Binary Tree traversal in C: In-Order, Pre-Order, Post-Order
10. Binary Tree Traversals from Graph Data Challenges
Write a C program to find the traversal order (pre-order, in-order, post-order) of a binary tree that represents a graph.
From Wikipdeia,
In computer science, graph traversal (also known as graph search) refers to the process of visiting (checking and/or updating) each vertex in a graph. Such traversals are classified by the order in which the vertices are visited. Tree traversal is a special case of graph traversal.
Sample Solution:
C Code:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <limits.h>
#include
#include
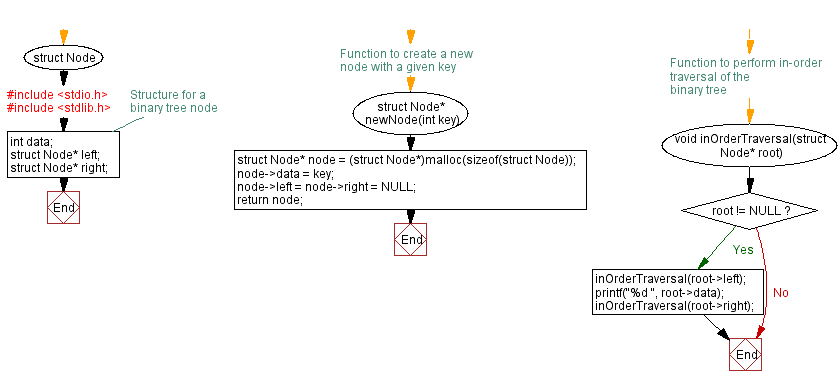
// Structure for a binary tree node
struct Node {
int data;
struct Node* left;
struct Node* right;
};
// Function to create a new node with a given key
struct Node* newNode(int key) {
struct Node* node = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
node->data = key;
node->left = node->right = NULL;
return node;
}
// Function to perform in-order traversal of the binary tree
void inOrderTraversal(struct Node* root) {
if (root != NULL) {
inOrderTraversal(root->left);
printf("%d ", root->data);
inOrderTraversal(root->right);
}
}
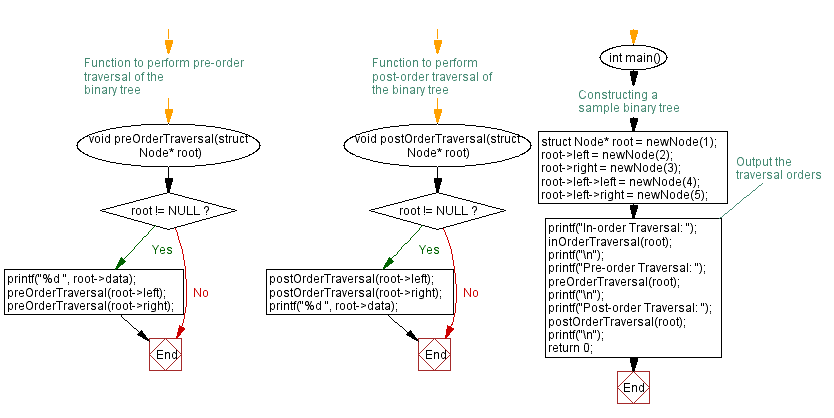
// Function to perform pre-order traversal of the binary tree
void preOrderTraversal(struct Node* root) {
if (root != NULL) {
printf("%d ", root->data);
preOrderTraversal(root->left);
preOrderTraversal(root->right);
}
}
// Function to perform post-order traversal of the binary tree
void postOrderTraversal(struct Node* root) {
if (root != NULL) {
postOrderTraversal(root->left);
postOrderTraversal(root->right);
printf("%d ", root->data);
}
}
int main() {
// Constructing a sample binary tree
struct Node* root = newNode(1);
root->left = newNode(2);
root->right = newNode(3);
root->left->left = newNode(4);
root->left->right = newNode(5);
// Output the traversal orders
printf("In-order Traversal: ");
inOrderTraversal(root);
printf("\n");
printf("Pre-order Traversal: ");
preOrderTraversal(root);
printf("\n");
printf("Post-order Traversal: ");
postOrderTraversal(root);
printf("\n");
return 0;
}
Output:
Binary Tree:
1
/ \
2 3
/ \
4 5
--------------------------------------------------
Traversal Orders:
In-order Traversal: 4 2 5 1 3
Pre-order Traversal: 1 2 4 5 3
Post-order Traversal: 4 5 2 3 1
Explanation:
In the exercise above,
- The struct Node represents a binary tree node with integer data, left child (left), and right child (right).
- The newNode function creates a new node with the given key.
- The "inOrderTraversal()", "preOrderTraversal()", and "postOrderTraversal()" functions perform in-order, pre-order, and post-order traversals, respectively, printing the node data at each step.
- In the "main()" function, a sample binary tree is constructed, and the three types of traversals are applied, printing the results.
Flowchart:
For more Practice: Solve these Related Problems:
- Write a C program to perform pre-order, in-order, and post-order traversals on a binary tree derived from a graph’s spanning tree.
- Write a C program to convert a graph into a binary tree using a selected root and then execute all three standard traversals.
- Write a C program to compare the pre-order, in-order, and post-order traversals of a binary tree with its level-order traversal.
- Write a C program to implement traversal orders on a binary tree that represents hierarchical data extracted from a graph.
Go to:
PREV : Dijkstra's Algorithm Extended Challenges.
NEXT : C Programming Numbers Exercises Home.
C Programming Code Editor:
Have another way to solve this solution? Contribute your code (and comments) through Disqus.
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
Test your Programming skills with w3resource's quiz.
