Python Exercise: Get Fizz, Buzz and FizzBuzz
10. FizzBuzz Variation
Write a Python program that iterates through integers from 1 to 50. For each multiple of three, print "Fizz" instead of the number; for each multiple of five, print "Buzz". For numbers that are multiples of both three and five, print "FizzBuzz".
The FizzBuzz problem is a common coding challenge that is often used in programming interviews to test basic programming skills. The problem typically requires writing a function that prints numbers from 1 to a given limit, but with a twist:
- For multiples of 3, print "Fizz" instead of the number.
- For multiples of 5, print "Buzz" instead of the number.
- For numbers which are multiples of both 3 and 5, print "FizzBuzz".
This problem helps assess the ability to use conditionals, loops, and modulus operations effectively.
Sample Solution:
Python Code:
# Iterate through numbers from 0 to 50 using the range function
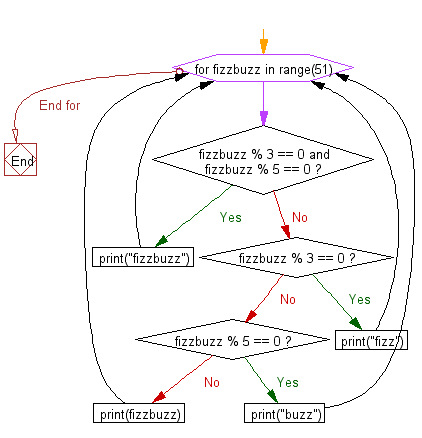
for fizzbuzz in range(51):
# Check if the current number is divisible by both 3 and 5 (i.e., divisible by 15)
if fizzbuzz % 3 == 0 and fizzbuzz % 5 == 0:
# If divisible by both 3 and 5, print "fizzbuzz" and continue to the next iteration
print("fizzbuzz")
continue
# Check if the current number is divisible only by 3
elif fizzbuzz % 3 == 0:
# If divisible only by 3, print "fizz" and continue to the next iteration
print("fizz")
continue
# Check if the current number is divisible only by 5
elif fizzbuzz % 5 == 0:
# If divisible only by 5, print "buzz" and continue to the next iteration
print("buzz")
continue
# If the number is neither divisible by 3 nor 5, print the number itself
print(fizzbuzz)
Flowchart:
Example: Customize the range and add input validation
This example allows users to specify any range of numbers for the FizzBuzz evaluation and provides basic input validation to ensure the start number is less than or equal to the end number.
Code:
def fizz_buzz(start, end):
"""
Print 'Fizz', 'Buzz', or 'FizzBuzz' for numbers in the specified range based on divisibility rules.
Parameters:
start (int): The starting number of the range.
end (int): The ending number of the range.
"""
if start > end:
print("Start should be less than or equal to end.")
return
for fizzbuzz in range(start, end + 1):
if fizzbuzz % 3 == 0 and fizzbuzz % 5 == 0:
print("FizzBuzz")
elif fizzbuzz % 3 == 0:
print("Fizz")
elif fizzbuzz % 5 == 0:
print("Buzz")
else:
print(fizzbuzz)
# Example usage
print("From 1 to 10")
fizz_buzz(1, 10)
print("\nFrom 50 to 75")
fizz_buzz(50, 75)
Output:
From 1 to 10 1 2 Fizz 4 Buzz Fizz 7 8 Fizz Buzz From 50 to 75 Buzz Fizz 52 53 Fizz Buzz 56 Fizz ....... 68 Fizz Buzz 71 Fizz 73 74 FizzBuzz
FizzBuzz Problem - Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the FizzBuzz problem?
The FizzBuzz problem is a common coding interview question that tests basic programming skills and logic. The task is to write a program that prints numbers from 1 to a specified limit, but for multiples of three, it prints "Fizz" instead of the number, for multiples of five, it prints "Buzz", and for numbers which are multiples of both three and five, it prints "FizzBuzz".
2. Why is the FizzBuzz problem popular in interviews?
The FizzBuzz problem is popular because it is simple yet effective in assessing a candidate's ability to implement basic control flow structures like loops and conditionals. It also helps interviewers see if the candidate can handle multiple conditions and edge cases.
3. What are the basic requirements to solve the FizzBuzz problem?
To solve the FizzBuzz problem, you need to:
- Loop through a range of numbers.
- Check if each number is divisible by 3, 5, or both.
- Print "Fizz" for numbers divisible by 3.
- Print "Buzz" for numbers divisible by 5.
- Print "FizzBuzz" for numbers divisible by both 3 and 5.
- Print the number itself if it is not divisible by either 3 or 5.
4. What are some common mistakes to avoid when solving the FizzBuzz problem?
Common mistakes include:
- Forgot to check the condition for "FizzBuzz" (multiples of both 3 and 5) first.
- Incorrectly using equality operators instead of modulus operators to check divisibility.
- Not handling the full range of numbers specified in the problem.
5. Can the FizzBuzz problem be solved using different programming paradigms?
Yes, the FizzBuzz problem can be solved using different paradigms such as:
- Imperative Programming: Using loops and conditionals.
- Functional Programming: Using higher-order functions like map, filter, and lambda expressions.
- Declarative Programming: Using list comprehensions or similar constructs.
6. How can the FizzBuzz problem be extended for more advanced practice?
Advanced extensions of the FizzBuzz problem can include:
- Changing the conditions to use different divisors.
- Outputting different strings for different conditions.
- Handling more complex combinations of conditions.
- Implementing the solution in a less conventional programming language.
- Optimizing the solution for performance and readability.
7. Why is it important to handle edge cases in the FizzBuzz problem?
Handling edge cases ensures that your solution is robust and can handle unexpected input gracefully. For instance, you need to ensure that the program correctly handles small ranges (like 1 to 1) or large ranges, and that it prints nothing if the range is invalid.
8. What is the significance of the modulus operator in the FizzBuzz problem?
The modulus operator (%) is significant because it helps determine if a number is divisible by another number. In the context of FizzBuzz, it is used to check if a number is divisible by 3 (num % 3 0), by 5 (num % 5 0), or by both 3 and 5 (num % 15 == 0).9. How can you test your FizzBuzz solution?
You can test your FizzBuzz solution by:
- Running the program with a small range of numbers to manually verify the output.
- Writing automated tests that check the output for known inputs.
- Using a variety of input ranges to ensure the program handles all cases correctly.
For more Practice: Solve these Related Problems:
- Write a Python program to iterate numbers from 1 to 50 and print "Fizz" for multiples of 3, "Buzz" for multiples of 5, and "FizzBuzz" for both.
- Write a Python program to implement FizzBuzz using a single line of code with list comprehension.
- Write a Python program to modify FizzBuzz so that it returns a list of strings for numbers 1 to 50.
- Write a Python program to implement FizzBuzz with user-defined multiples instead of 3 and 5.
Go to:
Previous: Write a Python program to get the Fibonacci series between 0 to 50.
Next: Write a Python program which takes two digits m (row) and n (column) as input and generates a two-dimensional array. The element value in the i-th row and j-th column of the array should be i*j.
Python Code Editor :
Have another way to solve this solution? Contribute your code (and comments) through Disqus.
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
Test your Programming skills with w3resource's quiz.
