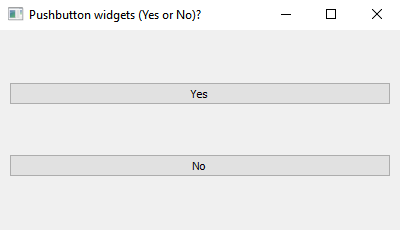
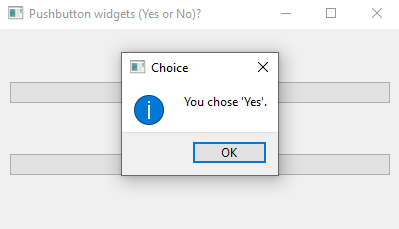
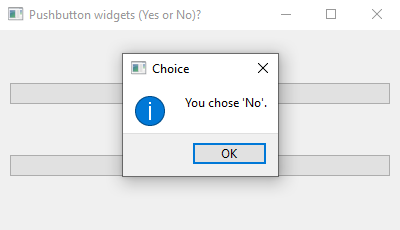
Python PyQt program - Yes or No buttons
Write a Python program that builds an application with two buttons "Yes" and "No" using PyQt. When the user clicks a button, display a message box with the corresponding choice.
From doc.qt.io:
QApplication Class: The QApplication class manages the GUI application's control flow and main settings.
QMainWindow Class: The QMainWindow class provides a main application window.
QPushButton: The push button, or command button, is perhaps the most commonly used widget in any graphical user interface. Push (click) a button to command the computer to perform some action, or to answer a question. Typical buttons are OK, Apply, Cancel, Close, Yes, No and Help.
QMessageBox Class: The QMessageBox class provides a modal dialog for informing the user or for asking the user a question and receiving an answer.
QVBoxLayout Class: The QVBoxLayout class lines up widgets vertically.
QWidget: The QWidget class is the base class of all user interface objects.
Sample Solution:
Python Code:
import sys
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QApplication, QMainWindow, QPushButton, QMessageBox, QVBoxLayout, QWidget
class YesNoApp(QMainWindow):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
# Set the window properties (title and initial size)
self.setWindowTitle("Pushbutton widgets (Yes or No)?")
self.setGeometry(100, 100, 400, 200) # (x, y, width, height)
# Create a central widget for the main window
central_widget = QWidget()
self.setCentralWidget(central_widget)
# Create QPushButton widgets for "Yes" and "No"
yes_button = QPushButton("Yes")
no_button = QPushButton("No")
# Connect button clicks to corresponding methods
yes_button.clicked.connect(self.show_yes_message)
no_button.clicked.connect(self.show_no_message)
# Create a layout for the central widget and add the buttons
layout = QVBoxLayout()
layout.addWidget(yes_button)
layout.addWidget(no_button)
# Set the layout for the central widget
central_widget.setLayout(layout)
def show_yes_message(self):
QMessageBox.information(self, "Choice", "You chose 'Yes'.")
def show_no_message(self):
QMessageBox.information(self, "Choice", "You chose 'No'.")
def main():
app = QApplication(sys.argv)
window = YesNoApp()
window.show()
sys.exit(app.exec_())
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
Explanation:
In the exercise above -
- Import the necessary modules.
- Create a "QMainWindow" named YesNoApp.
- Set the window's title and initial size.
- Create a central widget and set it as the central widget of the main window.
- Create "QPushButton" widgets for "Yes" and "No."
- Connect the button clicks to methods "show_yes_message()" and "show_no_message()", which will display message boxes with the corresponding choice when the buttons are clicked.
- Create a 'QVBoxLayout' for the central widget, add the buttons to it, and set it as the layout for the central widget.
- The "show_yes_message()" and "show_no_message()" methods use 'QMessageBox.information' to display message boxes with the user's choice.
- In the main function, we create the PyQt application, create an instance of the "YesNoApp" class, show the window, and run the application's event loop.
Output:
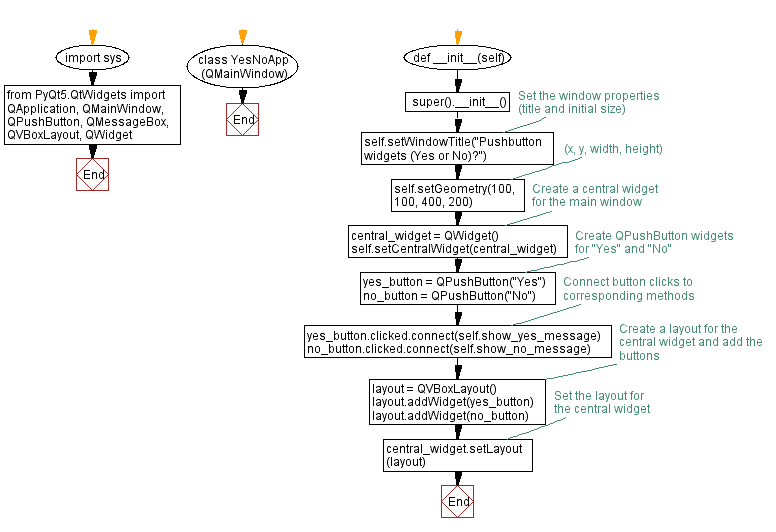
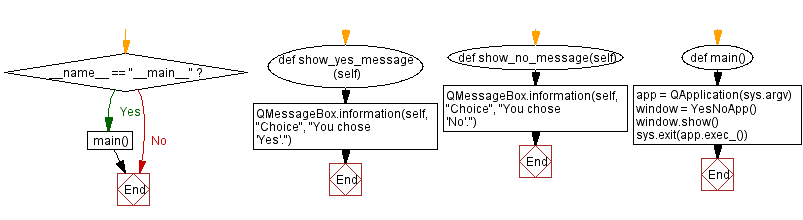
Flowchart:
Go to:
Previous: Display Hello, PyQt!.
Next: Simple text editor.
Python Code Editor:
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
Test your Programming skills with w3resource's quiz.