}
// Append "NULL" to indicate the end of the list
str += "NULL"
// Print the string containing the list elements
console.log(str);
}
}
// Create an instance of the SinglyLinkedList class
let numList = new SinglyLinkedList();
// Add nodes with data values to the list
numList.add(new Node(12));
numList.add(new Node(13));
numList.add(new Node(14));
numList.add(new Node(15));
// Display the original elements of the list
console.log("Original Linked list:");
numList.displayList();
// Insert a new node with data value 200 at the last position of the list
console.log("Insert 200 at last position:");
numList.insertLast(new Node(200));
numList.displayList();
// Insert a new node with data value 20 at the last position of the list
console.log("Insert 20 at last position:");
numList.insertLast(new Node(20));
numList.displayList();
Output:
12->13->14->15->NULL Insert 200 at last position: 12->13->14->15->200->NULL Insert 20 at last position: 12->13->14->15->200->20->NULL
Flowchart:
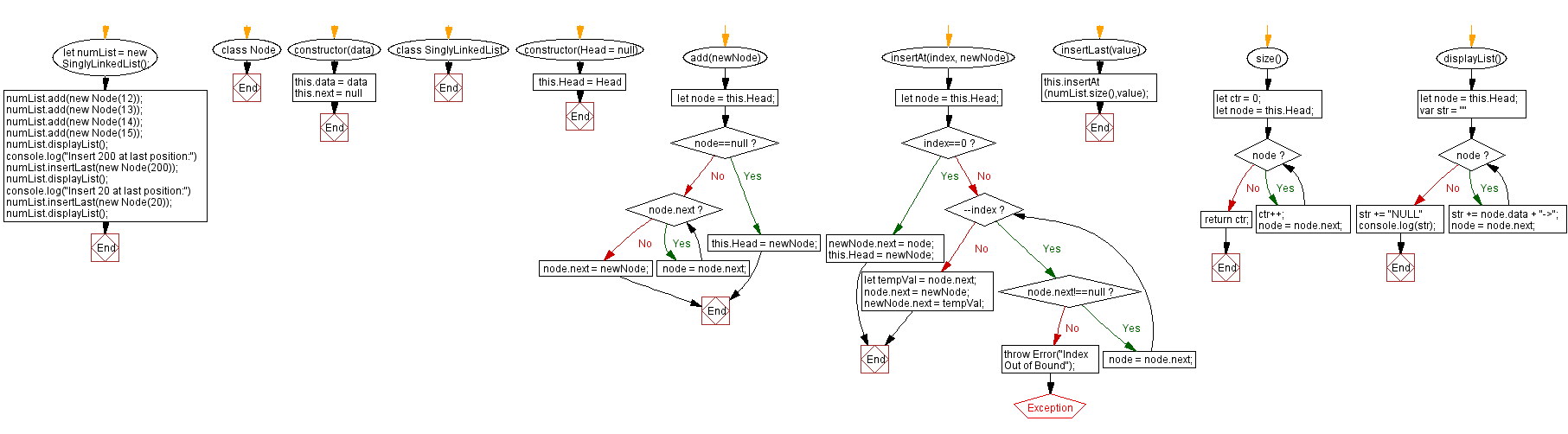
Live Demo:
See the Pen javascript-singly-linked-list-exercise-6 by w3resource (@w3resource) on CodePen.
For more Practice: Solve these Related Problems:
- Write a JavaScript function that appends a node to the end of a singly linked list by traversing the list.
- Write a JavaScript function that recursively finds the tail of a singly linked list and inserts a node there.
- Write a JavaScript function that inserts a node at the end of a singly linked list and returns the updated list.
- Write a JavaScript function that handles tail insertion in an empty singly linked list by initializing the head.
Go to:
PREV : Insert a node at the beginning of a SLL.
NEXT : Get a node in a SLL.
Improve this sample solution and post your code through Disqus
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
Test your Programming skills with w3resource's quiz.
