SQL Exercises: Highest salary drawar in a department
From the following table, write a SQL query to find those employees who earn the highest salary in a department. Return department ID, employee name, and salary.
Sample table: employees
+-------------+-------------+-------------+----------+--------------------+------------+------------+----------+----------------+------------+---------------+ | EMPLOYEE_ID | FIRST_NAME | LAST_NAME | EMAIL | PHONE_NUMBER | HIRE_DATE | JOB_ID | SALARY | COMMISSION_PCT | MANAGER_ID | DEPARTMENT_ID | +-------------+-------------+-------------+----------+--------------------+------------+------------+----------+----------------+------------+---------------+ | 100 | Steven | King | SKING | 515.123.4567 | 2003-06-17 | AD_PRES | 24000.00 | 0.00 | 0 | 90 | | 101 | Neena | Kochhar | NKOCHHAR | 515.123.4568 | 2005-09-21 | AD_VP | 17000.00 | 0.00 | 100 | 90 | | 102 | Lex | De Haan | LDEHAAN | 515.123.4569 | 2001-01-13 | AD_VP | 17000.00 | 0.00 | 100 | 90 | | 103 | Alexander | Hunold | AHUNOLD | 590.423.4567 | 2006-01-03 | IT_PROG | 9000.00 | 0.00 | 102 | 60 | | 104 | Bruce | Ernst | BERNST | 590.423.4568 | 2007-05-21 | IT_PROG | 6000.00 | 0.00 | 103 | 60 | | 105 | David | Austin | DAUSTIN | 590.423.4569 | 2005-06-25 | IT_PROG | 4800.00 | 0.00 | 103 | 60 | | 106 | Valli | Pataballa | VPATABAL | 590.423.4560 | 2006-02-05 | IT_PROG | 4800.00 | 0.00 | 103 | 60 | | 107 | Diana | Lorentz | DLORENTZ | 590.423.5567 | 2007-02-07 | IT_PROG | 4200.00 | 0.00 | 103 | 60 | | 108 | Nancy | Greenberg | NGREENBE | 515.124.4569 | 2002-08-17 | FI_MGR | 12008.00 | 0.00 | 101 | 100 | | 109 | Daniel | Faviet | DFAVIET | 515.124.4169 | 2002-08-16 | FI_ACCOUNT | 9000.00 | 0.00 | 108 | 100 | | 110 | John | Chen | JCHEN | 515.124.4269 | 2005-09-28 | FI_ACCOUNT | 8200.00 | 0.00 | 108 | 100 | .................... +-------------+-------------+-------------+----------+--------------------+------------+------------+----------+----------------+------------+---------------+
Sample Solution:
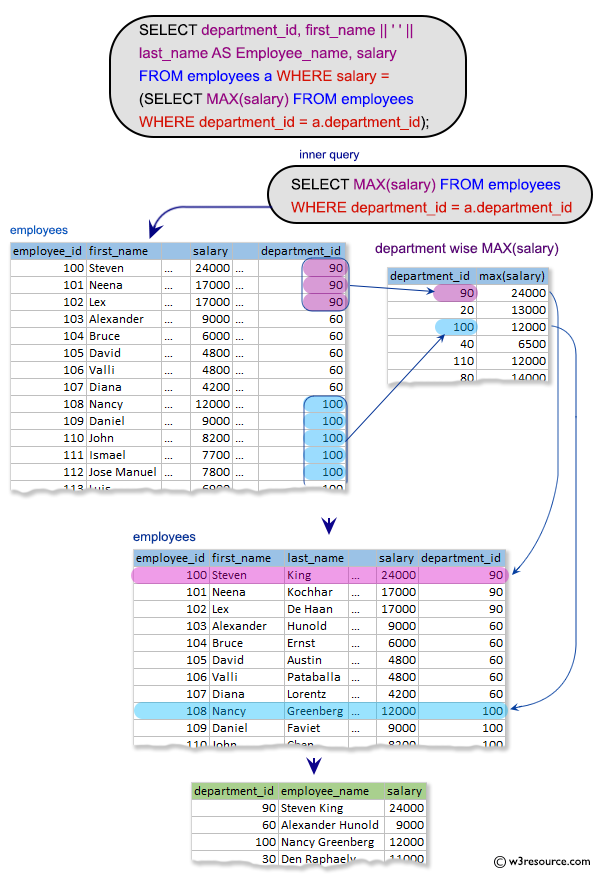
-- Selecting specific columns (department_id, a.first_name || ' ' || a.last_name AS Employee_name, salary) from the 'employees' table, aliased as 'a'
SELECT department_id, first_name || ' ' || last_name AS Employee_name, salary
-- Filtering rows from the 'employees' table, aliased as 'a', based on the condition that the 'salary' is equal to the maximum salary within the same 'department_id'
FROM employees a
-- Subquery to find the maximum 'salary' where the 'department_id' matches the 'department_id' in the outer query
WHERE salary =
(SELECT MAX(salary)
FROM employees
WHERE department_id = a.department_id);
Sample Output:
department_id employee_name salary 90 Steven King 24000.00 60 Alexander Hunold 9000.00 100 Nancy Greenberg 12000.00 30 Den Raphaely 11000.00 50 Adam Fripp 8200.00 80 John Russell 14000.00 0 Kimberely Grant 7000.00 10 Jennifer Whalen 4400.00 20 Michael Hartstein 13000.00 40 Susan Mavris 6500.00 70 Hermann Baer 10000.00 110 Shelley Higgins 12000.00
Code Explanation:
The said query in SQL that selects the "department_id", concatenated "first_name" and "last_name" as "Employee_name", and "salary" from the 'employees' table. It only selects the employees who have the maximum salary in their department. The subquery retrieves the maximum salary for each department, and the outer query filters the employees by comparing their salary with the maximum salary of their respective department.
Visual Presentation:
Alternative Solutions:
Using JOINs and Subqueries:
SELECT a.department_id,
a.first_name || ' ' || a.last_name AS Employee_name,
a.salary
FROM employees a
JOIN (
SELECT department_id, MAX(salary) AS max_salary
FROM employees
GROUP BY department_id
) b ON a.department_id = b.department_id
WHERE a.salary = b.max_salary;
Using a Window Function:
SELECT department_id,
first_name || ' ' || last_name AS Employee_name,
salary
FROM (
SELECT department_id,
first_name,
last_name,
salary,
ROW_NUMBER() OVER (PARTITION BY department_id ORDER BY salary DESC) AS rank
FROM employees
) ranked
WHERE rank = 1;
Using a Correlated Subquery with EXISTS:
SELECT a.department_id,
a.first_name || ' ' || a.last_name AS Employee_name,
a.salary
FROM employees a
WHERE EXISTS (
SELECT 1
FROM employees b
WHERE b.department_id = a.department_id
GROUP BY b.department_id
HAVING MAX(b.salary) = a.salary
);
Go to:
PREV : Display the details of departments managed by Susan.
NEXT : Employees who did not have any job in the past.
Practice Online
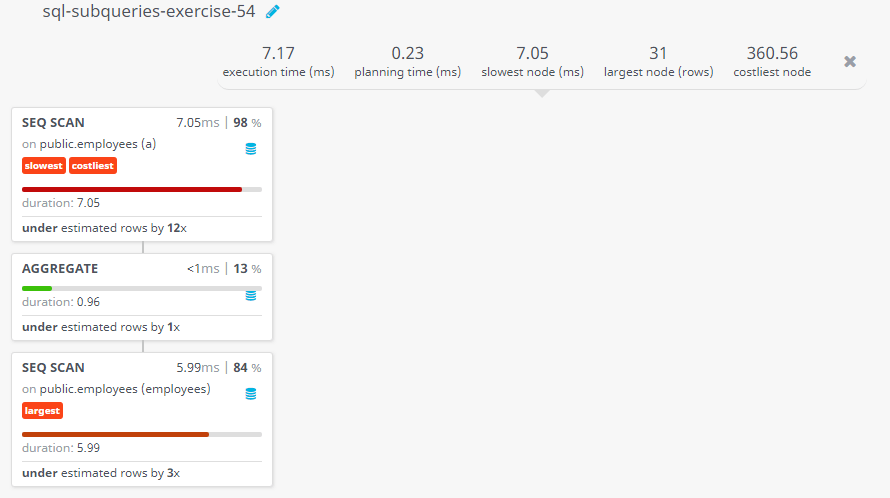
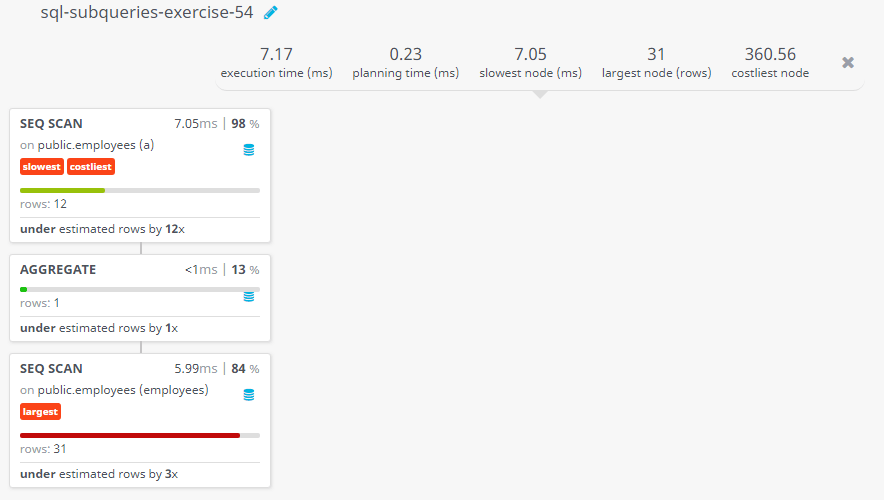
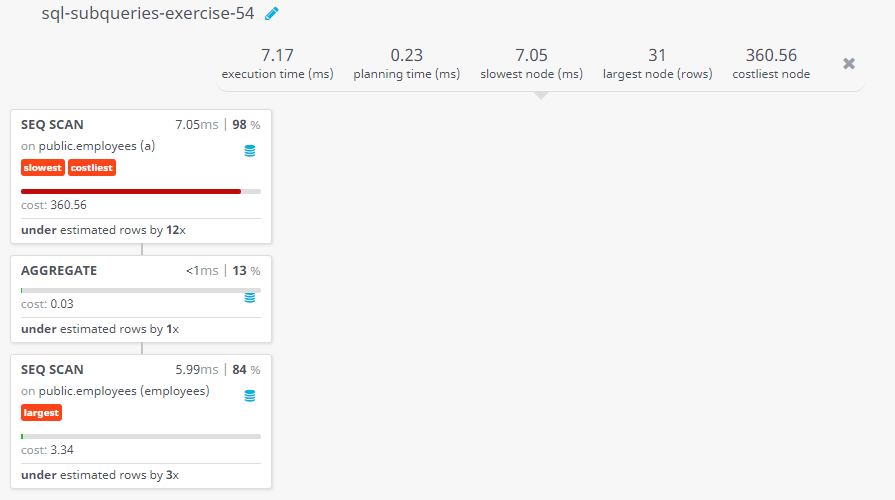
Query Visualization:
Duration:
Rows:
Cost:
Have another way to solve this solution? Contribute your code (and comments) through Disqus.
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
Test your Programming skills with w3resource's quiz.