Python Data Structures and Algorithms - Recursion: Sum of a list of numbers
1. Sum of List Using Recursion
Write a Python program to calculate the sum of a list of numbers using recursion.
Sample Solution:
Python Code:
# Define a function named list_sum that takes a list of numbers as input
def list_sum(num_List):
# Check if the length of the input list is 1
if len(num_List) == 1:
# If the list has only one element, return that element
return num_List[0]
else:
# If the list has more than one element, return the sum of the first element
# and the result of recursively calling the list_sum function on the rest of the list
return num_List[0] + list_sum(num_List[1:])
# Print the result of calling the list_sum function with the input [2, 4, 5, 6, 7]
print(list_sum([2, 4, 5, 6, 7]))
Sample Output:
24
Flowchart:
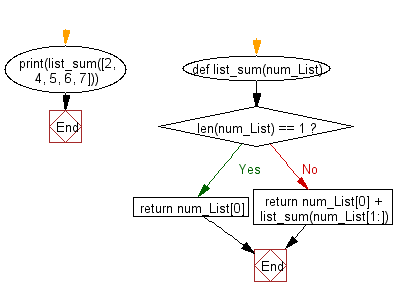
For more Practice: Solve these Related Problems:
- Write a Python program to recursively compute the sum of numbers in a list using slicing.
- Write a Python program to implement tail recursion to sum a list of integers without using loops.
- Write a Python program to calculate the sum of a list of numbers recursively and print each intermediate sum.
- Write a Python program to recursively reduce a list by summing its first element with the sum of the remaining elements.
Go to:
Previous: Python Recursion Exercise Home.
Next: Write a Python program to converting an integer to a string in any base.
Python Code Editor:
Contribute your code and comments through Disqus.
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
Test your Programming skills with w3resource's quiz.
