Java: Delete a specified node in the middle of a singly linked list
Delete Middle Node in Linked List
Write a Java program to delete a specified node in the middle of a singly linked list.
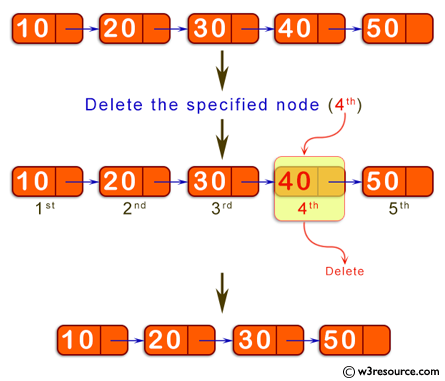
Sample Singly linked list: 10->20->30->40->50
Delete the fourth node i.e. 40
Result: 10->20->30->50
Visual Presentation:
Sample Solution:
Java Code:
// Importing necessary Java utilities
import java.util.*;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.LinkedList;
// ListNode class definition representing each node of the linked list
class ListNode {
int val;
ListNode next;
// Constructor to initialize the ListNode
ListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
this.next = null;
}
}
// Main class Solution
public class Solution {
// Initializing the head of the linked list with a node containing value 10
public static ListNode head = new ListNode(10);
// Main method
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Creating a linked list with nodes containing values 20, 30, 40, 50
head.next = new ListNode(20);
head.next.next = new ListNode(30);
head.next.next.next = new ListNode(40);
head.next.next.next.next = new ListNode(50);
ListNode p = head; // Creating a reference 'p' to the head node
System.out.println("Original Linked list:");
printList(p); // Printing the original linked list
System.out.println("\nAfter deleting the fourth node, Linked list becomes:");
deleteNode(head.next.next.next); // Deleting the fourth node in the list
p = head; // Updating reference 'p' to the head node after deletion
printList(p); // Printing the updated linked list
}
// Method to delete a node from the linked list
public static void deleteNode(ListNode node) {
// Check if the node to be deleted is not the last node in the list
if (node.next != null) {
int temp = node.val;
node.val = node.next.val;
node.next.val = temp;
node.next = node.next.next; // Skip the next node effectively deleting the current node
} else {
// If the node to be deleted is the last node, traverse to the previous node and delete it
ListNode p = head;
while (p.next.val != node.val) {
p = p.next;
}
p.next = null; // Set the next of the previous node to null
}
}
// Method to print the linked list
static void printList(ListNode p) {
while (p != null) {
System.out.print(p.val); // Printing the value of the current node
if (p.next != null) {
System.out.print("->"); // Adding an arrow for non-last nodes
}
p = p.next; // Move to the next node
}
}
}
Sample Output:
Original Linked list: 10->20->30->40->50 After deleting the fourth node, Linked list becomes: 10->20->30->50
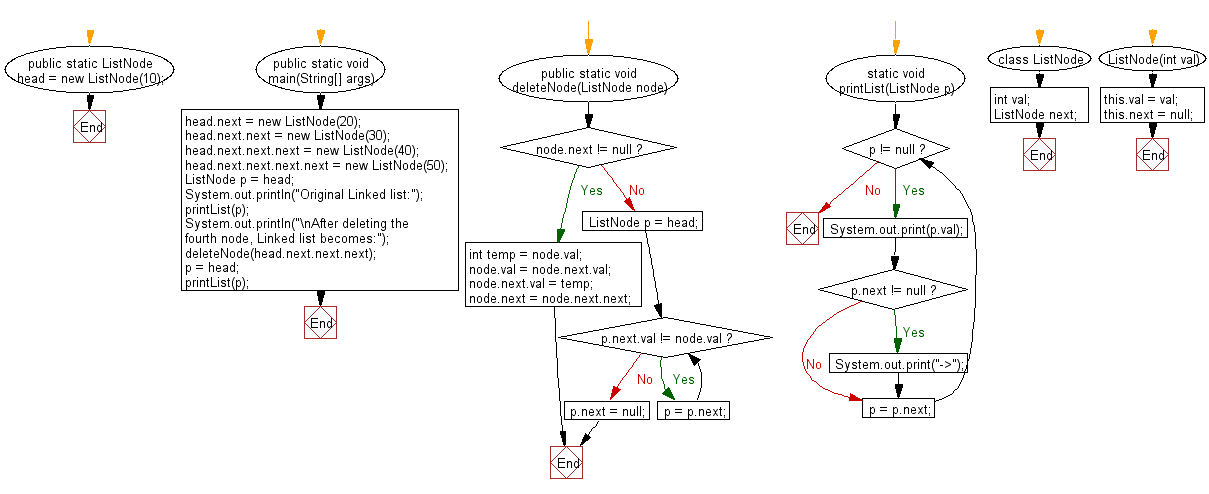
Flowchart:
For more Practice: Solve these Related Problems:
- Write a Java program to delete the nth node from the end of a singly linked list.
- Write a Java program to remove a node from a singly linked list given only a reference to that node.
- Write a Java program to remove duplicate nodes from a sorted linked list.
- Write a Java program to delete every alternate node in a singly linked list.
Go to:
PREV : Max in Sliding Window.
NEXT : Partition Even and Odd.
Java Code Editor:
Company: Adobe Apple Microsoft
Contribute your code and comments through Disqus.
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
Test your Programming skills with w3resource's quiz.