Java: Swap every two adjacent nodes of a given linked list
Swap Adjacent Nodes in List
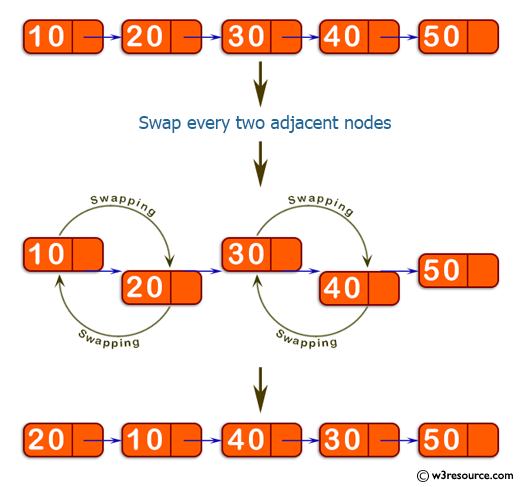
Write a Java program to swap two adjacent nodes in a linked list.
Visual Presentation:
Sample Solution:
Java Code:
// Importing necessary Java utilities
import java.util.*;
// Main class Solution
public class Solution {
// Main method
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Creating a linked list
ListNode l = new ListNode(10);
l.next = new ListNode(20);
l.next.next = new ListNode(30);
l.next.next.next = new ListNode(40);
l.next.next.next.next = new ListNode(50);
// Printing original linked list
System.out.println("\nOriginal Linked list:");
printList(l);
// Swapping pairs of nodes in the linked list
ListNode p = swap_Pairs(l);
// Printing linked list after swapping pairs
System.out.println("\n\nAfter swapping, Linked list becomes:");
printList(p);
}
// Method to swap pairs of nodes in a linked list
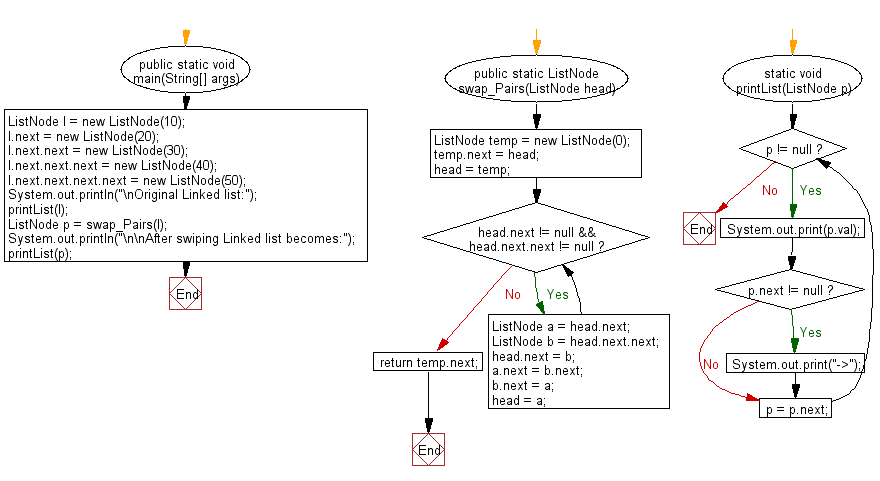
public static ListNode swap_Pairs(ListNode head) {
ListNode temp = new ListNode(0); // Creating a temporary node
temp.next = head; // Setting temp node's next to the head of the original linked list
head = temp; // Assigning head to temp
// Swapping pairs using iterative approach
while (head.next != null && head.next.next != null) {
ListNode a = head.next;
ListNode b = head.next.next;
head.next = b;
a.next = b.next;
b.next = a;
head = a;
}
return temp.next; // Returning the modified linked list
}
// Method to print the linked list
static void printList(ListNode p) {
while (p != null) {
System.out.print(p.val); // Printing node value
if (p.next != null) {
System.out.print("->"); // Adding "->" if more nodes are present
}
p = p.next; // Moving to the next node
}
}
}
// Definition of ListNode class
class ListNode {
int val;
ListNode next;
ListNode(int x) {
val = x;
}
}
Sample Output:
Original Linked list: 10->20->30->40->50 After swiping Linked list becomes: 20->10->40->30->50
Flowchart:
For more Practice: Solve these Related Problems:
- Write a Java program to reverse a linked list in pairs.
- Write a Java program to swap two nodes at specified indices in a singly linked list.
- Write a Java program to swap adjacent nodes in a linked list without swapping the actual node data.
- Write a Java program to swap every third node with its preceding node in a linked list.
Go to:
PREV :Add One to Array Number.
NEXT : Length of Last Word.
Java Code Editor:
Company: Uber Microsoft Bloomberg
Contribute your code and comments through Disqus.
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
Test your Programming skills with w3resource's quiz.
