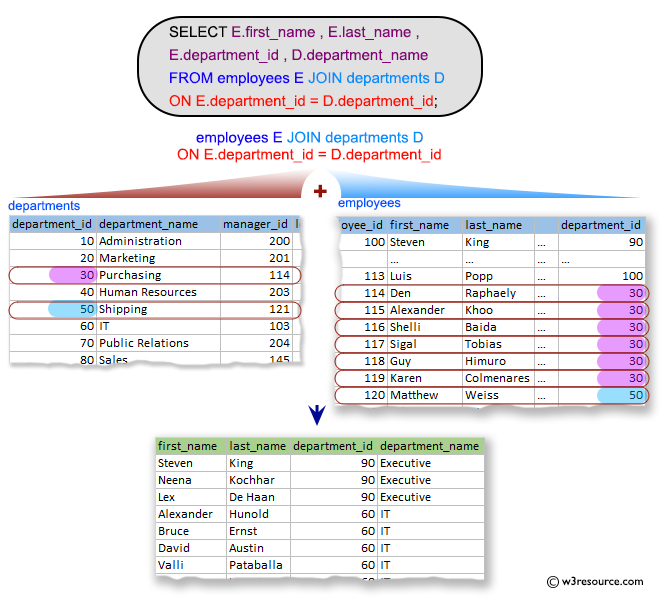
SQL Exercise: Display the name, department number, for each employee
1. From the following tables, write a SQL query to find the first name, last name, department number, and department name for each employee.
Sample table: departments
+---------------+----------------------+------------+-------------+ | DEPARTMENT_ID | DEPARTMENT_NAME | MANAGER_ID | LOCATION_ID | +---------------+----------------------+------------+-------------+ | 10 | Administration | 200 | 1700 | | 20 | Marketing | 201 | 1800 | | 30 | Purchasing | 114 | 1700 | | 40 | Human Resources | 203 | 2400 | | 50 | Shipping | 121 | 1500 | | 60 | IT | 103 | 1400 | | 70 | Public Relations | 204 | 2700 | | 80 | Sales | 145 | 2500 | | 90 | Executive | 100 | 1700 | | 100 | Finance | 108 | 1700 | ...... | 270 | Payroll | 0 | 1700 | +---------------+----------------------+------------+-------------+
Sample table: employees
+-------------+-------------+-------------+----------+--------------------+------------+------------+----------+----------------+------------+---------------+ | EMPLOYEE_ID | FIRST_NAME | LAST_NAME | EMAIL | PHONE_NUMBER | HIRE_DATE | JOB_ID | SALARY | COMMISSION_PCT | MANAGER_ID | DEPARTMENT_ID | +-------------+-------------+-------------+----------+--------------------+------------+------------+----------+----------------+------------+---------------+ | 100 | Steven | King | SKING | 515.123.4567 | 2003-06-17 | AD_PRES | 24000.00 | 0.00 | 0 | 90 | | 101 | Neena | Kochhar | NKOCHHAR | 515.123.4568 | 2005-09-21 | AD_VP | 17000.00 | 0.00 | 100 | 90 | | 102 | Lex | De Haan | LDEHAAN | 515.123.4569 | 2001-01-13 | AD_VP | 17000.00 | 0.00 | 100 | 90 | | 103 | Alexander | Hunold | AHUNOLD | 590.423.4567 | 2006-01-03 | IT_PROG | 9000.00 | 0.00 | 102 | 60 | | 104 | Bruce | Ernst | BERNST | 590.423.4568 | 2007-05-21 | IT_PROG | 6000.00 | 0.00 | 103 | 60 | | 105 | David | Austin | DAUSTIN | 590.423.4569 | 2005-06-25 | IT_PROG | 4800.00 | 0.00 | 103 | 60 | | 106 | Valli | Pataballa | VPATABAL | 590.423.4560 | 2006-02-05 | IT_PROG | 4800.00 | 0.00 | 103 | 60 | | 107 | Diana | Lorentz | DLORENTZ | 590.423.5567 | 2007-02-07 | IT_PROG | 4200.00 | 0.00 | 103 | 60 | | 108 | Nancy | Greenberg | NGREENBE | 515.124.4569 | 2002-08-17 | FI_MGR | 12008.00 | 0.00 | 101 | 100 | | 109 | Daniel | Faviet | DFAVIET | 515.124.4169 | 2002-08-16 | FI_ACCOUNT | 9000.00 | 0.00 | 108 | 100 | ...... | 206 | William | Gietz | WGIETZ | 515.123.8181 | 2002-06-07 | AC_ACCOUNT | 8300.00 | 0.00 | 205 | 110 | +-------------+-------------+-------------+----------+--------------------+------------+------------+----------+----------------+------------+---------------+
Sample Solution:
-- Selecting specific columns (E.first_name, E.last_name, E.department_id, D.department_name) from the 'employees' table, aliased as 'E', and the 'departments' table, aliased as 'D'
SELECT E.first_name, E.last_name, E.department_id, D.department_name
-- Performing an INNER JOIN between the 'employees' table (aliased as 'E') and the 'departments' table (aliased as 'D') based on the 'department_id' column
FROM employees E
JOIN departments D
ON E.department_id = D.department_id;
Sample Output:
first_name last_name department_id department_name Steven King 90 Executive Neena Kochhar 90 Executive Lex De Haan 90 Executive Alexander Hunold 60 IT Bruce Ernst 60 IT David Austin 60 IT Valli Pataballa 60 IT Diana Lorentz 60 IT Nancy Greenberg 100 Finance Daniel Faviet 100 Finance John Chen 100 Finance Ismael Sciarra 100 Finance Jose Manuel Urman 100 Finance Luis Popp 100 Finance Den Raphaely 30 Purchasing Alexander Khoo 30 Purchasing Shelli Baida 30 Purchasing Sigal Tobias 30 Purchasing Guy Himuro 30 Purchasing Karen Colmenares 30 Purchasing Matthew Weiss 50 Shipping Adam Fripp 50 Shipping Payam Kaufling 50 Shipping Shanta Vollman 50 Shipping Kevin Mourgos 50 Shipping Julia Nayer 50 Shipping Irene Mikkilineni 50 Shipping James Landry 50 Shipping Steven Markle 50 Shipping Laura Bissot 50 Shipping Mozhe Atkinson 50 Shipping James Marlow 50 Shipping TJ Olson 50 Shipping Jason Mallin 50 Shipping Michael Rogers 50 Shipping Ki Gee 50 Shipping Hazel Philtanker 50 Shipping Renske Ladwig 50 Shipping Stephen Stiles 50 Shipping John Seo 50 Shipping Joshua Patel 50 Shipping Trenna Rajs 50 Shipping Curtis Davies 50 Shipping Randall Matos 50 Shipping Peter Vargas 50 Shipping John Russell 80 Sales Karen Partners 80 Sales Alberto Errazuriz 80 Sales Gerald Cambrault 80 Sales Eleni Zlotkey 80 Sales Peter Tucker 80 Sales David Bernstein 80 Sales Peter Hall 80 Sales Christopher Olsen 80 Sales Nanette Cambrault 80 Sales Oliver Tuvault 80 Sales Janette King 80 Sales Patrick Sully 80 Sales Allan McEwen 80 Sales Lindsey Smith 80 Sales Louise Doran 80 Sales Sarath Sewall 80 Sales Clara Vishney 80 Sales Danielle Greene 80 Sales Mattea Marvins 80 Sales David Lee 80 Sales Sundar Ande 80 Sales Amit Banda 80 Sales Lisa Ozer 80 Sales Harrison Bloom 80 Sales Tayler Fox 80 Sales William Smith 80 Sales Elizabeth Bates 80 Sales Sundita Kumar 80 Sales Ellen Abel 80 Sales Alyssa Hutton 80 Sales Jonathon Taylor 80 Sales Jack Livingston 80 Sales Charles Johnson 80 Sales Winston Taylor 50 Shipping Jean Fleaur 50 Shipping Martha Sullivan 50 Shipping Girard Geoni 50 Shipping Nandita Sarchand 50 Shipping Alexis Bull 50 Shipping Julia Dellinger 50 Shipping Anthony Cabrio 50 Shipping Kelly Chung 50 Shipping Jennifer Dilly 50 Shipping Timothy Gates 50 Shipping Randall Perkins 50 Shipping Sarah Bell 50 Shipping Britney Everett 50 Shipping Samuel McCain 50 Shipping Vance Jones 50 Shipping Alana Walsh 50 Shipping Kevin Feeney 50 Shipping Donald OConnell 50 Shipping Douglas Grant 50 Shipping Jennifer Whalen 10 Administration Michael Hartstein 20 Marketing Pat Fay 20 Marketing Susan Mavris 40 Human Resources Hermann Baer 70 Public Relations Shelley Higgins 110 Accounting William Gietz 110 Accounting
Code Explanation:
The said query in SQL that joins the 'employees' table with the 'departments' table using the "department_id" column. It selects the "first_name", "last_name", "department_id", and "department_name" columns from both tables.
The result set includes one row for each combination of employee and department where the "department_id" values match between the two tables.
The "JOIN" keyword is used to combine the two tables based on the common column "department_id".
Relational Algebra Expression:
Relational Algebra Tree:
Visual Presentation:
Alternative Solutions:
Using WHERE Clause with Equality Check:
SELECT E.first_name, E.last_name, E.department_id, D.department_name
FROM employees E, departments D
WHERE E.department_id = D.department_id;
Using JOIN with ANSI-92 Syntax:
SELECT E.first_name, E.last_name, E.department_id, D.department_name
FROM employees E
JOIN departments D USING (department_id);
Using CROSS JOIN with WHERE Clause:
SELECT E.first_name, E.last_name, E.department_id, D.department_name
FROM employees E
CROSS JOIN departments D
WHERE E.department_id = D.department_id;
Go to:
PREV : SQL JOINS on HR Database Exercises Home
NEXT : Display name, department, city and state each employee.
Practice Online
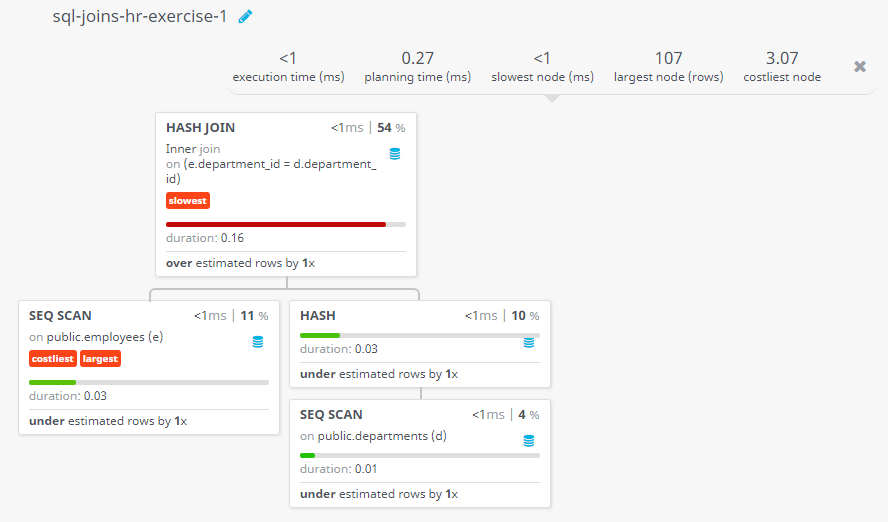
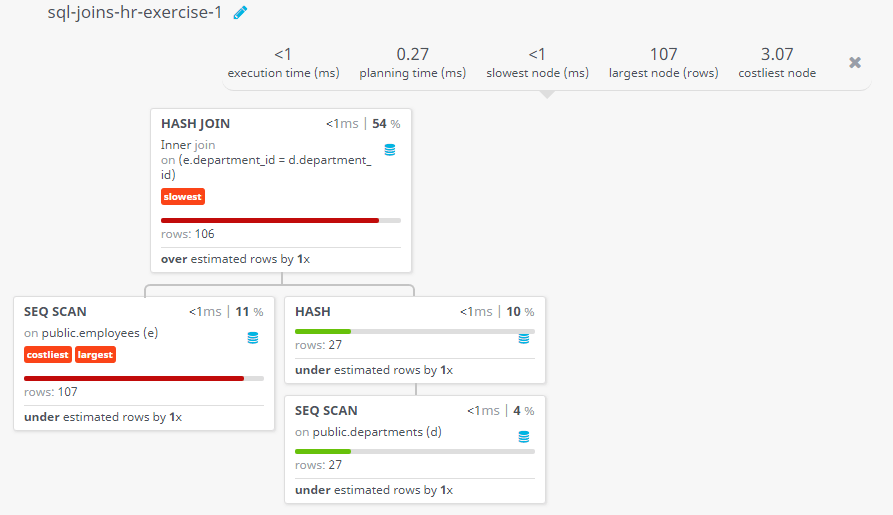
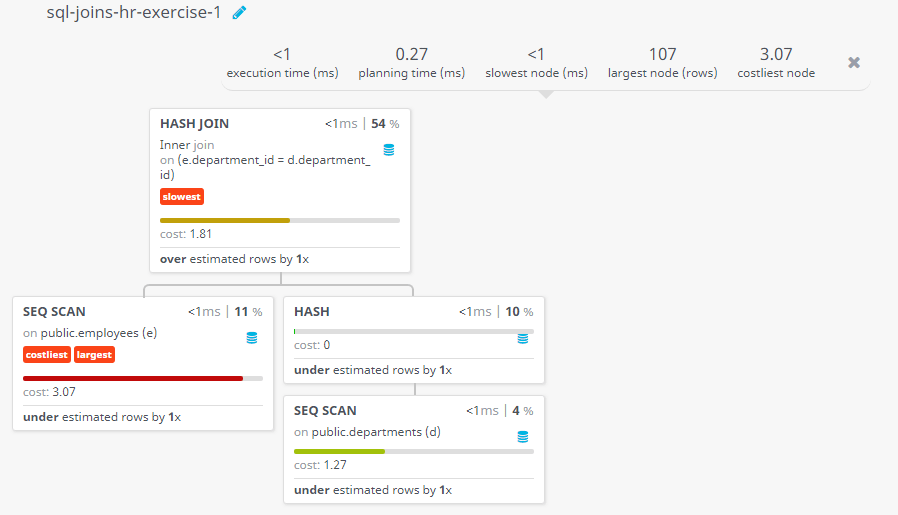
Query Visualization:
Duration:
Rows:
Cost:
Have another way to solve this solution? Contribute your code (and comments) through Disqus.
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
Test your Programming skills with w3resource's quiz.