Python: Add a prefix text to all of the lines in a string
Add prefix to each line of text.
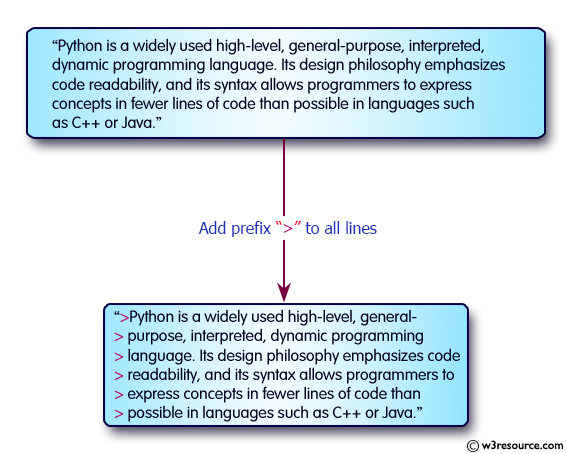
Write a Python program to add prefix text to all of the lines in a string.
Sample Solution:
Python Code:
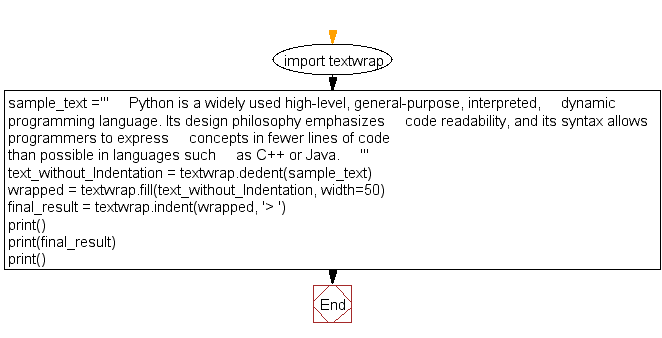
# Import the 'textwrap' module, which provides text formatting capabilities.
import textwrap
# Define a multi-line string 'sample_text' with text content that includes indentation.
sample_text = '''
Python is a widely used high-level, general-purpose, interpreted,
dynamic programming language. Its design philosophy emphasizes
code readability, and its syntax allows programmers to express
concepts in fewer lines of code than possible in languages such
as C++ or Java.
'''
# Use 'textwrap.dedent' to remove the common leading whitespace (indentation) from 'sample_text'.
text_without_Indentation = textwrap.dedent(sample_text)
# Print an empty line for spacing.
print()
# Print the 'text_without_Indentation', which is the 'sample_text' with indentation removed.
print(text_without_Indentation)
# Print an empty line for spacing.
print()
Sample Output:
> Python is a widely used high-level, general- > purpose, interpreted, dynamic programming > language. Its design philosophy emphasizes code > readability, and its syntax allows programmers to > express concepts in fewer lines of code than > possible in languages such as C++ or Java.
Flowchart:
For more Practice: Solve these Related Problems:
- Write a Python program to prepend a given prefix to every line in a multi-line string.
- Write a Python program to split a text into lines, add a prefix to each, and rejoin them with newline characters.
- Write a Python program to use map() to add a custom prefix to each line of an input string.
- Write a Python program to implement a function that takes a prefix and a text, and returns the text with the prefix added to every line.
Go to:
Previous: Write a Python program to remove existing indentation from all of the lines in a given text.
Next: Write a Python program to set the indentation of the first line.
Python Code Editor:
Contribute your code and comments through Disqus.
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
Test your Programming skills with w3resource's quiz.
