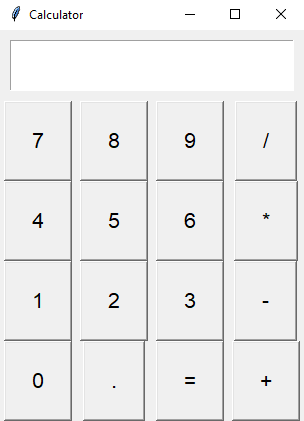
Build a Python calculator interface with Tkinter's grid manager
Write a Python program that develops a calculator interface with buttons for digits and operators, arranging them in a grid.
Sample Solution:
Python Code:
import tkinter as tk
# Function to update the calculator display
def update_display(value):
current_text = display.get()
new_text = current_text + value
display.set(new_text)
# Function to calculate and display the result
def calculate_result():
try:
result = eval(display.get())
display.set(str(result))
except Exception as e:
display.set("Error")
# Function to clear the calculator display
def clear_display():
display.set("")
# Create the main Tkinter window
parent = tk.Tk()
parent.title("Calculator")
# Create a StringVar to store the display value
display = tk.StringVar()
display.set("")
# Create the calculator display Entry widget
display_entry = tk.Entry(parent, textvariable=display, font=("Arial", 18), justify="right")
display_entry.grid(row=0, column=0, columnspan=4, padx=10, pady=10, ipadx=10, ipady=10)
# Define the button labels for digits, operators, and special functions
button_labels = [
'7', '8', '9', '/',
'4', '5', '6', '*',
'1', '2', '3', '-',
'0', '.', '=', '+'
]
# Create and arrange the buttons in a grid
row_val = 1
col_val = 0
for label in button_labels:
if label == '=':
tk.Button(parent, text=label, padx=20, pady=20, font=("Arial", 16), command=calculate_result).grid(row=row_val, column=col_val)
elif label == 'C':
tk.Button(parent, text=label, padx=20, pady=20, font=("Arial", 16), command=clear_display).grid(row=row_val, column=col_val)
else:
tk.Button(parent, text=label, padx=20, pady=20, font=("Arial", 16), command=lambda l=label: update_display(l)).grid(row=row_val, column=col_val)
col_val += 1
if col_val > 3:
col_val = 0
row_val += 1
# Run the Tkinter main loop
parent.mainloop()
Explanation:
In the exercise above -
- Import the 'tkinter' module as 'tk'.
- Create the main Tkinter window using tk.Tk() and set its title to "Calculator."
- Use a "StringVar" named display to store the current display value, initially set to an empty string.
- Create an "Entry" widget (display_entry) to display the calculator's input and output. The textvariable option is set to display to link it with the StringVar.
- Define functions for updating the display (update_display()), calculating the result (calculate_result()), and clearing the display (clear_display()).
- Next define button labels for digits (0-9), operators (+, -, *, /), decimal point (.), equals sign (=), and clear (C).
- Create buttons for each label and arrange them in a grid layout using loops. When a button is clicked, it performs the desired action.
- Finally, root.mainloop() starts the Tkinter main loop, which keeps the GUI application running and displays a grid of buttons as the calculator interface.
Sample Output:
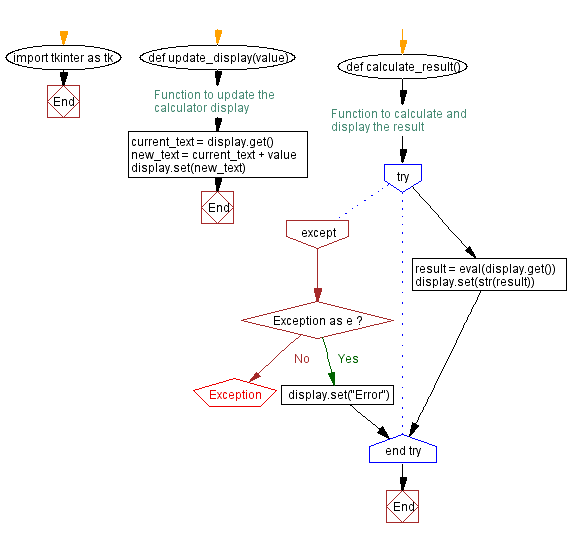
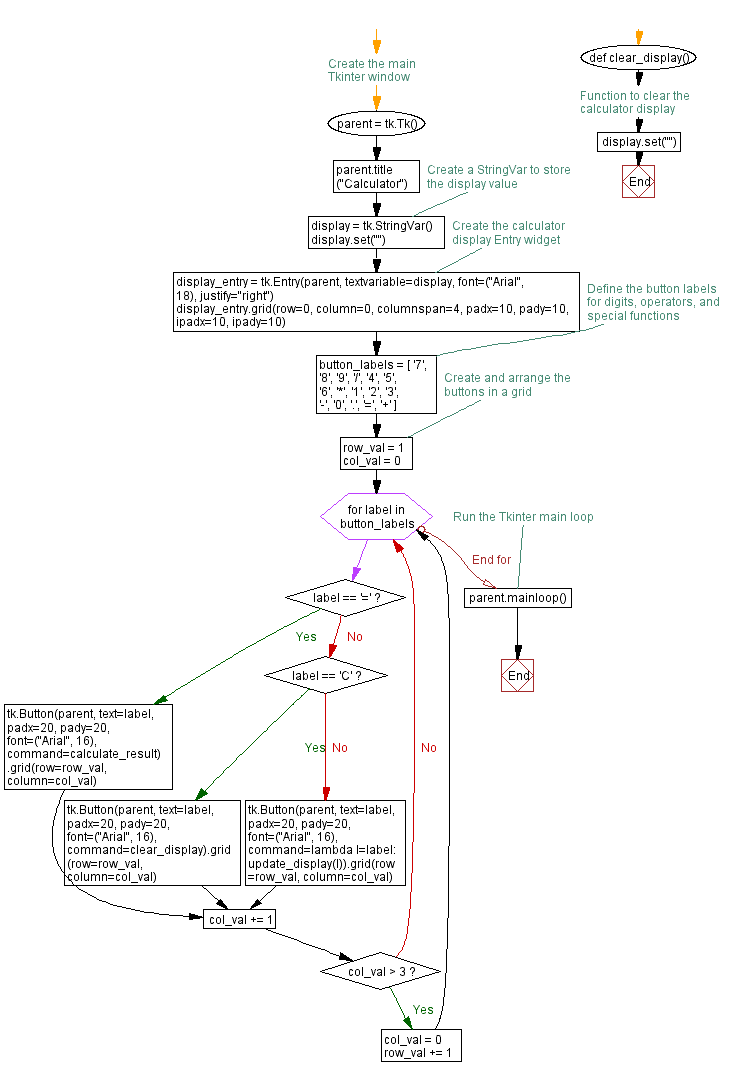
Flowchart:
Go to:
Previous: Create a Python login form with Tkinter's grid manager.
Next: Build a Tkinter window with frame and place manager in Python.
Python Code Editor:
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
Test your Programming skills with w3resource's quiz.