PostgreSQL CROSS JOIN
How does Cross Join work in PostgreSQL?
The Cross Join creates a cartesian product between two sets of data. This type of join does not maintain any relationship between the sets; instead returns the result, which is the number of rows in the first table multiplied by the number of rows in the second table. It is called a product because it returns every possible combination of rows between the joined sets.
Syntax:
SELECT [* | column_list] FROM table1 CROSS JOIN table2;
OR
SELECT [* | column_list] FROM table1,table2;
The sample tables
Customer:

Item :
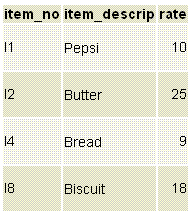
Invoice:

SQL
Code:
SELECT * FROM customer
CROSS JOIN
invoice;
OR
Code:
SELECT * FROM
customer,invoice;
OR
Code:
SELECT customer.cust_no, customer.cust_name,
invoice.invoice_no,invoice.cust_no,invoice.item_no,
invoice.sold_qty,invoice.disc_per
FROM customer,invoice;
Output:
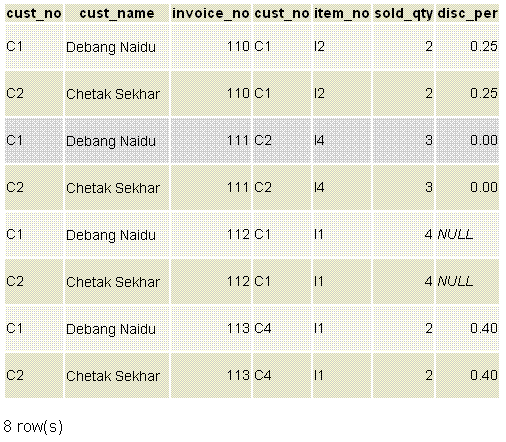
Explanation
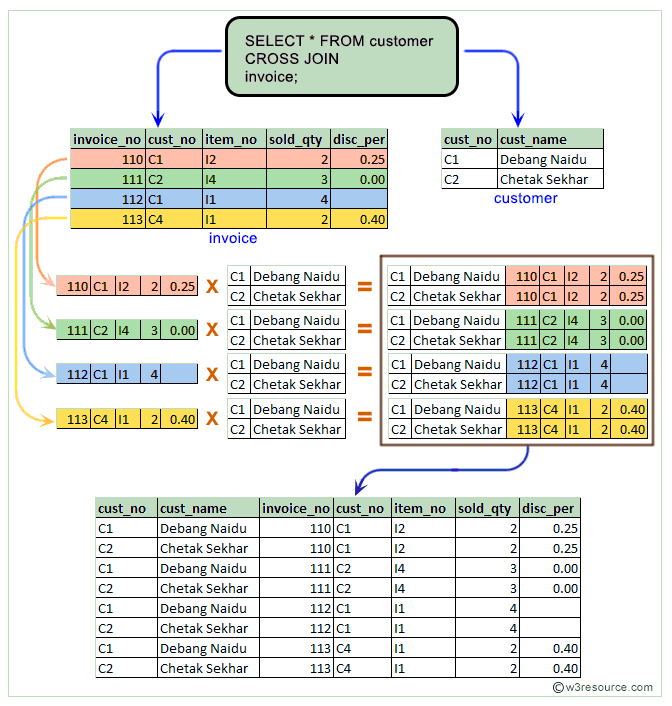
In the above example, the 'customer' table and 'invoice' table join together to return a cartesian product. Here in the above example the two rows of 'customer' table joining with 4 rows of 'invoice' table and makes a product of 4*2 rows.
Pictorial Presentation :
Previous: Introduction to JOIN
Next: INNER JOIN
