Python: Capitalize first and last letters of each word of a given string
Capitalize first and last letters of words.
Write a Python program to capitalize the first and last letters of each word in a given string.
Visual Presentation:
Sample Solution-1:
Python Code:
# Define a function 'capitalize_first_last_letters' that takes a string 'str1' as input.
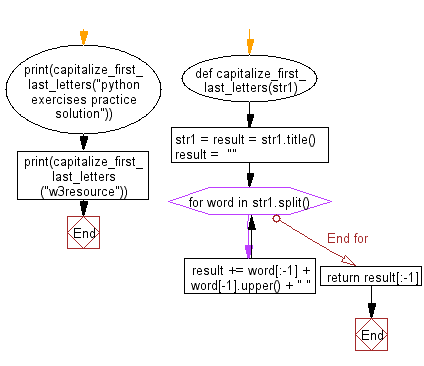
def capitalize_first_last_letters(str1):
# Capitalize the first letter of each word and store the result in 'str1' and 'result'.
str1 = result = str1.title()
# Initialize an empty string 'result' to store the final result.
result = ""
# Split the 'str1' into words and iterate through each word.
for word in str1.split():
# Append the word with the last letter capitalized to the 'result' string, followed by a space.
result += word[:-1] + word[-1].upper() + " "
# Remove the trailing space and return the modified string.
return result[:-1]
# Call the 'capitalize_first_last_letters' function with different input strings and print the results.
print(capitalize_first_last_letters("python exercises practice solution"))
print(capitalize_first_last_letters("w3resource"))
Sample Output:
PythoN ExerciseS PracticE SolutioN W3ResourcE
Flowchart:
Sample Solution-2:
Capitalizes the first letter of a string.
- Use list slicing and str.upper() to capitalize the first letter of the string.
- Use str.join() to combine the capitalized first letter with the rest of the characters.
- Omit the lower_rest parameter to keep the rest of the string intact, or set it to True to convert to lowercase.
Python Code:
# Define a function 'capitalize_first_letter' that takes a string 's' as input.
# The 'lower_rest' parameter determines whether the rest of the string should be in lowercase.
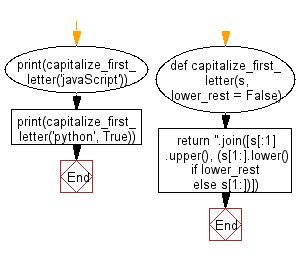
def capitalize_first_letter(s, lower_rest=False):
# Create a new string by joining the following components:
# 1. The first character of the input string 's' capitalized using '.upper()'.
# 2. The rest of the string in lowercase (if 'lower_rest' is True) or as is (if 'lower_rest' is False).
return ''.join([s[:1].upper(), (s[1:].lower() if lower_rest else s[1:])])
# Call the 'capitalize_first_letter' function with different input strings and 'lower_rest' values.
print(capitalize_first_letter('javaScript'))
print(capitalize_first_letter('python', True))
Sample Output:
JavaScript Python
Flowchart:
For more Practice: Solve these Related Problems:
- Write a Python program to capitalize the first and last letters of each word in a sentence using split and join methods.
- Write a Python program to iterate over words in a string and transform each by capitalizing the first and last characters.
- Write a Python program to use list comprehension to modify each word so that its first and last letters are in uppercase.
- Write a Python program to implement this transformation using slicing and conditional expressions for words of varying lengths.
Go to:
Previous: Write a Python program to find the maximum occuring character in a given string.
Next: Write a Python program to remove duplicate characters of a given string.
Python Code Editor:
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
Test your Programming skills with w3resource's quiz.
