C Exercises: Find the number occurring odd number of times in an array
34. Find Element Occurring Odd Number of Times
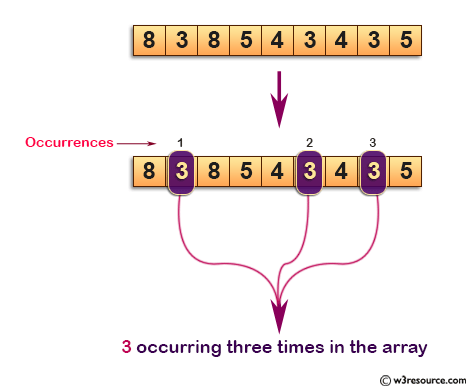
Write a program in C to find the number occurring odd number of times in an array.
All numbers occur even number of times except one number which occurs odd number of times.
This problem involves writing a C program to find the single number in an array that appears an odd number of times, while all other numbers appear an even number of times. The program should iterate through the array and identify the number that meets this condition.
Visual Presentation:
Sample Solution:
C Code:
#include <stdio.h>
// Function to find the element occurring odd number of times in the array using XOR operation
int findOddCountElem(int *arr1, int n) {
int i, ResultXor = 0;
// Performing XOR operation on all array elements
for (i = 0; i < n; i++) {
ResultXor = ResultXor ^ arr1[i];
}
return ResultXor; // Returns the element occurring odd number of times
}
// Main function
int main() {
int i;
int arr1[] = {8, 3, 8, 5, 4, 3, 4, 3, 5};
int ctr = sizeof(arr1) / sizeof(arr1[0]);
// Display the given array
printf("The given array is : ");
for (i = 0; i < ctr; i++) {
printf("%d ", arr1[i]);
}
printf("\n");
// Function call to find the element occurring odd number of times
printf("Number of odd number occur(s) : %d times.\n", findOddCountElem(arr1, ctr));
return 0;
}
Sample Output:
The given array is : 8 3 8 5 4 3 4 3 5 Number of odd number occur(s) : 3 times.
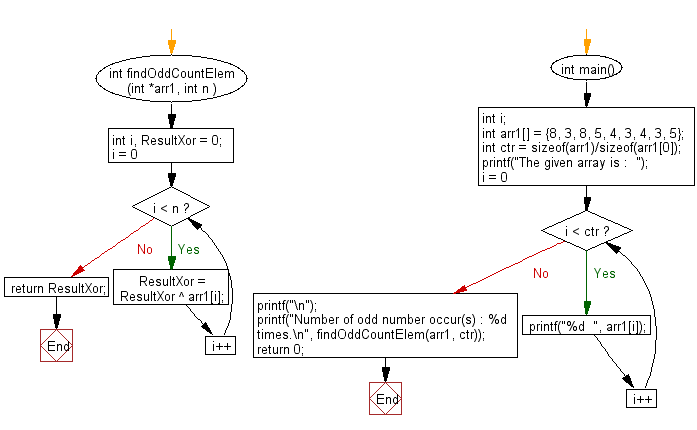
Flowchart :
For more Practice: Solve these Related Problems:
- Write a C program to find the element that appears an odd number of times using bitwise XOR.
- Write a C program to count frequencies and then identify the element with an odd count.
- Write a C program to determine the element with odd occurrences using a hash table implemented with arrays.
- Write a C program to find the element that occurs an odd number of times and then verify by summing its bits.
Go to:
PREV : Majority Element.
NEXT : Largest Sum of Contiguous Subarray.
C Programming Code Editor:
Have another way to solve this solution? Contribute your code (and comments) through Disqus.
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
Test your Programming skills with w3resource's quiz.
