C++ Exercises: Prime decomposition
34. Prime Decomposition of a Given Number
Write a function which returns an array or collection which contains the prime decomposition of a given number greater than 1.
By the fundamental theorem of arithmetic, every positive integer has a unique prime factorization. Given a general algorithm for integer factorization, any integer can be factored into its constituent prime factors by repeated application of this algorithm.
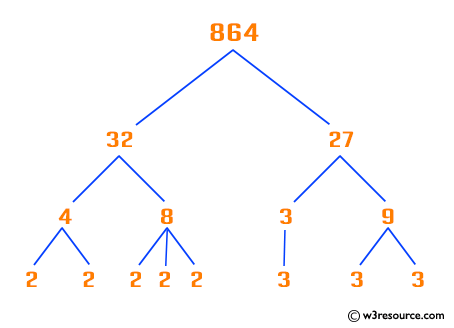
The prime decomposition of a number consists of a list of prime numbers which, when multiplied together, equal the number.
Example: 18 = 2 x 3 x 3
So prime decomposition of 18 is {2, 3, 3}
Test Data:
Sample Solution:
C++ Code :
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
// Alias declarations for better readability
using long_pair = std::pair<long, long>; // Alias for a pair of long values
using lp_vec = std::vector<long_pair>; // Alias for a vector of long_pair
using namespace std;
// Function to factorize a number and return its prime decomposition
lp_vec factorize(long n) {
lp_vec fs; // Create a vector of pairs to store factors and their counts
int cnt = 0; // Initialize a counter for factor exponentiation
// Factorize using 2, since 2 is the only even prime number
for (; n % 2 == 0; n /= 2)
cnt++; // Increment counter for the power of 2
if (cnt > 0)
fs.push_back({2, cnt}); // Store factor and its count in the vector
// Continue factorizing using odd numbers starting from 3
for (long i = 3; i * i <= n; i += 2) {
cnt = 0; // Reset counter for the new factor
for (; n % i == 0; n /= i)
cnt++; // Increment counter for the power of the factor 'i'
if (cnt > 0)
fs.push_back({i, cnt}); // Store factor and its count in the vector
}
// If there is a remaining factor greater than 1, add it to the vector
if (n > 1)
fs.push_back({n, 1});
return fs; // Return the vector with prime decomposition
}
int main() {
long n;
cout << "Input a number: ";
cin >> n; // Take user input for the number to factorize
cout << "\nPrime decomposition of the given number:\n";
auto fs = factorize(n); // Calculate prime factors and their counts
// Display each factor and its power in the prime decomposition
for (auto fp : fs) {
cout << fp.first << "^" << fp.second << "\n";
}
return 0;
}
Sample Output:
Input a number: 18 Prime decomposition of said number: 2^1 3^2
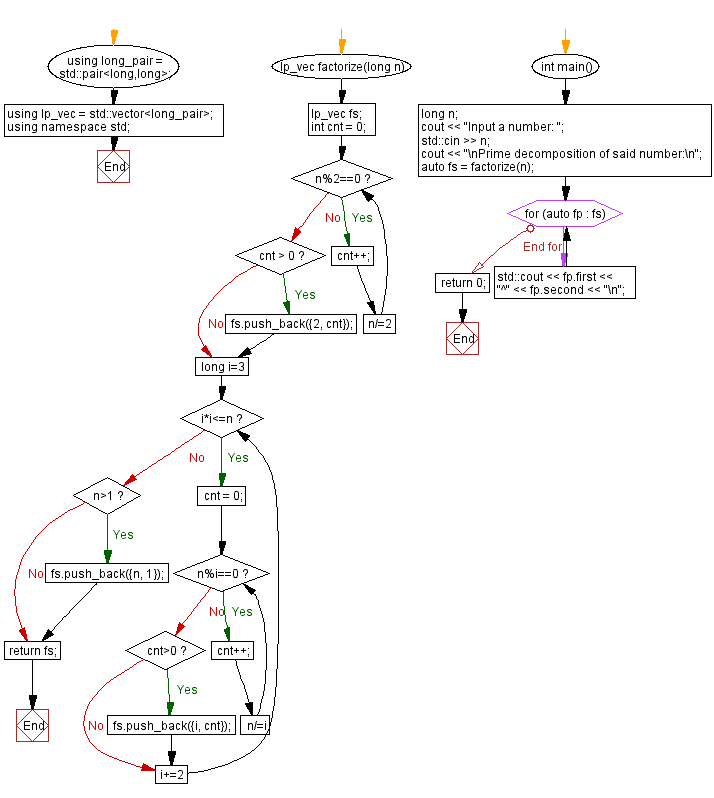
Flowchart:
For more Practice: Solve these Related Problems:
- Write a C++ program to perform prime factorization of an integer using recursion and return the factors in a vector.
- Write a C++ program that decomposes a number into its prime factors and prints them in ascending order.
- Write a C++ program to implement a function that returns an array containing the prime factors of a given number, including multiplicities.
- Write a C++ program to factorize a number into primes using trial division and display the result in exponent form.
Go to:
PREV : Product of Prime Factors for Numbers 1 to n.
NEXT : Generate a Sequence of Primes Using Trial Division.
C++ Code Editor:
Contribute your code and comments through Disqus.
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
