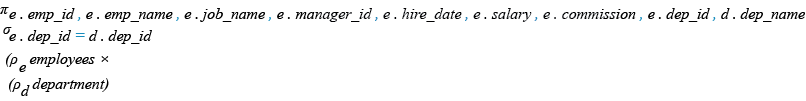SQL Exercise: List the employees along with department name
[An editor is available at the bottom of the page to write and execute the scripts.]
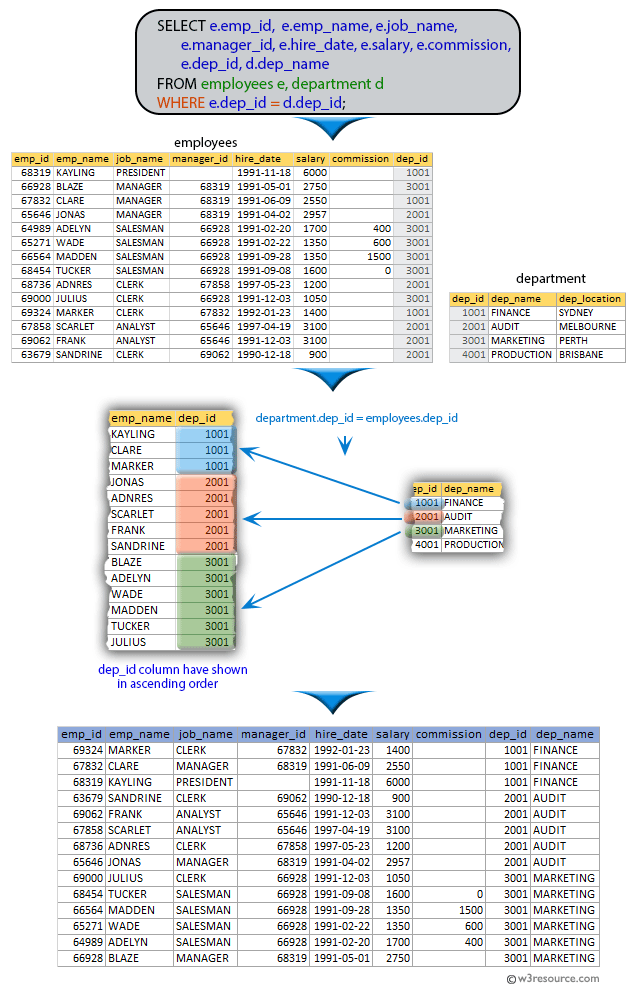
52. From the following table, write a SQL query to find employees along with their department details. Return employee ID, employee name, job name, manager ID, hire date, salary, commission, department ID, and department name.
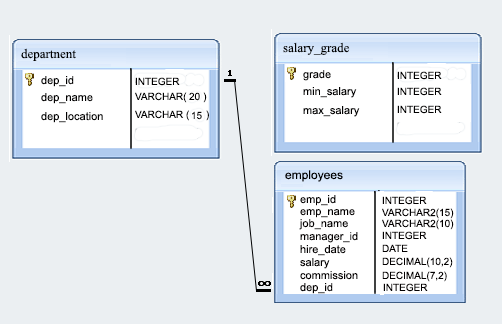
Sample table: employees
+-------------+-------------+-------------+----------+--------------------+------------+------------+----------+----------------+------------+---------------+ | EMPLOYEE_ID | FIRST_NAME | LAST_NAME | EMAIL | PHONE_NUMBER | HIRE_DATE | JOB_ID | SALARY | COMMISSION_PCT | MANAGER_ID | DEPARTMENT_ID | +-------------+-------------+-------------+----------+--------------------+------------+------------+----------+----------------+------------+---------------+ | 100 | Steven | King | SKING | 515.123.4567 | 2003-06-17 | AD_PRES | 24000.00 | 0.00 | 0 | 90 | | 101 | Neena | Kochhar | NKOCHHAR | 515.123.4568 | 2005-09-21 | AD_VP | 17000.00 | 0.00 | 100 | 90 | | 102 | Lex | De Haan | LDEHAAN | 515.123.4569 | 2001-01-13 | AD_VP | 17000.00 | 0.00 | 100 | 90 | | 103 | Alexander | Hunold | AHUNOLD | 590.423.4567 | 2006-01-03 | IT_PROG | 9000.00 | 0.00 | 102 | 60 | | 104 | Bruce | Ernst | BERNST | 590.423.4568 | 2007-05-21 | IT_PROG | 6000.00 | 0.00 | 103 | 60 | | 105 | David | Austin | DAUSTIN | 590.423.4569 | 2005-06-25 | IT_PROG | 4800.00 | 0.00 | 103 | 60 | | 106 | Valli | Pataballa | VPATABAL | 590.423.4560 | 2006-02-05 | IT_PROG | 4800.00 | 0.00 | 103 | 60 | | 107 | Diana | Lorentz | DLORENTZ | 590.423.5567 | 2007-02-07 | IT_PROG | 4200.00 | 0.00 | 103 | 60 | | 108 | Nancy | Greenberg | NGREENBE | 515.124.4569 | 2002-08-17 | FI_MGR | 12008.00 | 0.00 | 101 | 100 | | 109 | Daniel | Faviet | DFAVIET | 515.124.4169 | 2002-08-16 | FI_ACCOUNT | 9000.00 | 0.00 | 108 | 100 | ......... | 206 | William | Gietz | WGIETZ | 515.123.8181 | 2002-06-07 | AC_ACCOUNT | 8300.00 | 0.00 | 205 | 110 | +-------------+-------------+-------------+----------+--------------------+------------+------------+----------+----------------+------------+---------------+
Sample table: department
departmentid | name | head
--------------+------------------+------
1 | General Medicine | 4
2 | Surgery | 7
3 | Psychiatry | 9
Pictorial Presentation:
Sample Solution:
SELECT e.emp_id,
e.emp_name,
e.job_name,
e.manager_id,
e.hire_date,
e.salary,
e.commission,
e.dep_id,
d.dep_name
FROM employees e,
department d
WHERE e.dep_id = d.dep_id;
Sample Output:
emp_id | emp_name | job_name | manager_id | hire_date | salary | commission | dep_id | dep_name --------+----------+-----------+------------+------------+---------+------------+--------+---------- 68319 | KAYLING | PRESIDENT | | 1991-11-18 | 6000.00 | | 1001 | FINANCE 66928 | BLAZE | MANAGER | 68319 | 1991-05-01 | 2750.00 | | 3001 | MARKETING 67832 | CLARE | MANAGER | 68319 | 1991-06-09 | 2550.00 | | 1001 | FINANCE 65646 | JONAS | MANAGER | 68319 | 1991-04-02 | 2957.00 | | 2001 | AUDIT 67858 | SCARLET | ANALYST | 65646 | 1997-04-19 | 3100.00 | | 2001 | AUDIT 69062 | FRANK | ANALYST | 65646 | 1991-12-03 | 3100.00 | | 2001 | AUDIT 63679 | SANDRINE | CLERK | 69062 | 1990-12-18 | 900.00 | | 2001 | AUDIT 64989 | ADELYN | SALESMAN | 66928 | 1991-02-20 | 1700.00 | 400.00 | 3001 | MARKETING 65271 | WADE | SALESMAN | 66928 | 1991-02-22 | 1350.00 | 600.00 | 3001 | MARKETING 66564 | MADDEN | SALESMAN | 66928 | 1991-09-28 | 1350.00 | 1500.00 | 3001 | MARKETING 68454 | TUCKER | SALESMAN | 66928 | 1991-09-08 | 1600.00 | 0.00 | 3001 | MARKETING 68736 | ADNRES | CLERK | 67858 | 1997-05-23 | 1200.00 | | 2001 | AUDIT 69000 | JULIUS | CLERK | 66928 | 1991-12-03 | 1050.00 | | 3001 | MARKETING 69324 | MARKER | CLERK | 67832 | 1992-01-23 | 1400.00 | | 1001 | FINANCE (14 rows)
Explanation:
The said statement in SQL that selects the employee ID, employee name, job name, manager ID, hire date, salary, commission, department ID, and department name for all employees in the employees table who belong to a department that exists in the department table.
An inner join happens to combine the data from the tables employees and department based on the dep_id column, which is common to both tables. This allows the query to match up each employee with their corresponding department based on the department ID.
The WHERE clause checks whether the dep_id column in the employees table matches the dep_id column in the department table.
Using aliases e and d can make the query easier to read and write by shortening the table names and reducing repetition.
Relational Algebra Expression:
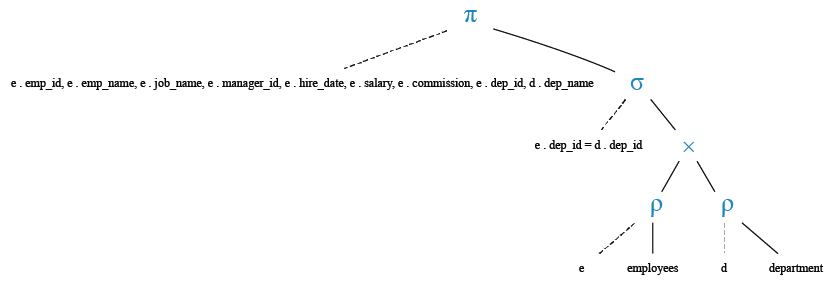
Relational Algebra Tree:
Go to:
PREV : List all the employees who joined before or after 1991.
NEXT : Employees earning 60000 or not working as analysts.
Practice Online
Sample Database: employees
Have another way to solve this solution? Contribute your code (and comments) through Disqus.
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
Test your Programming skills with w3resource's quiz.